Quickstart 3: Monitor and Debug Workflows
Estimated time: 2min
Orkes Conductor provides comprehensive views into each workflow execution, enabling you to debug and monitor them while in development or production.
The workflow introspection dashboard can be found in Executions > Workflow, where each workflow execution is identified by a workflow ID.
Try it out
Check out the execution of the helloWorld workflow you’ve just run. If successful, the workflow should have a Completed status, with each task highlighted in green. Otherwise, the workflow diagram will highlight the failed task in red.
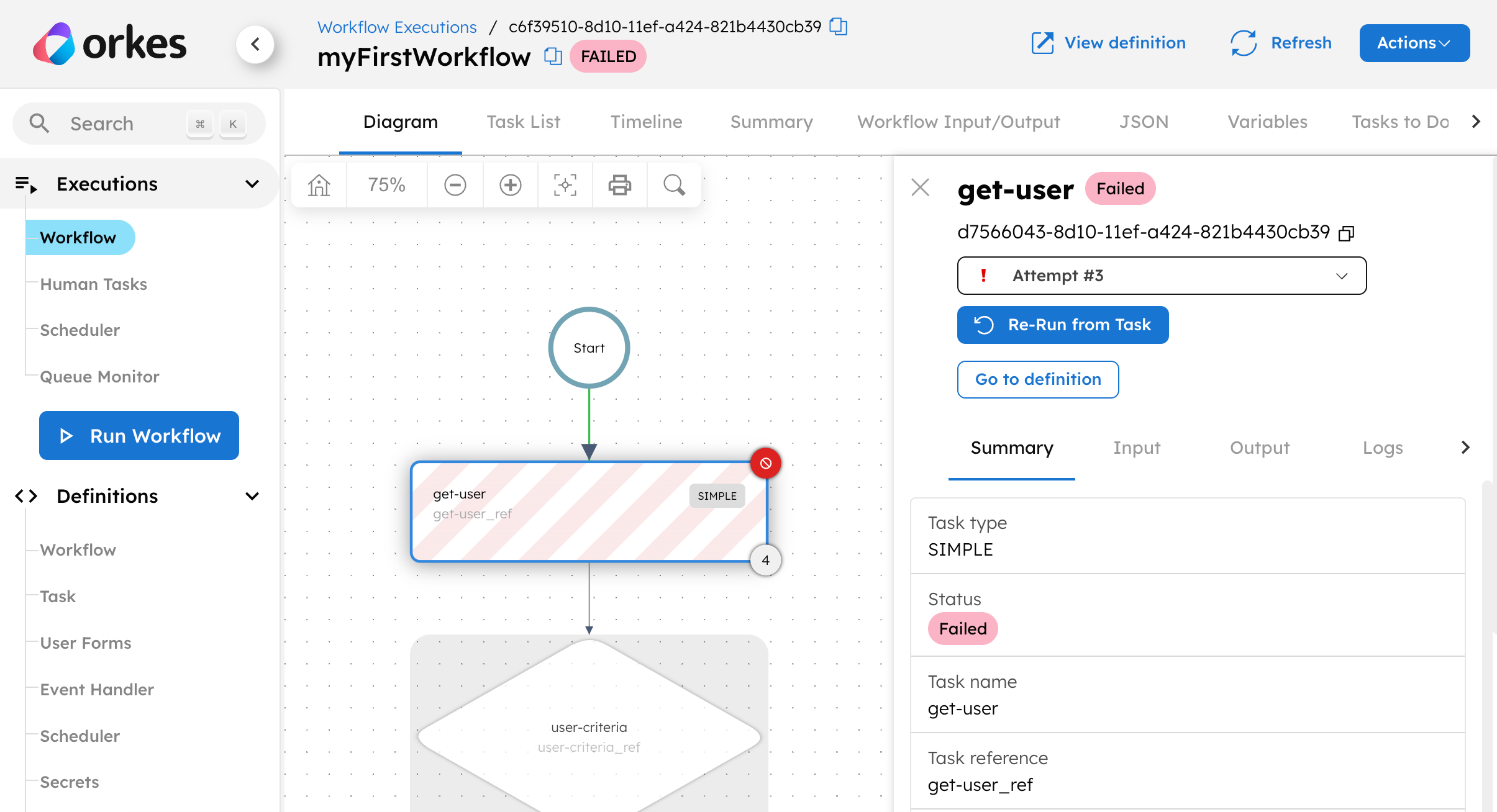
However, a workflow can still successfully run to completion, even with the wrong logic. You can check if the data have been correctly passed between tasks by selecting a task, followed by its Input or Output tab.
