Worker Task
A Worker task (Simple task) is used to run custom logic implemented in any language. The custom logic can be deployed anywhere, and the Worker task requires an external worker for polling. A worker is a service you run that polls Conductor for Worker tasks, executes them, and returns the results.
Before adding a Worker task to a workflow, you should complete the following:
- Create and run a worker that polls Conductor and executes the Worker task.
- Create the task definition in Conductor (UI or API) so the workflow can reference it by name. The Worker task name in your workflow must match the Task Definition name you created in Conductor.
For a full guide on how to use workers, refer to Writing Workers.
Task parameters
To configure a Worker task, set inputParameters to the inputs your worker expects. The inputs can be passed as a dynamic variable.
The following are generic configuration parameters that can be applied to the task and are not specific to the Worker task.
Caching parameters
You can cache the task outputs using the following parameters. Refer to Caching Task Outputs for a full guide.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| cacheConfig.ttlInSecond | The time to live in seconds, which is the duration for the output to be cached. | Required if using cacheConfig. |
| cacheConfig.key | The cache key is a unique identifier for the cached output and must be constructed exclusively from the task’s input parameters. It can be a string concatenation that contains the task’s input keys, such as ${uri}-${method} or re_${uri}_${method}. | Required if using cacheConfig. |
Schema parameters
You can enforce input/output validation for the task using the following parameters. Refer to Schema Validation for a full guide.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| taskDefinition.enforceSchema | Whether to enforce schema validation for task inputs/outputs. Set to true to enable validation. | Optional. |
| taskDefinition.inputSchema | The name and type of the input schema to be associated with the task. | Required if enforceSchema is set to true. |
| taskDefinition.outputSchema | The name and type of the output schema to be associated with the task. | Required if enforceSchema is set to true. |
Other generic parameters
Here are other parameters for configuring the task behavior.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| optional | Whether the task is optional. If set to true, any task failure is ignored, and the workflow continues with the task status updated to COMPLETED_WITH_ERRORS. However, the task must reach a terminal state. If the task remains incomplete, the workflow waits until it reaches a terminal state before proceeding. | Optional. |
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for a Worker task.
{
"name": "sayHello",
"taskReferenceName": "sayHello_ref",
"type": "SIMPLE",
"inputParameters": {
"firstName": "${workflow.input.firstName}",
"lastName": "${workflow.input.lastName}"
}
}
Task output
The Worker task will return the output defined in your worker code.
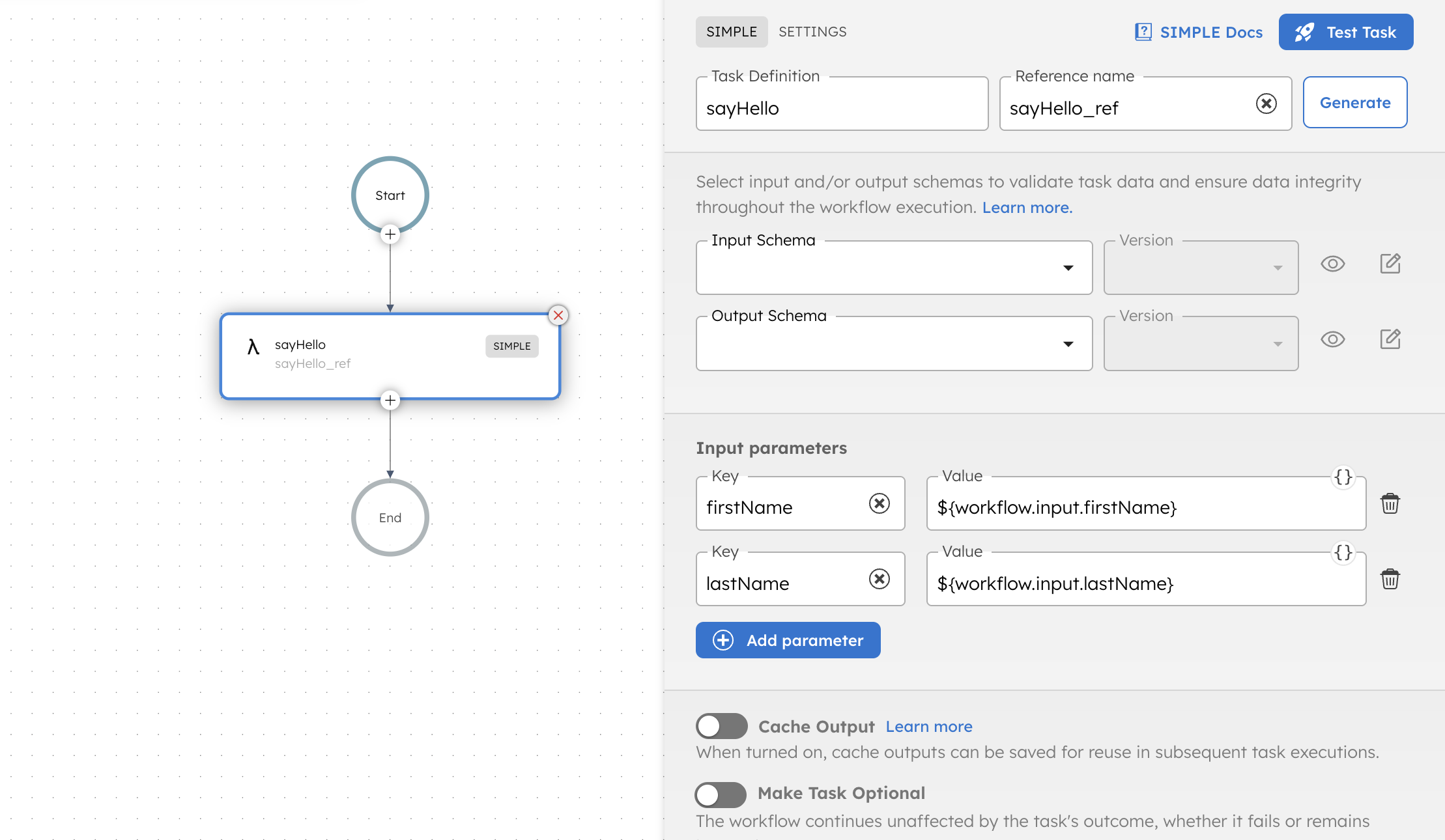
Adding a Worker task in UI
To add a Worker task:
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon to add a new task. You can add a Worker task in either of these ways:
- Search for your task by its name, then select to add it to the workflow.
