Quickstart 2: Create Your First Workflow
Estimated time: 8min
In Conductor, workflow definitions are stored as JSON. These workflows can be created using a code-based approach or a UI-based approach:
- Workflow as code: Using the Conductor SDKs, define and execute your workflow in your preferred language.
- Visual workflow editor: Using the Conductor UI, define and execute your workflow visually.
In this quickstart, you will use your preferred option to:
- Create and register a workflow definition consisting of a system task, a custom task, and an operator.
- Test run the workflow.
Create and register a workflow
Follow along to build your first workflow, a conditional helloWorld flow that greets users based on their location.
- Visual workflow builder
- Workflow as code
Use the visual workflow builder in Conductor UI to create your helloWorld workflow.
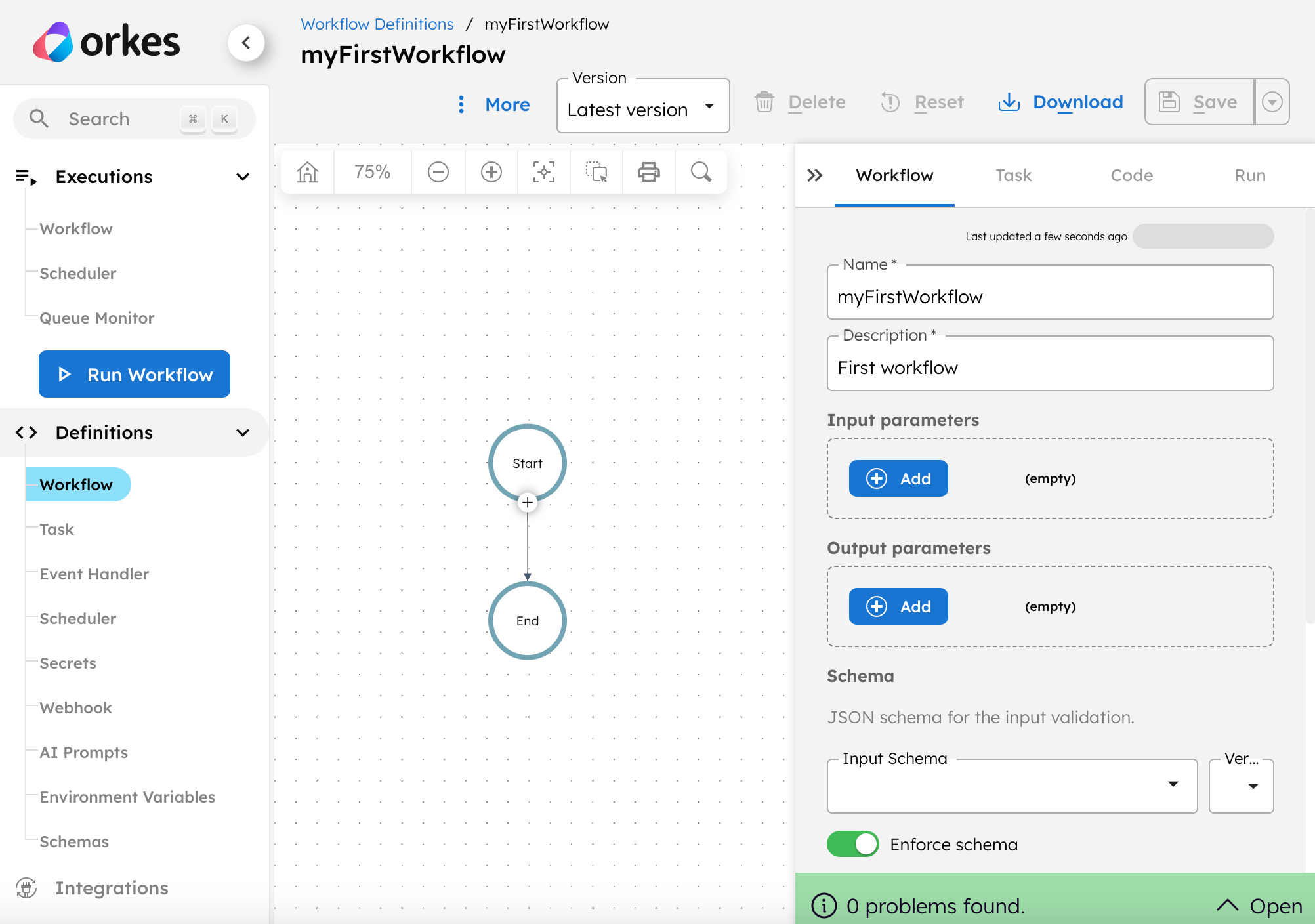
To create a workflow:
- Log in to your Conductor cluster or the Developer Edition.
