Managing Applications
An application represents a non-human identity, such as a script, service, task worker, client, or CI/CD pipeline, that interacts with a Conductor server via APIs or SDKs. The application layer in Conductor provides application-based access to resources in your cluster.
Each application can also have one or more access key/secret pairs, which are used to grant access to the Conductor SDK and API. Learn more about authentication in Authentication and Access Keys.
Applications as service accounts
In Orkes Conductor, applications are the equivalent of service accounts used in traditional systems. They are designed to represent non-human identities, such as CI/CD pipelines, automated scripts, microservices, or system integrations, that need to authenticate and interact with Conductor programmatically. Instead of creating a user with an email address, you can create an application and assign it the appropriate roles and permissions for the resources it needs to perform. For example:
- A CI/CD pipeline that creates or updates workflow definitions.
- A background service that polls and executes tasks.
Each application can have one or more access keys, which include a key ID and a secret. These keys can be securely stored and used to authenticate API or SDK requests. This setup enables automated access without relying on human credentials or email-based accounts, following industry-standard service account patterns.
Application roles
By default, all applications can manage workflow and task executions if they have access to the required resources. For example, an application can execute someWorkflow as long as Execute permission is granted for those resources. Likewise, an application can view workflow executions if Read permission is granted.
Application roles grant additional access on top of this default behavior and should be selected only if your application is used for another purpose besides managing workflow execution. There are two categories of application roles available:
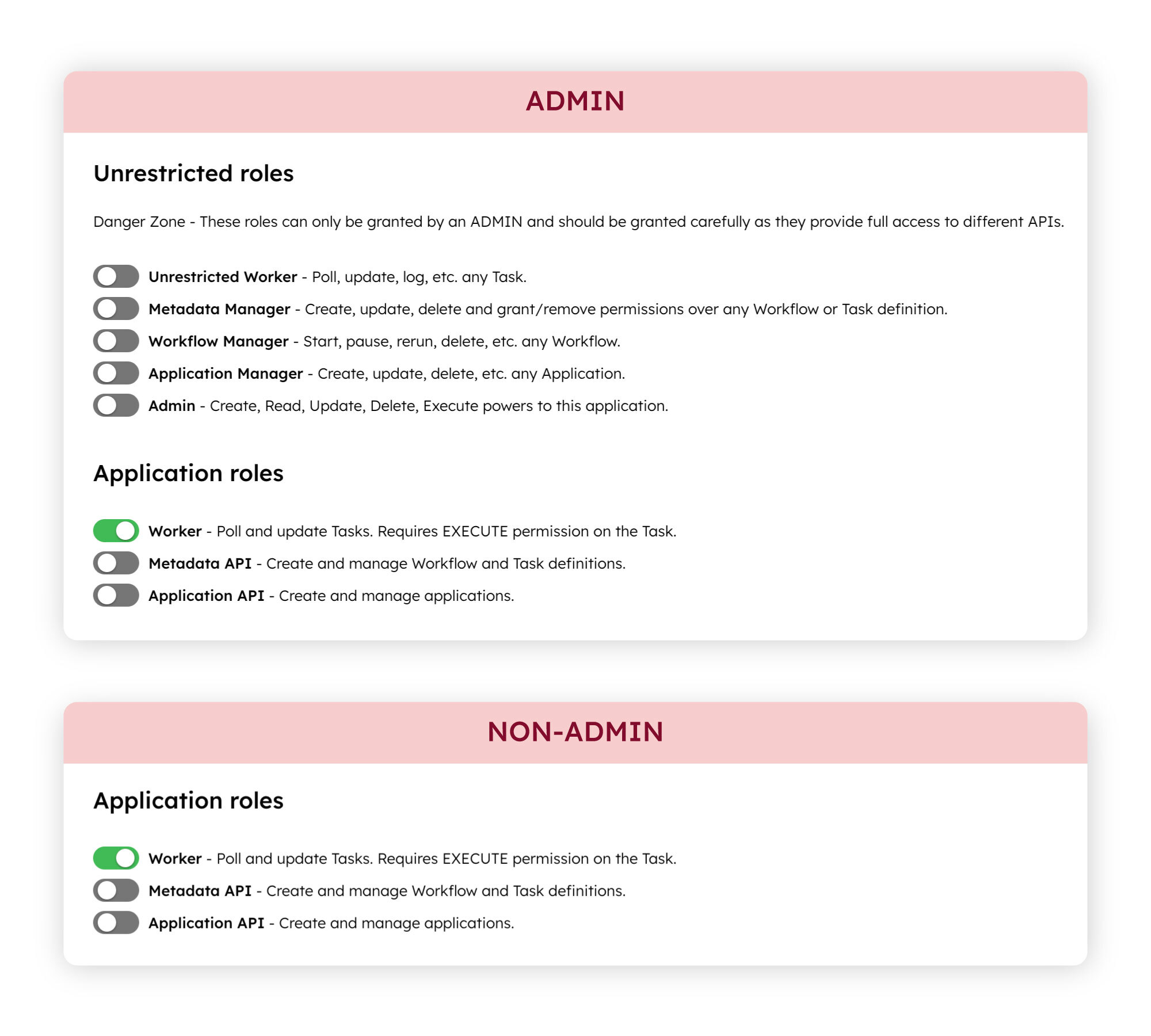
- Unrestricted Roles: Roles that can be granted only by a cluster Admin.
