Routing Tasks (Task-to-domain)
In Conductor, tasks are executed by workers, and the Conductor server manages task distribution through a task queue. The task-to-domain feature allows tasks to be routed to specific sets of workers based on domain labels. This gives you finer control over task execution, enabling you to assign tasks to workers with specific capabilities, permissions, or configurations.
What is task-to-domain?
Task-to-domain mapping allows you to route task executions to a specific pool of workers. The domain is an arbitrary string that can be freely defined, allowing you to split your task traffic by application, client type, and so on.
To better understand the concept of routing tasks, consider an example task, send_email. By default, the task queue distributes this task to all available workers, as shown:
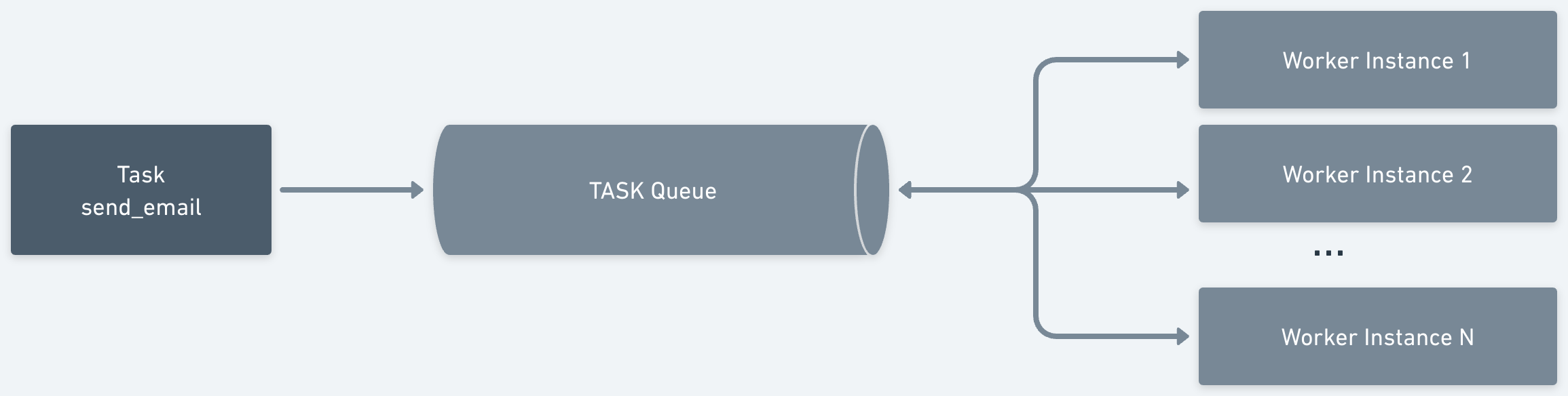
To route this task to a specific group of workers, you can assign it a domain when triggering the workflow. The task is then routed only to workers configured for that domain.
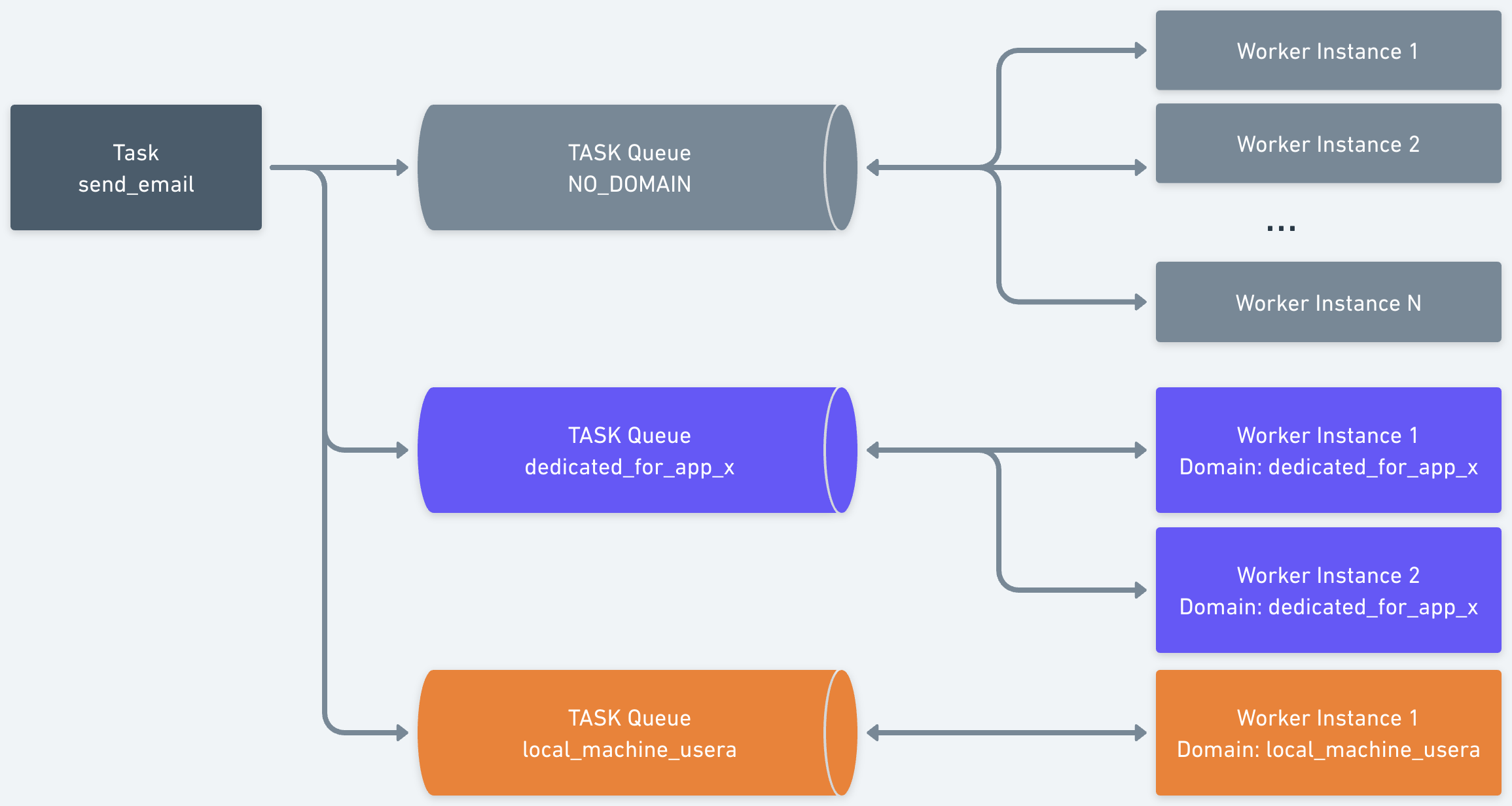
Here, the send_email task has two additional sets of worker instances that listen to specific domain-based tasks. For example, all the tasks triggered with the domain dedicated_for_app_x are sent to the workers configured with the domain dedicated_for_app_x.