Here’s a successful workflow execution, for example.
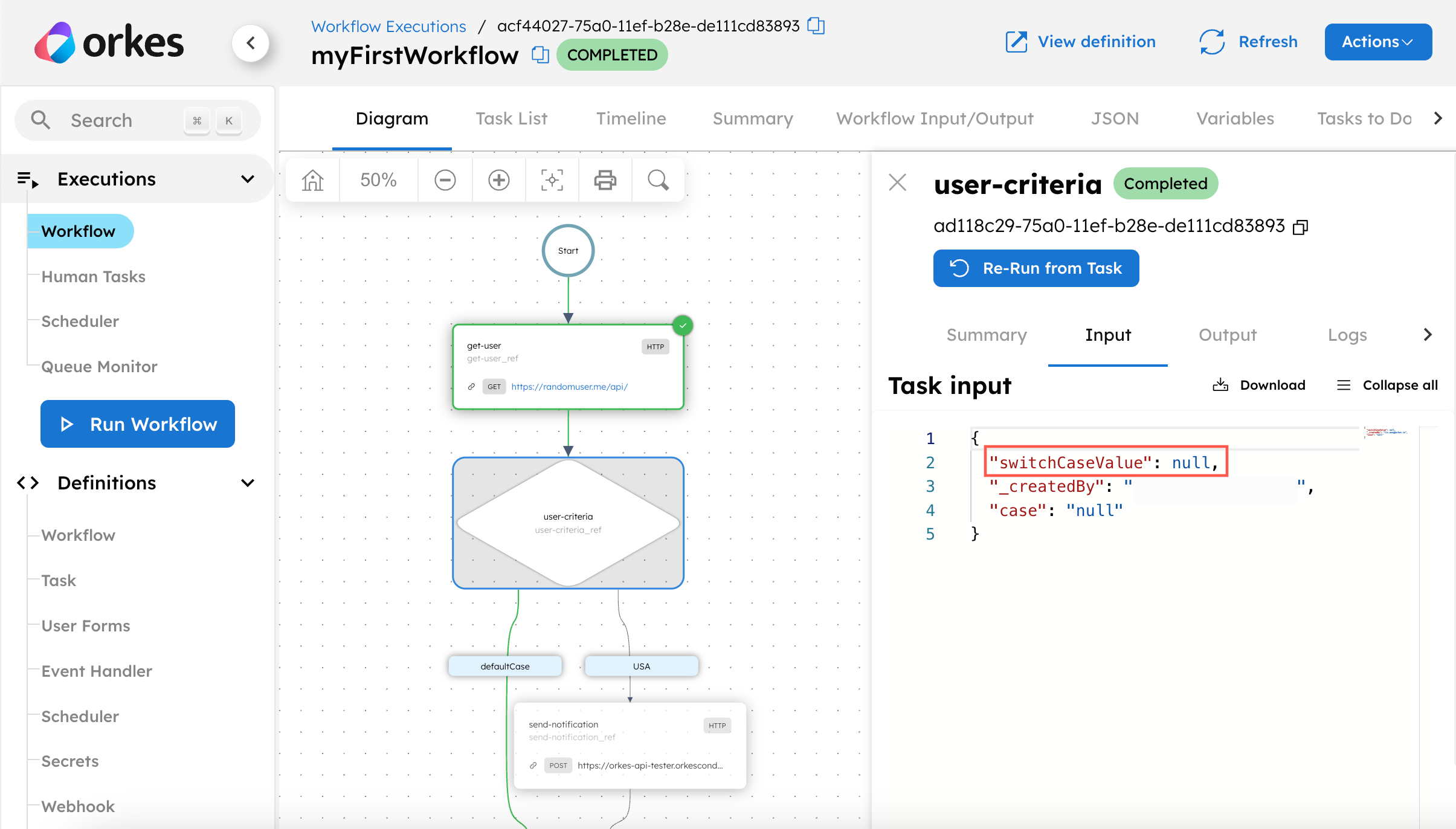
However, the workflow should have flowed through the United States path instead of the defaultCase path, because the user’s location was the United States. Inspecting the Switch task input, we can deduce that the input had not been correctly passed from the get-user task to the Switch task. This sort of visibility into the workflow execution enables you to quickly pinpoint and fix any errors.