- Application Roles: The roles available to any user with access to applications.
- Unrestricted Roles
- Application Roles
Unrestricted roles can only be added by a cluster Admin. Unrestricted roles include:
- Unrestricted Worker: Worker role with full access to poll and execute any task in the cluster.
- Metadata Manager: Can manage all workflow and task definitions in the cluster, including performing any action regardless of workflow or task ownership. Can view and manage API Gateway configurations. Can create integrations and secrets.
- Workflow Manager: Can view, execute, and manage all workflow executions in the system, including start, pause, resume, rerun, retry, restart, terminate, and delete actions. Has execute and read access to workflow and task definitions.
- Application Manager: Can create, update, and delete any application in the cluster. Can also view and manage API Gateway configurations.
- Admin: Full control over that particular application, including creating, viewing, modifying, deleting, and executing it.
Application roles can be added by any user with access to applications. General application roles include:
- Worker: Can poll and execute tasks for which it has Execute permissions for. This role should be granted to a task worker application that is responsible for polling and executing a task.
- Metadata API: Can create and view workflow definitions, task definitions, and user forms. This role should be granted to an application that is responsible for retrieving and managing workflow and task definitions, such as for testing or CI/CD integration purposes.
- Application API: Can create and view applications. This role should be granted to an application that is responsible for managing other applications in the cluster.
Configuring applications
Configure the application’s roles and permissions to control what your application can do and what resources it can access, including workflows, tasks, secrets, environment variables, tags, domains, integrations, and prompts.
To configure an application:
- Create an application.
- Go to Access Control > Applications from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Create application.
- Enter the application name.
- Select Save. The application has been created. You can proceed to add roles or permissions to the application.
- Add roles to the application.
- In the Application roles or Unrestricted roles section, toggle the different application roles for your application.
- Generate access keys.
- In the Access Keys section, select + Create access key to generate the Server URL, a unique Key Id and a Key Secret. The Key Secret is shown only once, so make sure to copy and store it securely.
- Add permissions to grant application-level access to resources, including workflows, tasks, secrets, environment variables, tags, domains, integrations, and prompts.
- In the Permissions section, select + Add permission.
- Toggle between each resource type and select the resources to provide access to.
- Toggle the access levels for your selected resource:
- Read: The application will be able to view the resource.
- Update: The application will be able to update the resource. The application must also have the Metadata API role to update metadata resources.
- Execute: The application will be able to execute the resource. The application must also have the Worker role to execute resources.
- Delete: The application will be able to delete the resource. The application must also have the Metadata API role to delete metadata resources.
You can grant permissions to tags, rather than to individual resources. Tags can be added to multiple resources, so that when you grant a permission to a tag, it instantly provides access to all tagged resources. Learn more about tags in Managing Tags.
Editing applications
You can edit an application’s name, role, or permissions anytime.