The task-to-domain feature is useful in the following scenarios:
- Ensuring that the task is routed to a worker with the appropriate permissions.
- Load balancing or prioritizing some tasks with a set of dedicated workers.
- Implementing unique task-related configuration by domain, such as a retry policy.
- Debugging a task with a worker deployed on a local machine or a worker running a different version of the code.
While these use cases can be achieved by creating separate task definitions, task-to-domain is more flexible. For example, instead of creating new task definitions in production environments, you can use the same one while customizing routing based on the domain.
Routing tasks using task-to-domain
To successfully route a task by domain:
- Configure workers to poll for tasks mapped to a specific domain.
- When triggering the workflow, ensure
taskToDomainis mapped to the correct domain.
Worker configuration
Workers must be configured to listen for tasks mapped with a specific domain. Below are examples demonstrating how to set up workers to poll for tasks in the test domain across various programming languages:
- Java
- Python
- JavaScript
- Typescript
- Clojure
The following table shows the order of precedence when initializing the task domain for a worker. Suppose a system property is set according to the table below. In that case, it takes priority over initializing the taskToDomain map or passing the domain as an argument when using annotations. If ${TASK_NAME} is replaced by all in the system property name, then all workers will pick up that task domain.
| Description | PropertyName | Example |
|---|---|---|
| System property by taskName | conductor.worker.${TASK_NAME}.domain | conductor.worker.taskName.domain=test |
| System property for all workers | conductor.worker.all.domain | conductor.worker.all.domain=test |
Class TaskRunner constructor param | taskToDomain | taskToDomain=Map.of("taskName", "test") |
Annotation @WorkerTask constructor param | domain | @WorkerTask(value="taskName", domain="test") |
Code example for TaskRunner:
Map<String, String> taskToDomains = new HashMap<>();
taskToDomains.put("taskName", "test");
Map<String, Integer> taskThreadCount = new HashMap<>();
TaskRunnerConfigurer.Builder builder = new TaskRunnerConfigurer.Builder(taskClient, workers);
TaskRunnerConfigurer taskRunner = builder.withTaskToDomain(taskToDomains).build();
Code example for @WorkerTask:
@WorkerTask(value="taskName", domain="test")
public TaskResult sendAnnotatedTaskDomain(Task task) {
TaskResult result = new TaskResult(task);
// Populate result here
return result;
}
In the example above, we map the task taskName to the domain test. Only workers configured to poll for the test domain will execute the task when the workflow is triggered. See the complete code here.
# Function Worker
def execute(task: Task) -> TaskResult:
task_result = TaskResult(
task_id=task.task_id,
workflow_instance_id=task.workflow_instance_id,
worker_id='your_custom_id'
)
task_result.add_output_data('worker_style', 'function')
task_result.status = TaskResultStatus.COMPLETED
return task_result
# Class Worker
class SimpleWorker(WorkerInterface):
def execute(self, task: Task) -> TaskResult:
task_result = self.get_task_result_from_task(task)
task_result.add_output_data('worker_style', 'class')
task_result.status = TaskResultStatus.COMPLETED
return task_result
def get_polling_interval_in_seconds(self) -> float:
return 0.4
# Overriding it for specifying the DOMAIN of class workers
def get_domain(self) -> str:
return "test"
def startTaskRunnerWorkers():
configuration = Configuration(
authentication_settings=AuthenticationSettings(
key_id='key',
key_secret='secret'
),
server_api_url='https://developer.orkescloud.com/api',
debug=True
)
workers = [
Worker(
task_definition_name='task_1',
execute_function=execute,
poll_interval=0.25,
domain="test" # specifying DOMAIN for function workers
),
SimpleWorker(task_definition_name="task_2")
]
In this example, we configure the SimpleWorker to listen for tasks with the test domain by implementing the get_domain() method. See additional examples.