- Add a Worker Task and enter the task name in Task Definition.
- Configure the task, such as its inputs, caching, schema validation, and optionality.
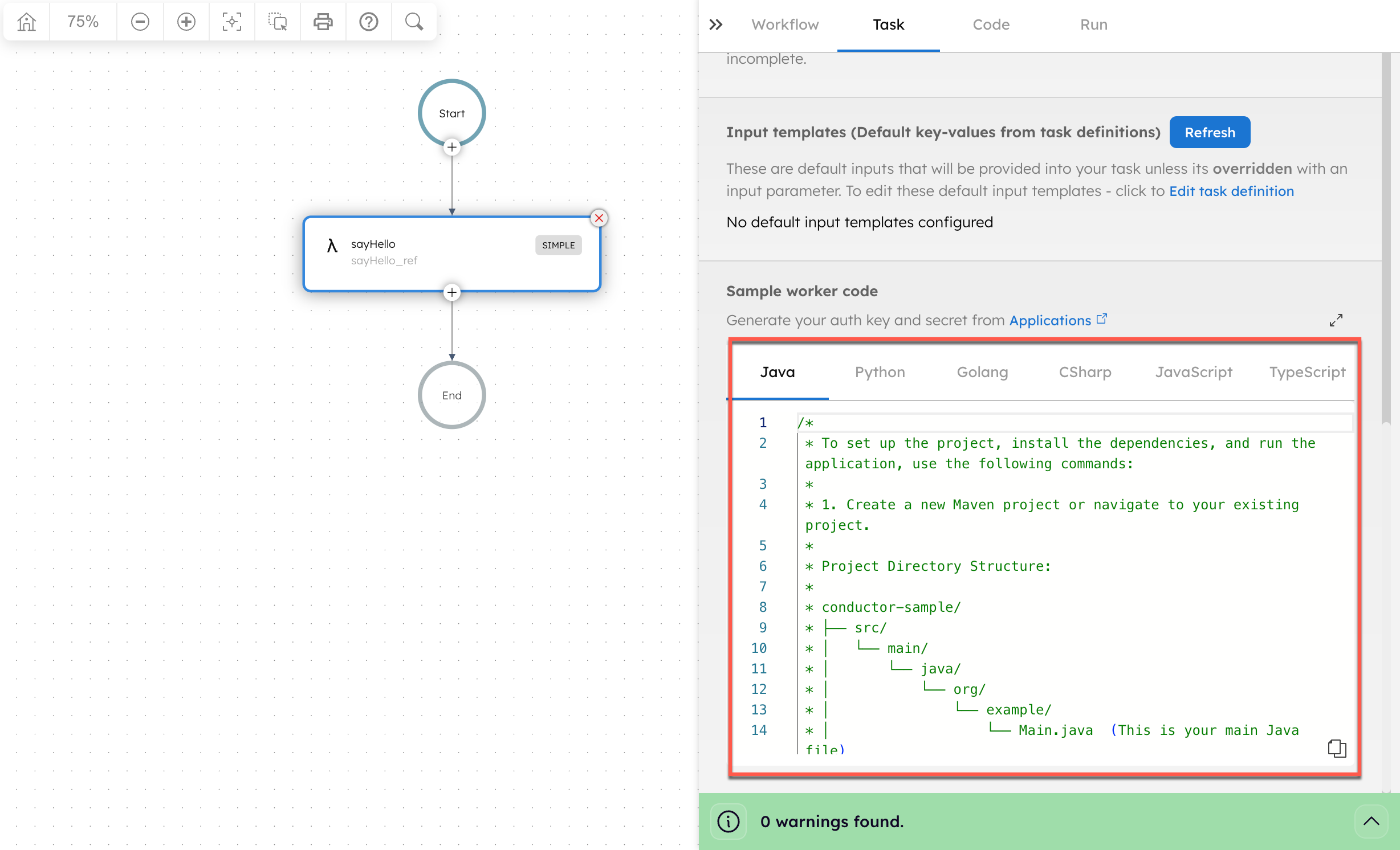
Sample worker code snippets are available in the Conductor UI for reference.
Examples
Using a Worker task
See an example of how to add and run a Worker task in our Quickstart guide.