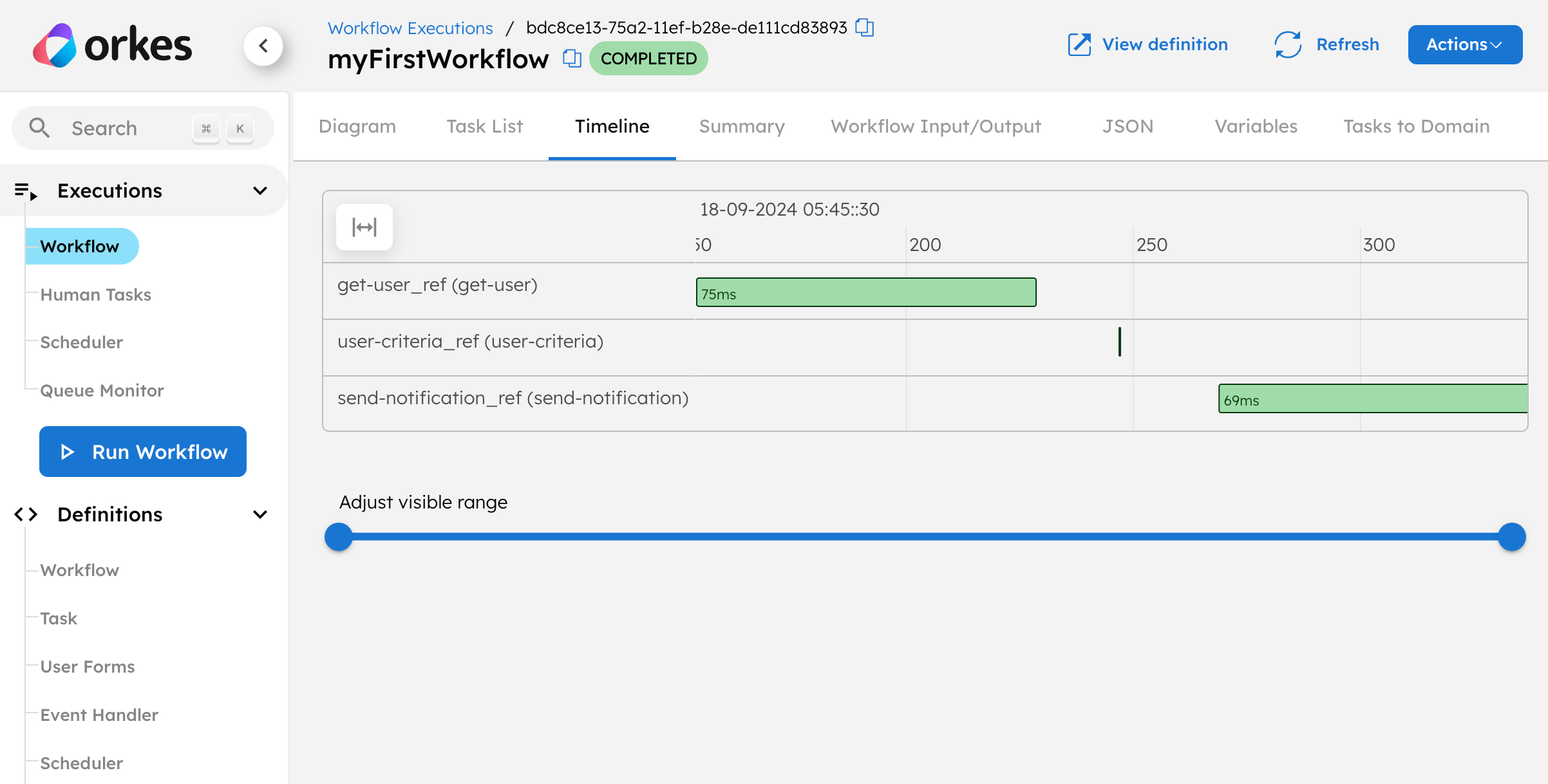
You might also be interested in how long each task took to complete to find the bottlenecks in your execution performance. To inspect this, go to Timeline in the top navigation bar.
What’s next?
Congratulations! You have successfully created, executed, and debugged a Conductor workflow within 15 minutes. Gain deeper mastery by exploring each topic in detail:
- Code with Conductor: SDK Guides
- Build more complex workflows, using LLM chaining, human-in-workflows, eventing, secrets, and more: Build Workflows
- Run workflows at production-level: Run Workflows
- Debug and monitor workflows by exploring both the execution dashboard and metrics dashboard in greater detail. Deploy and Monitor Workflows