// You can specify on the worker
export const userInfoWorker = () => {
return {
domain: "myDomain",
taskDefName: GET_USER_INFO,
execute: async ({ inputData }) => {
const userId = inputData?.userId;
return {
outputData: {
email: `${userId}@email.com`,
phoneNumber: "555-555-5555",
},
status: "COMPLETED",
};
},
};
};
// or on the Poller Option
new TaskManager(client, workers, {
logger: console,
options: { concurrency: 5, pollInterval: 100, domain: "domain" },
});
// *Note* worker domain has precedence over the domain passed in the poller
// You can specify on the worker
export const userInfoWorker = (): ConductorWorker => {
return {
domain: "myDomain",
taskDefName: GET_USER_INFO,
execute: async ({ inputData }) => {
const userId = inputData?.userId;
return {
outputData: {
email: `${userId}@email.com`,
phoneNumber: "555-555-5555",
},
status: "COMPLETED",
};
},
};
};
// or on the Poller Option
new TaskManager(client, workers, {
logger: console,
options: { concurrency: 5, pollInterval: 100, domain: "domain" },
});
// *Note* worker domain has precedence over the domain passed in the poller
(runner-executer-for-workers options [worker] 1 {:domain 'some-domain'})
Workflow configuration
When you start a workflow, you can specify which tasks must run on which domains.
- Using Conductor UI
- Using API
For running a workflow from the Conductor UI, define the following task-to-domain mapping:
{
"task_x": "test"
}
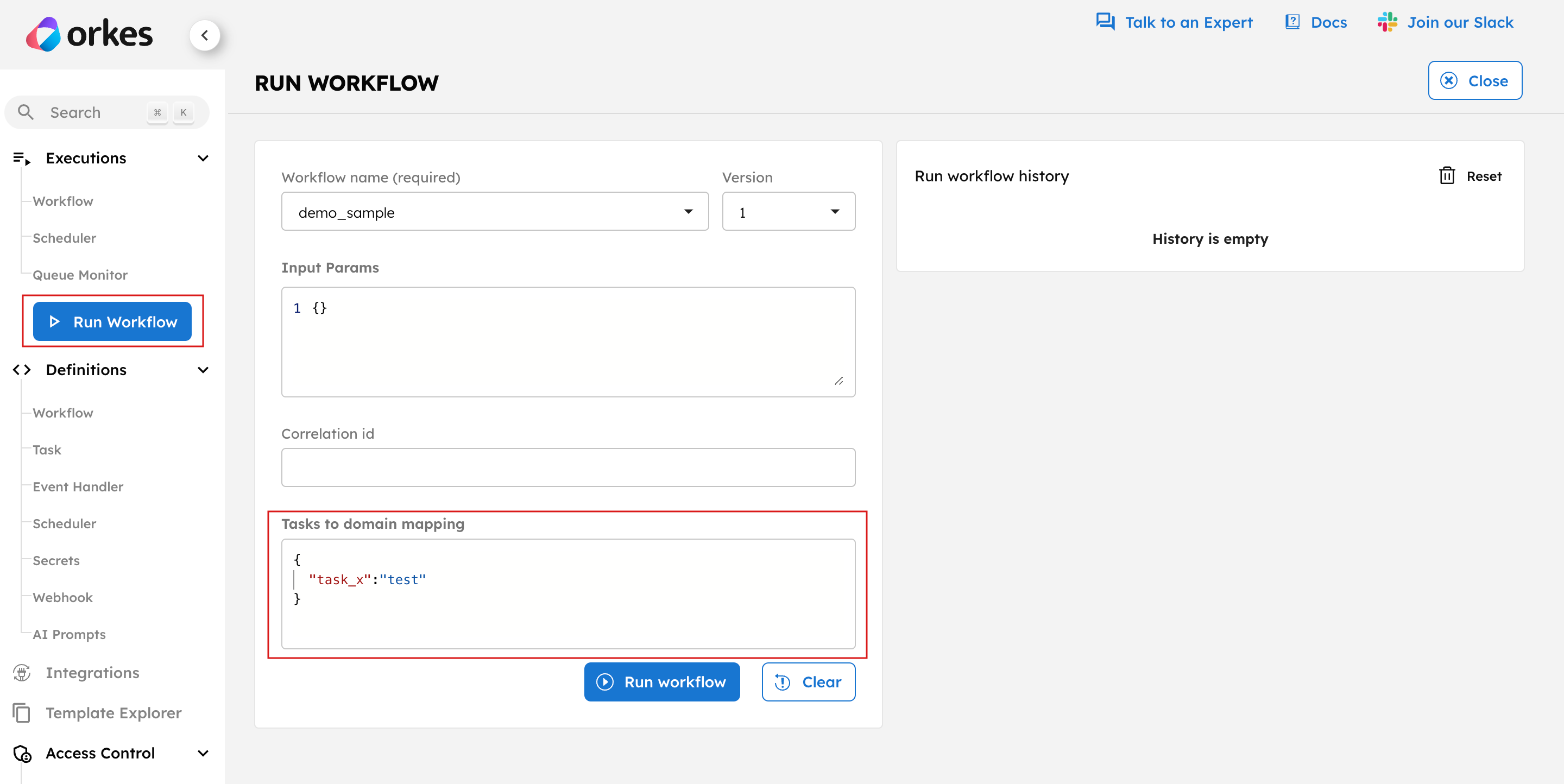
Use the Start Workflow Execution API to trigger the workflow by providing the taskToDomain as the input payload.