- In the left navigation menu, go to Definitions > Workflow.
- Select + Define workflow.
-
Copy the JSON code below into the Code tab of the workflow builder.
{
"name": "helloWorld",
"description": "Hello World workflow that greets a user. Uses a Switch task, HTTP task, and Simple task.",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "get-user",
"taskReferenceName": "get-user_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://randomuser.me/api/",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
},
"type": "HTTP"
},
{
"name": "user-criteria",
"taskReferenceName": "user-criteria_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"switchCaseValue": "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].location.country}"
},
"type": "SWITCH",
"decisionCases": {
"United States": [
{
"name": "myTask",
"taskReferenceName": "myTask_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"name": "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].name.first}"
},
"type": "SIMPLE"
}
]
},
"defaultCase": [],
"evaluatorType": "value-param",
"expression": "switchCaseValue"
}
],
"inputParameters": [],
"outputParameters": {},
"failureWorkflow": "",
"schemaVersion": 2
} -
To register the workflow, select Save > Confirm.
Your first workflow has been created!
Note how the code above references myTask - this tells the workflow to push tasks on a queue with that name. Your local worker is then constantly polling for work on that queue (pointed to via the worker's taskDefName field). To learn more about how tasks are routed, see Routing Tasks.
Code your Hello World workflow using Conductor SDKs.
Step 1: Create your workflow in code
Create a project for your workflow client where you can define, register, and execute workflows programmatically. To get started quickly, download one of our sample workflow as code projects in your preferred language:
gh repo clone conductor-oss/conductor-apps
- Python
- Java
- JavaScript
- C#
- Go
- Clojure
This sample Python code demonstrates how to create, register, and execute a workflow in Conductor.
from conductor.client.http.models import StartWorkflowRequest
from conductor.client.configuration.configuration import Configuration
from conductor.client.configuration.settings.authentication_settings import AuthenticationSettings
from conductor.client.workflow.conductor_workflow import ConductorWorkflow
from conductor.client.workflow.executor.workflow_executor import WorkflowExecutor
from conductor.client.workflow.task.simple_task import SimpleTask
from conductor.client.workflow.task.http_task import HttpTask
from conductor.client.workflow.task.switch_task import SwitchTask
def main():
# Set up an application in your Orkes Conductor cluster. Sign up for a Developer Edition account at https://developer.orkescloud.com.
# - Set your cluster's URL as base_url (e.g., "https://developer.orkescloud.com" for Developer Edition).
# - Use the application's Key ID and Secret here.
conf = Configuration(base_url='_CHANGE_ME_',
authentication_settings=AuthenticationSettings(key_id='_CHANGE_ME_',
key_secret='_CHANGE_ME_'))
# A WorkflowExecutor instance is used to register and execute workflows.
executor = WorkflowExecutor(conf)
# Create the workflow definition.
workflow = ConductorWorkflow(
executor=executor,
name='myFirstWorkflow',
description='Workflow that greets a user. Uses a Switch task, HTTP task, and Simple task.',
version=1
)