To edit an application:
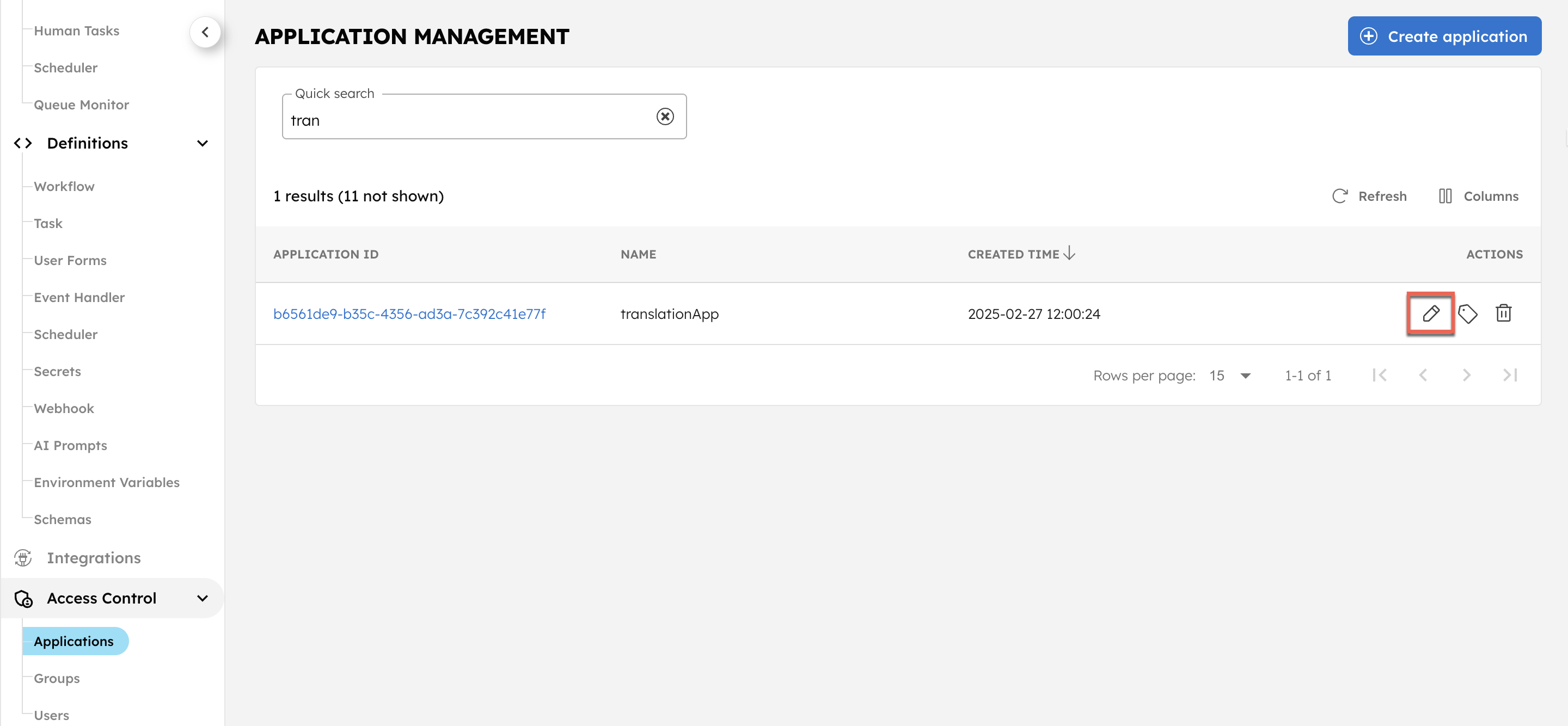
- Go to Access Control > Applications from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select the Application ID or the Edit icon located next to the application name.
- Update the application’s name, roles, or permissions as desired.
Deleting applications
To delete an application from your cluster:
- Go to Access Control > Applications from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select the Delete icon located next to the application name.
- Confirm the action by entering the application name and selecting Confirm.
Example application setup
Example
In this example, two programs have access to Orkes Conductor workflows. Both of these workflows rely on the same task, Task X, which is performed by a worker application, Worker X.