POST /api/workflow/{name}
RBAC configuration
While configuring groups or applications in Conductor, you can add granular permissions to access specific resources. This includes granting permission to specific domains and allowing applications or groups to execute all tasks under that domain by eliminating the need to configure access for individual tasks.
To enable domain permissions:
- Go to Access Control > Applications/Groups from the left menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select your application or group.
- Scroll down to Permissions, and select + Add permission.
- In the Domain tab, select + Add, and enter the domain name.
- Enable the Execute toggle.
- Select Add Permissions.
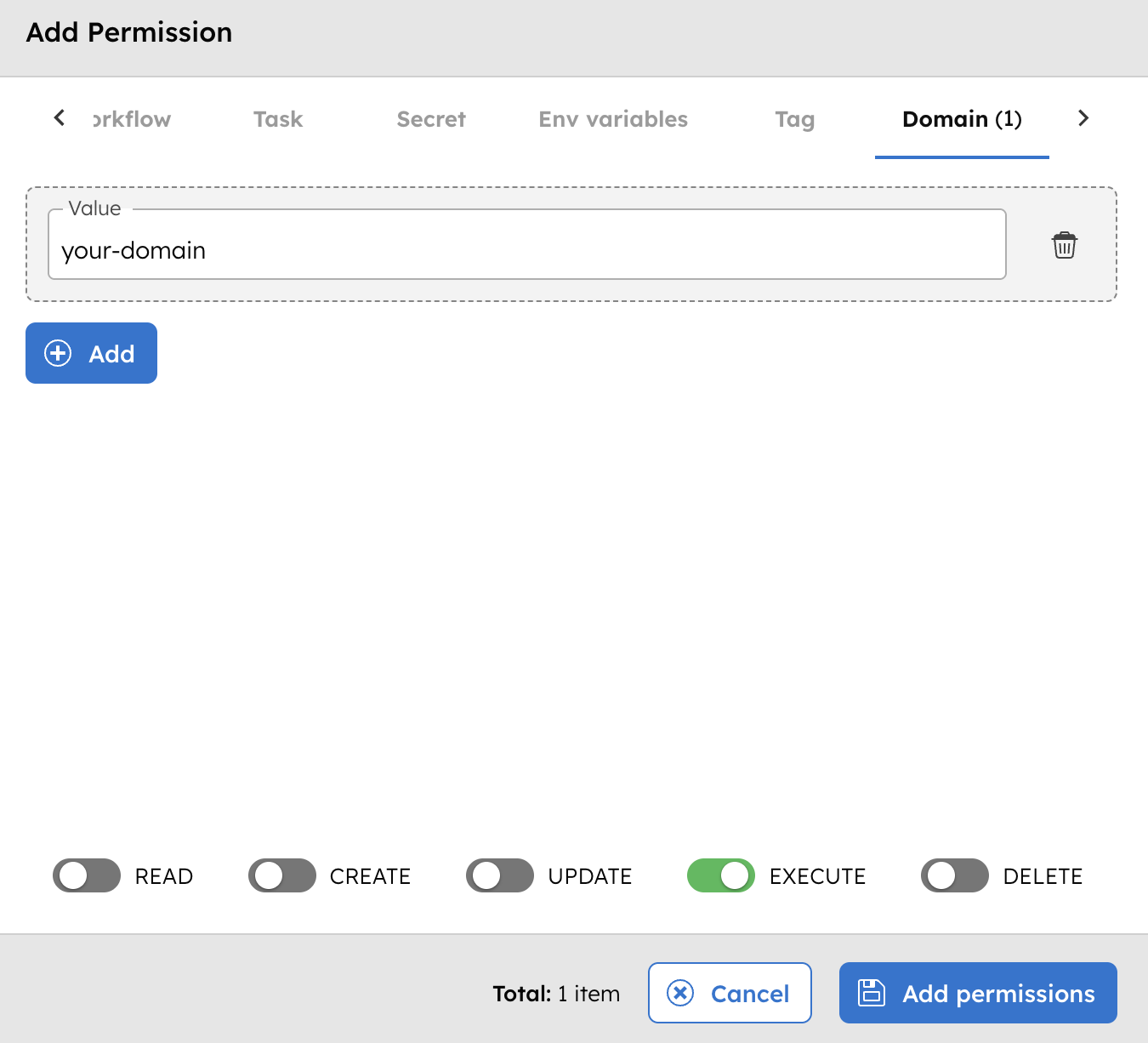
The application/group can now execute all tasks under the specified domain.
Fallback task-to-domain
A fallback domain is a secondary or backup domain that the system will use if the primary domain fails or is unreachable. These domains can only be specified when triggering a workflow, as clients polling for tasks can use only one domain at a time.
Conductor tracks the last polling time for each worker. When assigning tasks, it first checks if any active workers are available for the primary domain. If no active workers are found, the Conductor tries the next domain in the fallback sequence.
- A worker is considered active if the polled time is within the active threshold, which defaults to 10 seconds.
- Workers do not poll when they are busy doing work and resume polling after completing their tasks.
- The active threshold can be adjusted using the configuration field
conductor.app.activeWorkerLastPollTimeout. This applies to all worker tasks, so extending the duration slows down the fallback response behavior across all tasks. - The domain of a task is determined at the time when the task is scheduled. Therefore, a domain worker becoming available after a task is scheduled will not change the domain of the already scheduled task.