# Create the tasks.
httpTask = HttpTask('get-user_ref', {'uri': 'https://randomuser.me/api/'})
switchTask = SwitchTask('user-criteria_ref', '${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].location.country}').switch_case(
'United States', SimpleTask('helloWorld', 'simple_ref').input(
key='user', value='${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].name.first}'))
# Add the tasks to the workflow using `add` method or the `>>` operator.
workflow.add(httpTask)
workflow >> switchTask
# Register the workflow.
workflow.register(True)
print(f"Registered workflow {workflow.name}")
# Start the workflow.
request = StartWorkflowRequest()
request.name = 'myFirstWorkflow'
request.version = 1
id = executor.start_workflow(request)
print(f"Started workflow {id}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
This sample Java code demonstrates how to create, register, and execute a workflow in Conductor.
import com.netflix.conductor.sdk.workflow.def.ConductorWorkflow;
import com.netflix.conductor.sdk.workflow.def.WorkflowBuilder;
import com.netflix.conductor.sdk.workflow.def.tasks.Http;
import com.netflix.conductor.sdk.workflow.def.tasks.SimpleTask;
import com.netflix.conductor.sdk.workflow.def.tasks.Switch;
import com.netflix.conductor.sdk.workflow.executor.WorkflowExecutor;
import io.orkes.conductor.client.ApiClient;
import java.util.Map;
public class WorkflowAsCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set up an application in your Orkes Conductor cluster. Sign up for a Developer Edition account at https://developer.orkescloud.com.
// - Set your cluster's API URL as basePath (e.g., "https://developer.orkescloud.com/api" for Developer Edition).
// - Use the application's Key ID and Secret here.
ApiClient client = ApiClient.builder()
.basePath("_CHANGE_ME_")
.credentials("_CHANGE_ME_", "_CHANGE_ME_")
.build();
// A WorkflowExecutor instance is used to register and execute workflows.
int pollingInterval = 50;
WorkflowExecutor executor = new WorkflowExecutor(client, pollingInterval);
// Create the workflow definition.
ConductorWorkflow<Object> workflow = new WorkflowBuilder<>(executor)
.name("myFirstWorkflow")
.version(1)
.description("Workflow that greets a user. Uses a Switch task, HTTP task, and Simple task.")
.add(new Http("get-user_ref").url("https://randomuser.me/api/"))
// This switch task will execute the "helloWorld" task if the user's country is "United States"
.add(new Switch("user-criteria_ref", "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].location.country}")
.switchCase("United States", new SimpleTask("helloWorld", "simple_ref")
.input("user", "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].name.first}")))
.build();
// Register the workflow with overwrite = true and registerTasks = true.
workflow.registerWorkflow(true, true);
// Start the workflow.
String id = executor.startWorkflow(workflow.getName(), workflow.getVersion(), Map.of());
System.out.printf("Started workflow %s%n", id);
executor.shutdown();
}
}
This sample JavaScript code demonstrates how to create, register, and execute a workflow in Conductor.
import {
orkesConductorClient,
WorkflowExecutor,
httpTask,
simpleTask,
switchTask,
} from "@io-orkes/conductor-javascript";
// Set up an application in your Orkes Conductor cluster. Sign up for a Developer Edition account at https://developer.orkescloud.com.
// - Set your cluster's API URL as the serverUrl (e.g., "https://developer.orkescloud.com/api" for Developer Edition).