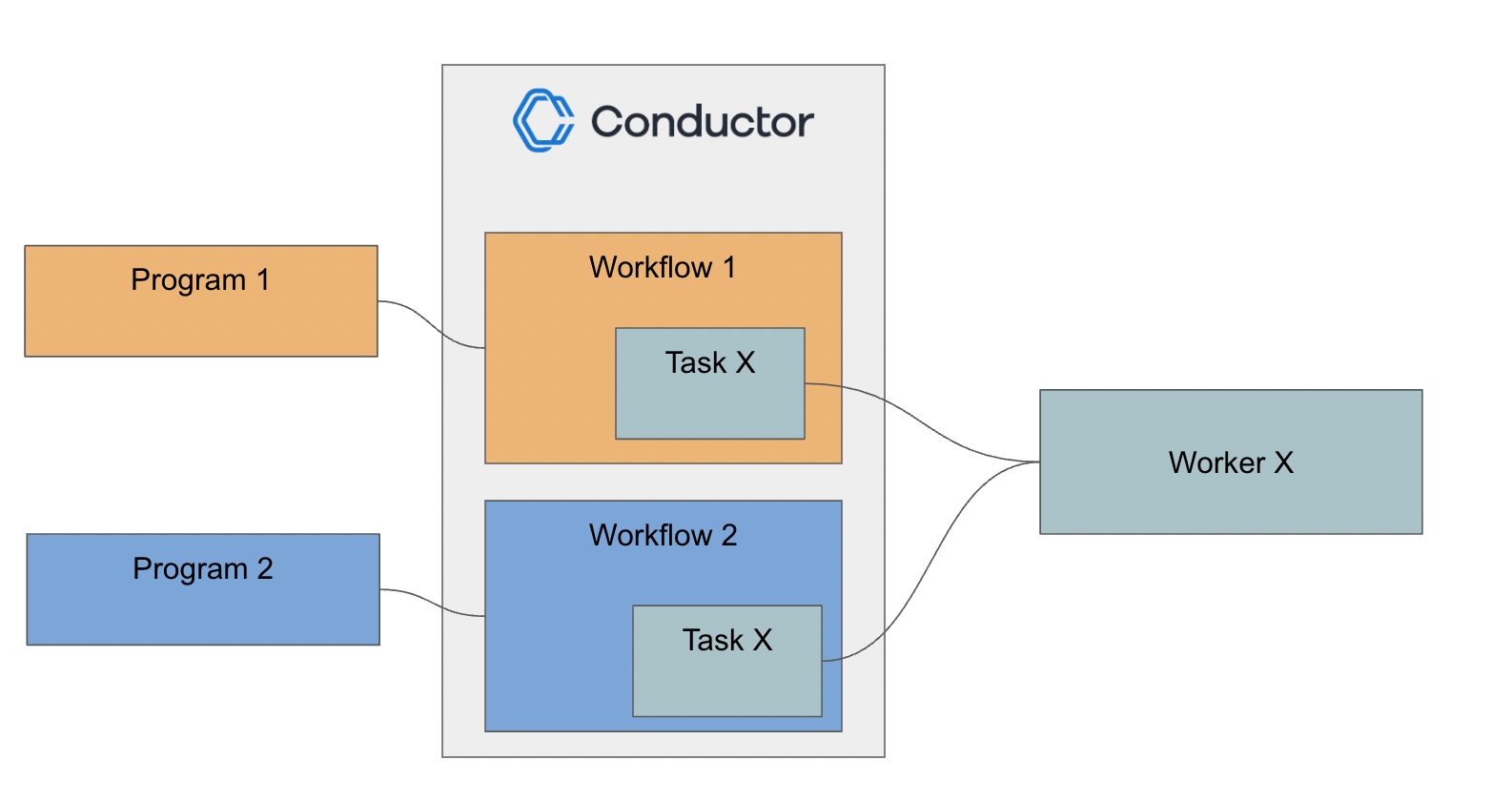
One way to handle this is to create a single application with Execute access to Workflow 1, Workflow 2, and Task X and provide the application keys/secrets to Program 1, Program 2, and Worker X. However, this setup violates the principle of least privilege, where applications should only have access to the endpoints they require. In this case, Worker X should not have Execute access for the workflows.
To satisfy the principle of least privilege, we will create three applications instead:
- Application Worker X: Has the Worker role and Execute permission for Task X. This allows the worker to poll the task queue for work.
- Application Program 1: Has Execute permission for Workflow 1 and for Task X so that it can successfully invoke Workflow 1. No additional application role is required.
- Application Program 2: Has Execute permission for Workflow 2 and for Task X so that it can successfully invoke Workflow 2. No additional application role is required.
With this set-up, the worker application has no access to the workflows, since it only needs to poll the task. Likewise, the other two applications only have the required access to execute the workflow and its necessary tasks, and no other workflows.