A fallback mapping for `task_x’ is as follows:
{
"task_x": "test,fallback,NO_DOMAIN"
}
In this configuration,
- Conductor first assigns the task to workers in the
testdomain if available. - If no workers are active in the
testdomain, it tries thefallbackdomain. - If neither
testnorfallbackhas active workers, the task is assigned toNO_DOMAIN.
NO_DOMAINis a generic keyword for workers with no domain.- Always use
NO_DOMAINas the final fallback option. - If
NO_DOMAINis not included, the task falls back to subsequent domains. If it reaches an inactive domain, it remains there indefinitely until workers for that domain become active. - Use the
*token to apply domains for all tasks. This can be overridden by providing task-specific mappings along with*.
Example
Task-to-domain implementation using Java Spring Boot
Let’s create a simple workflow that includes a worker task (SIMPLE) and configure it to poll only from a specific domain.
Step 1: Create a task definition
To create a task definition:
- Go to Definitions > Task from the left menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define task.
- In Code tab, paste the following JSON:
{
"name": "hello_task",
"description": "Sample",
"retryCount": 3,
"timeoutSeconds": 3600,
"inputKeys": [],
"outputKeys": [],
"timeoutPolicy": "TIME_OUT_WF",
"retryLogic": "FIXED",
"retryDelaySeconds": 60,
"responseTimeoutSeconds": 600,
"concurrentExecLimit": 0,
"inputTemplate": {},
"rateLimitPerFrequency": 0,
"rateLimitFrequencyInSeconds": 1,
"ownerEmail": "john.doe@acme.com",
"pollTimeoutSeconds": 3600,
"backoffScaleFactor": 1,
"totalTimeoutSeconds": 0,
"enforceSchema": false
}
- Select Save > Confirm Save.
Step 2: Create a workflow definition
To create a workflow definition:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow from the left menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In Code tab, paste the following JSON:
{
"name": "hello_world_workflow",
"description": "A simple workflow that runs the hello_task in test_domain",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "hello_task",
"taskReferenceName": "hello_ref",
"type": "SIMPLE"
}
],
"schemaVersion": 2
}
- Select Save > Confirm Save.
Step 3: Configure task-to-domain routing in Spring Boot
This Spring Boot worker configuration connects to your Orkes Conductor cluster and sets up domain-based task polling. This configuration:
- Loads a task-to-domain mapping
- Registers the worker
- Routes
hello_tasktotest_domain
package com.example.demo.condutor;
import com.netflix.conductor.client.automator.TaskRunnerConfigurer;
import com.netflix.conductor.client.http.TaskClient;
import com.netflix.conductor.client.worker.Worker;
import io.orkes.conductor.client.ApiClient;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Configuration
public class ConductorConfig {
private static final String CONDUCTOR_SERVER = "http://<YOUR-SERVER-URL>/api";
private static final String KEY = "<YOUR-ACCESS-KEY>";
private static final String SECRET = "<YOUR-ACCESS-SECRET>";
// Environment properties simulation
private static final Map<String, String> environment = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static {
// Initialize environment properties
environment.put("conductor.server.url", CONDUCTOR_SERVER);
environment.put("conductor.security.client.key-id", KEY);
environment.put("conductor.security.client.secret", SECRET);
environment.put("verifySsl", "N");
environment.put("isTaskToDomainEnabled", "Y");
// Sample task to domain mapping
environment.put("taskToDomain",
"{\"task_example\": \"test_domain\", \"hello_task\": \"test_domain\", \"*\": \"default_domain\"}");
}
@Bean
public TaskClient taskClient(ApiClient apiClient) {
return new TaskClient(apiClient);
}
@Bean
@Primary
public TaskRunnerConfigurer domainAwareTaskRunnerConfigurer(TaskClient taskClient) {
List<Worker> workers = List.of(new HelloWorldWorker());
// Create taskToDomain map from properties
Map<String, String> taskToDomain = loadTaskToDomainMap();
// Log what we're doing (for debugging)
System.out.println("Creating domain-aware TaskRunnerConfigurer with domains: " + taskToDomain);
// Create the TaskRunnerConfigurer with domain settings