// - Use the application's Key ID and Secret here.
const config = {
serverUrl: "_CHANGE_ME_",
keyId: "_CHANGE_ME_",
keySecret: "_CHANGE_ME_",
};
const client = await orkesConductorClient(config);
// A WorkflowExecutor instance is used to register and execute workflows.
const executor = new WorkflowExecutor(client);
// Create the workflow definition.
const wf = {
name: "myFirstWorkflow",
version: 1,
description:
"Workflow that greets a user. Uses a Switch task, HTTP task, and Simple task.",
tasks: [
httpTask("get-user_ref", { uri: "https://randomuser.me/api/" }),
switchTask(
"user-criteria_ref",
"${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].location.country}",
{
"United States": [
simpleTask("simple_ref", "helloWorld", {
user: "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].name.first}",
}),
],
}
),
],
};
// Register the workflow with overwrite = true.
await executor.registerWorkflow(true, wf);
// Start the workflow.
const id = await executor.startWorkflow({name: wf.name, version: wf.version});
console.log(`Started workflow: ${id}`);
client.stop()
This sample C# code demonstrates how to create, register, and execute a workflow in Conductor.
using Conductor.Client.Authentication;
using Conductor.Client.Models;
using Conductor.Client;
using Conductor.Definition;
using Conductor.Executor;
using Conductor.Definition.TaskType;
// Set up an application in your Orkes Conductor cluster. Sign up for a Developer Edition account at https://developer.orkescloud.com.
// - Set your cluster's API URL as the BasePath (e.g., "https://developer.orkescloud.com/api" for Developer Edition).
// - Use the application's Key ID and Secret here.
var conf = new Configuration
{
BasePath = "_CHANGE_ME_",
AuthenticationSettings = new OrkesAuthenticationSettings("_CHANGE_ME_", "_CHANGE_ME_")
};
// A WorkflowExecutor instance is used to register and execute workflows.
var executor = new WorkflowExecutor(conf);
// Create the workflow definition.
var workflow = new ConductorWorkflow()
.WithName("myFirstWorkflow")
.WithDescription("Workflow that greets a user. Uses a Switch task, HTTP task, and Simple task.")
.WithVersion(1)
.WithTask(new HttpTask("get-user_ref", new HttpTaskSettings { uri = "https://randomuser.me/api/" }))
.WithTask(new SwitchTask("user-criteria_ref", "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].location.country}")
.WithDecisionCase("United States",
[new SimpleTask("helloWorld", "simple_ref").WithInput("user", "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].name.first}")]));
// Register the workflow with overwrite = true.
executor.RegisterWorkflow(
workflow: workflow,
overwrite: true
);
// Start the workflow.
var workflowId = executor.StartWorkflow(new StartWorkflowRequest(name: workflow.Name, version: workflow.Version));
Console.WriteLine($"Started Workflow: {workflowId}");
This sample Go code demonstrates how to create, register, and execute a workflow in Conductor.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/conductor-sdk/conductor-go/sdk/client"
"github.com/conductor-sdk/conductor-go/sdk/model"
"github.com/conductor-sdk/conductor-go/sdk/settings"
"github.com/conductor-sdk/conductor-go/sdk/workflow"
"github.com/conductor-sdk/conductor-go/sdk/workflow/executor"
)
// Set up an application in your Orkes Conductor cluster. Sign up for a Developer Edition account at https://developer.orkescloud.com.
// - Use the application's Key ID and Secret here.
// - Set your cluster's API URL as the SERVER_URL (e.g., "https://developer.orkescloud.com/api" for Developer Edition).
const SERVER_URL = "_CHANGE_ME_"
const KEY_ID = "_CHANGE_ME_"
const SECRET = "_CHANGE_ME_"
var (
apiClient = client.NewAPIClient(
settings.NewAuthenticationSettings(KEY_ID, SECRET),
settings.NewHttpSettings(SERVER_URL))
// A WorkflowExecutor instance is used to register and execute workflows.
workflowExecutor = executor.NewWorkflowExecutor(apiClient)
)
func main() {
// Create the workflow definition.
wf := workflow.NewConductorWorkflow(workflowExecutor).
Name("myFirstWorkflowGo").
Version(1).
Description("Workflow that greets a user. Uses a Switch task, HTTP task, and Simple task.")
httpTask := workflow.NewHttpTask("get-user_ref", &workflow.HttpInput{Uri: "https://randomuser.me/api/"})
switchTask := workflow.NewSwitchTask("user-criteria_ref", "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].location.country}").