TaskRunnerConfigurer configurer = new TaskRunnerConfigurer.Builder(taskClient, workers)
.withThreadCount(5) // Use your desired thread count
.withTaskToDomain(taskToDomain)
.build();
configurer.init();
return configurer;
}
private Map<String, String> loadTaskToDomainMap() {
Map<String, String> taskToDomain = new HashMap<>();
String isTaskToDomainEnabled = "Y";
if ("Y".equals(isTaskToDomainEnabled)) {
String taskToDomainJsonStr = environment.get("taskToDomain");
if (taskToDomainJsonStr != null && !taskToDomainJsonStr.isEmpty()) {
try {
JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
JSONObject taskToDomainJson = (JSONObject) parser.parse(taskToDomainJsonStr);
// Convert JSON object to Map<String, String>
for (Object key : taskToDomainJson.keySet()) {
String taskName = (String) key;
String domainValue = (String) taskToDomainJson.get(key);
taskToDomain.put(taskName, domainValue);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error parsing taskToDomain JSON: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
return taskToDomain;
}
@Bean
public static ApiClient getApiClientForOrkes() throws Exception {
// Initialize the API client first
String envKey = (String) env.getProperty("conductor.security.client.key-id");
String envSecret = (String) env.getProperty("conductor.security.client.secret");
String rootUrl = (String) env.getProperty("conductor.server.url");
boolean verifySsl = env.getProperty("verifySsl", "N").equals("Y");
ApiClient apiClient = ApiClient.builder()
.basePath(CONDUCTOR_SERVER)
.credentials(envKey, envSecret)
.verifyingSsl(verifySsl)
.readTimeout(50000)
.build();
// Initialize TaskClient with the API client
TaskClient taskClient = new TaskClient(apiClient);
// Set up taskToDomain mapping
Map<String, String> taskToDomain = new HashMap<>();
String isTaskToDomainEnabled = "Y";
if ("Y".equals(isTaskToDomainEnabled)) {
String taskToDomainJsonStr = environment.get("taskToDomain");
if (taskToDomainJsonStr != null && !taskToDomainJsonStr.isEmpty()) {
try {
JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
JSONObject taskToDomainJson = (JSONObject) parser.parse(taskToDomainJsonStr);
// Convert JSON object to Map<String, String>
for (Object key : taskToDomainJson.keySet()) {
String taskName = (String) key;
String domainValue = (String) taskToDomainJson.get(key);
taskToDomain.put(taskName, domainValue);
}
// Log the taskToDomain map to verify it's populated
System.out.println("Task to Domain mapping: " + taskToDomain);
} catch (org.json.simple.parser.ParseException e) {
System.err.println("Error parsing taskToDomain JSON: " + e.getMessage());
// Don't throw runtime exception - continue with empty map instead
}
}
}
return apiClient;
}
}
Step 4: Generate access keys
To connect your Java Spring Boot worker to a Conductor cluster, you must generate application credentials with the required permissions:
To generate the access keys:
- Go to Access Control > Applications from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Create application.
- Name your application and enable Application roles > Worker.
- Select + Create access key.
- Store the key ID and key secret, as the secret would be shown only once.
- In Permissions section, select + Add permission.
- In the Workflow tab, search for
hello_world_workflowand enable EXECUTE permission. - In the Task tab, search for
hello_taskand enable EXECUTE permission.
Then update the following lines in your worker code with your credentials:
private static final String CONDUCTOR_SERVER = "http://<YOUR-SERVER-URL>/api";
private static final String KEY = "<YOUR-ACCESS-KEY>";
private static final String SECRET = "<YOUR-ACCESS-SECRET>";
Step 5: Run your Spring Boot application
Once configured, start your Java application. Your worker will register and start polling tasks.
Step 6: Run the workflow
To run the workflow:
- From your workflow definition, go to the Run tab.
- In Tasks to domain mapping, enter the following mapping:
{
"hello_task": "test_domain"
}
- Select Run workflow.
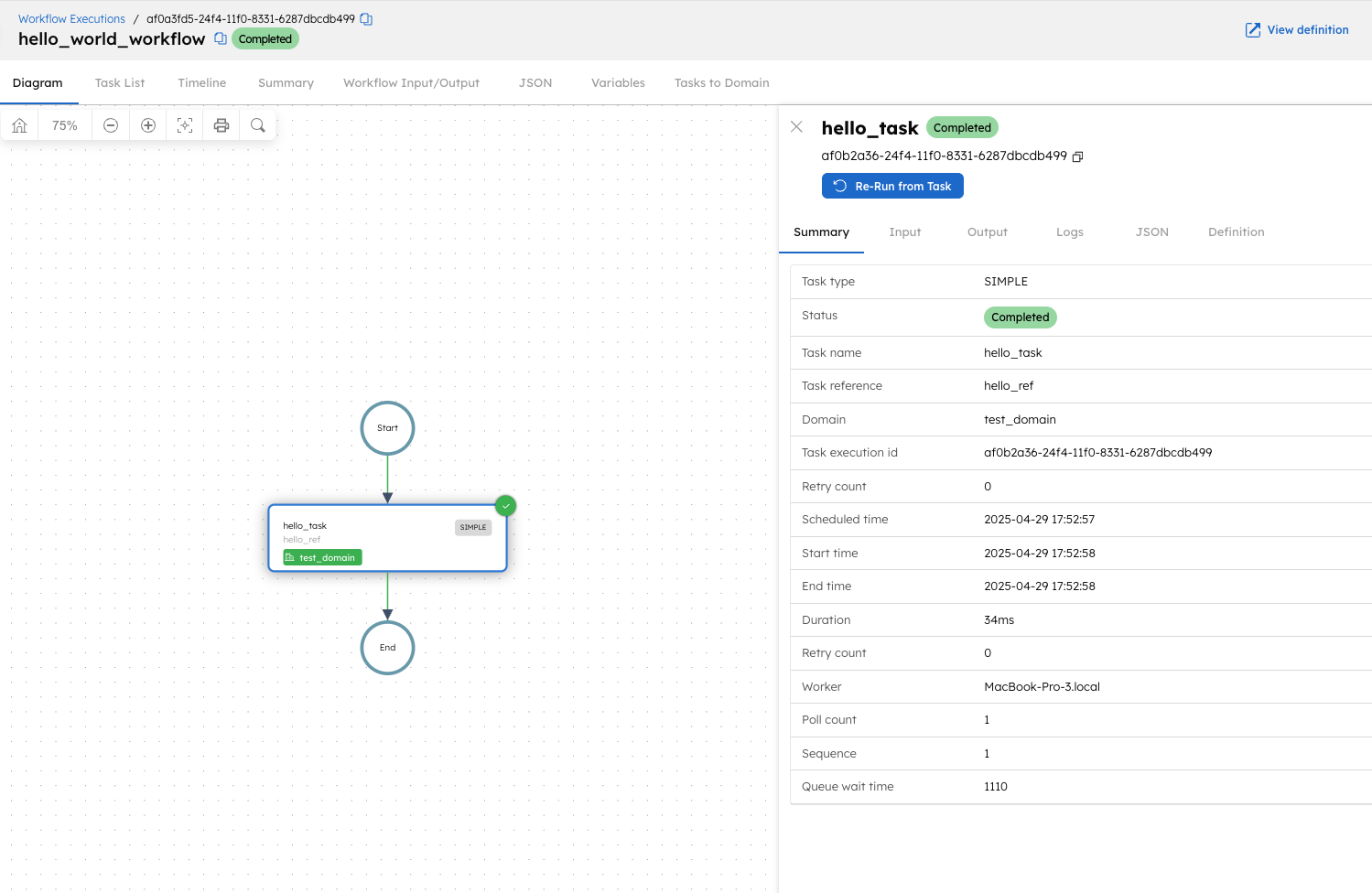
The hello_task will be picked up only by the worker polling test_domain. You can verify this in the Conductor UI under Executions > Workflows, where the task’s domain will be shown as test_domain.
Task-to-domain implementation using a Java client
This example shows how to configure domain-based task routing in a Java application.
What this setup does:
- Connects to your Orkes Conductor cluster using access credentials
- Maps
hello_taskto thetest_domainusing a task-to-domain map - Defines a
HelloWorldWorkerto process the task - Registers a sample workflow (
hello_world_workflow) - Starts the workflow and verifies that the task runs in the right domain
- Prints workflow status and task output
How to run this example:
To connect your Java worker to a Conductor cluster, you must generate access keys.
To generate the access keys:
- Go to Access Control > Applications from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Create application.
- Name your application and enable Application roles > Worker.
- Select + Create access key.
- Store the key ID and key secret, as the secret would be shown only once.
- Replace the credentials and cluster URL in the code below:
import com.netflix.conductor.client.automator.TaskRunnerConfigurer;
import com.netflix.conductor.client.http.MetadataClient;
import com.netflix.conductor.client.http.TaskClient;
import com.netflix.conductor.client.worker.Worker;
import com.netflix.conductor.common.metadata.tasks.Task;
import com.netflix.conductor.common.metadata.tasks.TaskResult;
import com.netflix.conductor.common.metadata.workflow.StartWorkflowRequest;
import com.netflix.conductor.common.metadata.workflow.WorkflowDef;
import com.netflix.conductor.common.run.Workflow;
import io.orkes.conductor.client.ApiClient;
import io.orkes.conductor.client.http.OrkesWorkflowClient;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class ConductorClientTest {
private static final String CONDUCTOR_SERVER = "http://<YOUR-SERVER-URL>/api";
private static final String KEY = "<YOUR-ACCESS-KEY>";
private static final String SECRET = "<YOUR-ACCESS-SECRET>";
private static final Map<String, String> environment = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static {
environment.put("conductor.server.url", CONDUCTOR_SERVER);
environment.put("conductor.security.client.key-id", KEY);
environment.put("conductor.security.client.secret", SECRET);
environment.put("verifySsl", "N");
environment.put("isTaskToDomainEnabled", "Y");
environment.put("taskToDomain",
"{\"task_example\": \"test_domain\", \"hello_task\": \"test_domain\", \"*\": \"default_domain\"}");
}
public static class HelloWorldWorker implements Worker {
@Override
public String getTaskDefName() {
return "hello_task";
}
@Override
public TaskResult execute(Task task) {
System.out.println("===> Worker started executing task: " + task.getTaskDefName());
TaskResult result = new TaskResult(task);
result.setStatus(TaskResult.Status.COMPLETED);
result.addOutputData("greeting", "Hello " + task.getInputData().getOrDefault("name", "World"));
System.out.println("===> Task completed with output: " + result.getOutputData());
return result;
}
}
public static class Environment {
public Object getProperty(String key) {
return environment.get(key);
}
public Object getProperty(String key, String defaultValue) {
return environment.getOrDefault(key, defaultValue);
}
}
public static ApiClient getApiClientForOrkes(Environment env) throws Exception {
String envKey = (String) env.getProperty("conductor.security.client.key-id");
String envSecret = (String) env.getProperty("conductor.security.client.secret");
String rootUrl = (String) env.getProperty("conductor.server.url");
boolean verifySsl = env.getProperty("verifySsl", "N").equals("Y");
ApiClient apiClient = ApiClient.builder()
.basePath(rootUrl)
.credentials(envKey, envSecret)
.verifyingSsl(verifySsl)
.readTimeout(50000)
.build();
TaskClient taskClient = new TaskClient(apiClient);
Map<String, String> taskToDomain = new HashMap<>();
String taskToDomainJsonStr = (String) env.getProperty("taskToDomain");
if (taskToDomainJsonStr != null && !taskToDomainJsonStr.isEmpty()) {
JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
JSONObject taskToDomainJson = (JSONObject) parser.parse(taskToDomainJsonStr);
for (Object key : taskToDomainJson.keySet()) {
taskToDomain.put((String) key, (String) taskToDomainJson.get(key));
}
System.out.println("Task to Domain mapping: " + taskToDomain);
}
List<Worker> workers = List.of(new HelloWorldWorker());
TaskRunnerConfigurer configurer = new TaskRunnerConfigurer.Builder(taskClient, workers)
.withTaskToDomain(taskToDomain)
.withThreadCount(5)
.build();
configurer.init();
return apiClient;
}
public static void registerWorkflow(ApiClient apiClient, String workflowJson) throws Exception {
MetadataClient metadataClient = new MetadataClient(apiClient);
JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
JSONObject workflowObj = (JSONObject) parser.parse(workflowJson);
WorkflowDef workflowDef = new WorkflowDef();