SwitchCase("United States", workflow.NewSimpleTask("helloWorld", "simple_ref").Input("user", "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].name.first}"))
wf.Add(httpTask)
wf.Add(switchTask)
// Register the workflow with overwrite = true.
err := wf.Register(true)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to register workflow: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Registered workflow: %s\n", wf.GetName())
// Start the workflow.
id, err := workflowExecutor.StartWorkflow(&model.StartWorkflowRequest{
Name: wf.GetName(),
Version: wf.GetVersion(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error when starting workflow: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Started workflow: %s\n", id)
}
This sample Clojure code demonstrates how to create, register, and execute a workflow in Conductor.
(ns wac.core
(:require [io.orkes.workflow-resource :as wr]
[io.orkes.sdk :as sdk]
[io.orkes.metadata :as metadata])
(:gen-class))
; Set up an application in your Orkes Conductor cluster. Sign up for a Developer Edition account at https://developer.orkescloud.com.
; - Set your cluster's API URL as url (e.g., "https://developer.orkescloud.com/api/" for Developer Edition).
; - Use the application's Key ID and Secret here.
(def options
{:url "_CHANGE_ME_"
:app-key "_CHANGE_ME_"
:app-secret "_CHANGE_ME_"})
; Function that creates the tasks.
(defn create-tasks
[]
(vector (sdk/http-task "get-user_ref" {:uri "https://randomuser.me/api/"})
(sdk/switch-task "user-criteria_ref" "${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].location.country}"
{"United States" [(sdk/simple-task "simple_ref"
"helloWorld"
{"user"
"${get-user_ref.output.response.body.results[0].name.first}"})]}
[])))
; Function that creates the workflow definition.
(defn create-workflow
[tasks]
(merge (sdk/workflow "myFirstWorkflow" tasks)))
(defn -main
[]
; Register the workflow with overwrite = true
(metadata/register-workflow-def options (-> (create-tasks) (create-workflow)) true)
; Start the workflow
(let [workflow-id (wr/start-workflow options {:name "myFirstWorkflow" :version 1})]
(println "Started workflow:" workflow-id)))
Step 2: Get access credentials for your workflow client
To connect your workflow-as-code project, you must again use an application in Conductor, which is an access layer with its own permissions and access tokens. This time, the application should have the Metadata API role.
To create an application for your workflow client:
- In the left navigation menu of the Conductor UI, go to Access Control > Applications.
- Select + Create application and enter a Name for it. For example, myWorkflowClient or myApp.
- Enable the Metadata API application role, which allows the application to create and manage workflows and tasks.
- Select + Create access key and store the generated credentials securely.
- Set the Server URL, Key ID, and Key Secret in your project.
Example (Java)
ApiClient client = ApiClient.builder()
.basePath("[https://SERVER_URL/api](https://SERVER_URL/api)") // e.g., “[https://developer.orkescloud.com/api](https://developer.orkescloud.com/api)” for Developer Edition
.credentials("_CHANGE_ME_", "_CHANGE_ME_")
.build();
The application account can now create, manage, and execute the workflow.
Run workflow
Let’s give your first workflow a test run.
Before running the workflow, make sure that your myTask worker is actively polling the Conductor server. Otherwise, go back and start your worker again.
- Visual workflow builder
- Workflow as code
Inside the workflow visual builder, go to the Run tab and select Execute.
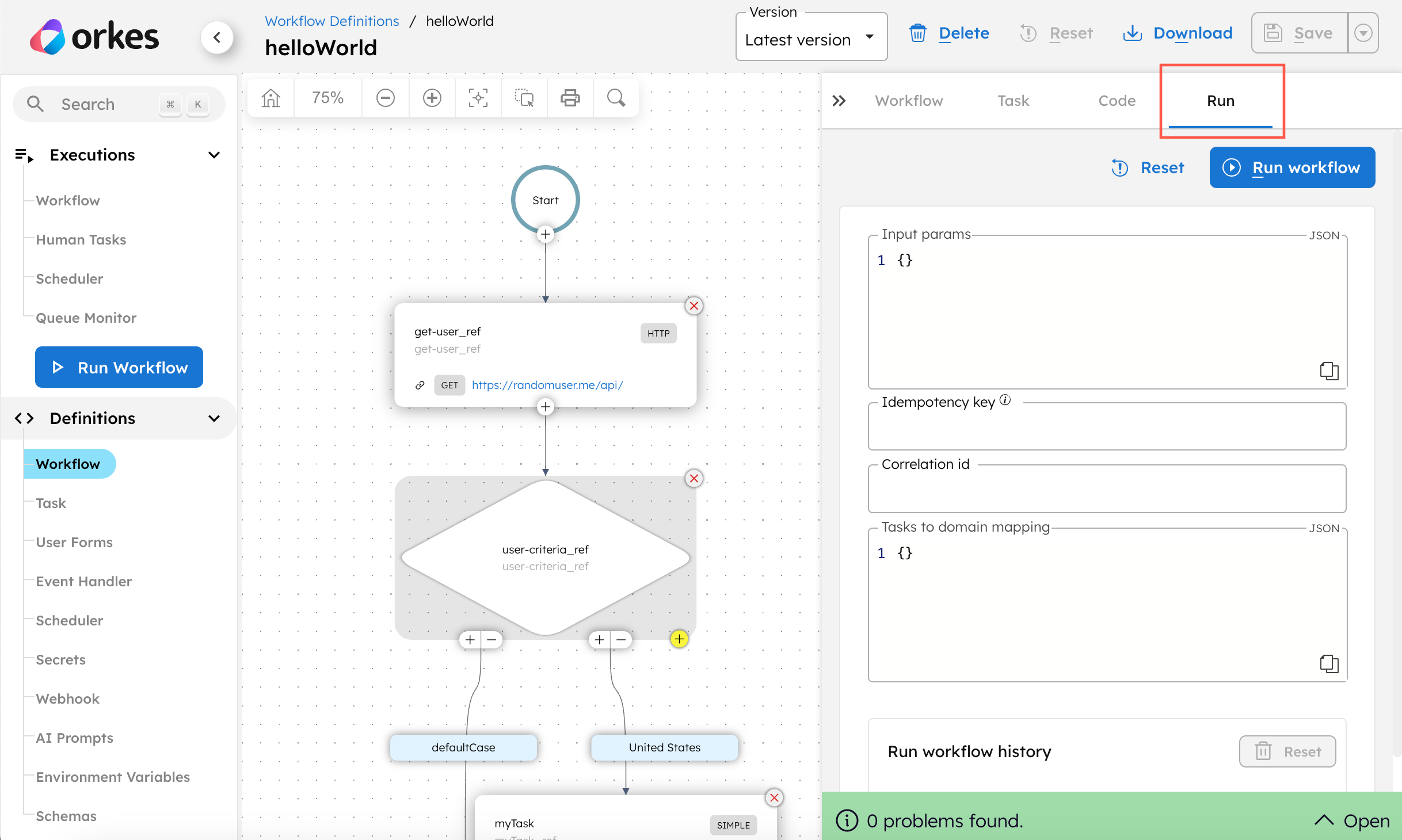
Using the command line, launch the workflow client. The commands depend on your language and project configuration. You can follow the README instructions in the sample workflow-as-code project to register and run the workflow.
Example (Java)
./gradlew build
./gradlew run
Done! To track the workflow progress, go to Executions > Workflow in the Conductor UI.
Now that you have gotten the hang of creating workflows, let’s discover the power of Conductor in monitoring and debugging workflow executions in the next quickstart.