workflowDef.setName((String) workflowObj.get("name"));
workflowDef.setDescription((String) workflowObj.get("description"));
workflowDef.setVersion(((Long) workflowObj.getOrDefault("version", 1L)).intValue());
workflowDef.setSchemaVersion(((Long) workflowObj.getOrDefault("schemaVersion", 2L)).intValue());
List<com.netflix.conductor.common.metadata.workflow.WorkflowTask> workflowTasks = new ArrayList<>();
org.json.simple.JSONArray tasksArray = (org.json.simple.JSONArray) workflowObj.get("tasks");
for (Object taskObj : tasksArray) {
JSONObject task = (JSONObject) taskObj;
com.netflix.conductor.common.metadata.workflow.WorkflowTask workflowTask =
new com.netflix.conductor.common.metadata.workflow.WorkflowTask();
workflowTask.setName((String) task.get("name"));
workflowTask.setTaskReferenceName((String) task.get("taskReferenceName"));
workflowTask.setType((String) task.get("type"));
if (task.containsKey("inputParameters")) {
JSONObject inputParams = (JSONObject) task.get("inputParameters");
Map<String, Object> inputMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Object key : inputParams.keySet()) {
inputMap.put((String) key, inputParams.get(key));
}
workflowTask.setInputParameters(inputMap);
}
workflowTasks.add(workflowTask);
}
workflowDef.setTasks(workflowTasks);
if (workflowObj.containsKey("outputParameters")) {
JSONObject outputParams = (JSONObject) workflowObj.get("outputParameters");
Map<String, Object> outputMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Object key : outputParams.keySet()) {
outputMap.put((String) key, outputParams.get(key));
}
workflowDef.setOutputParameters(outputMap);
}
metadataClient.registerWorkflowDef(workflowDef);
System.out.println("Workflow registered successfully: " + workflowDef.getName());
}
public static void startWorkflow(ApiClient apiClient, String workflowName) throws Exception {
OrkesWorkflowClient workflowClient = new OrkesWorkflowClient(apiClient);
StartWorkflowRequest request = new StartWorkflowRequest();
request.setName(workflowName);
request.setVersion(1);
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("name", "Orkes User");
request.setInput(input);
Map<String, String> taskToDomainForWorkflow = new HashMap<>();
taskToDomainForWorkflow.put("hello_task", "test_domain");
request.setTaskToDomain(taskToDomainForWorkflow);
String workflowId = workflowClient.startWorkflow(request);
System.out.println("Workflow started with ID: " + workflowId);
Workflow workflow = workflowClient.getWorkflow(workflowId, true);
System.out.println("Workflow status: " + workflow.getStatus());
if (!workflow.getTasks().isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("First task status: " + workflow.getTasks().get(0).getStatus());
System.out.println("First task domain: " + workflow.getTasks().get(0).getDomain());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Environment env = new Environment();
ApiClient apiClient = getApiClientForOrkes(env);
String sampleWorkflowJson = getSampleWorkflowJson();
registerWorkflow(apiClient, sampleWorkflowJson);
startWorkflow(apiClient, "hello_world_workflow");
System.out.println("Worker is polling. Press Ctrl+C to exit.");
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error running client: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static String getSampleWorkflowJson() {
return "{\n" +
" \"name\": \"hello_world_workflow\",\n" +
" \"description\": \"A simple Hello World workflow\",\n" +
" \"version\": 1,\n" +
" \"tasks\": [\n" +
" {\n" +
" \"name\": \"hello_task\",\n" +
" \"taskReferenceName\": \"hello_ref\",\n" +
" \"inputParameters\": {\n" +
" \"name\": \"${workflow.input.name}\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"type\": \"SIMPLE\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" ],\n" +
" \"outputParameters\": {\n" +
" \"greeting\": \"${hello_ref.output.greeting}\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"schemaVersion\": 2\n" +
"}";
}
}
Compile and run the Java worker. This registers and starts the workflow.
The hello_task will be picked up only by the worker polling test_domain. You can verify this in the Conductor UI under Executions > Workflows, where the task’s domain will be shown as test_domain.

Using fallback domain
In this example, we’ll assume the taskToDomain mapping is as follows:
"taskToDomain": {
"*": "mydomain",
"task-a": "NO_DOMAIN",
"task-b": "abc, NO_DOMAIN",
"task-c": "someInactiveDomain1, someInactiveDomain2"
}
Here,
- The
task-ais routed to theNO_DOMAINqueue, meaning it doesn't have an assigned domain. - The
task-bis routed first to theabcdomain if available, or otherwise to the default domain (NO_DOMAIN). - The
task-cis routed to thesomeInactiveDomain1and then to thesomeInactiveDomain2, but these are inactive, so they may not be processed in these domains. - All other tasks in this workflow are routed to
mydomain.