Build a Ticket Service Using Orkes MCP Gateway
This tutorial shows how to expose an API as an MCP tool using the MCP Gateway. You will build a simple ticket service that accepts issue details from an AI agent, validates the input, and triggers a workflow to generate a mock ticket ID that the agent can use in follow-up actions.
In this tutorial, you will:
- Create a ticket workflow in Orkes Conductor.
- Define an input schema for the workflow.
- Create an application.
- Configure authentication settings for the MCP service.
- Create a ticket service.
- Create a route.
- Test endpoint.
- Verify using MCP Inspector.
By the end of this tutorial, you will have an MCP tool backed by an Orkes Conductor workflow.
To follow along, ensure you have access to the free Orkes Developer Edition.
Step 1: Create a ticket workflow in Orkes Conductor
In this step, you create the workflow logic that the MCP Gateway executes when an AI agent invokes the tool.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following code:
{
"name": "create_ticket_wf",
"description": "Workflow to generate a mock ticket ID based on issue details.",
"version": 1,
"schemaVersion": 2,
"inputParameters": [
"issue",
"priority",
"details",
"email",
"name",
"source"
],
"tasks": [
{
"name": "generate_ticket_id",
"taskReferenceName": "generate_ticket_id",
"type": "INLINE",
"inputParameters": {
"evaluatorType": "graaljs",
"expression": "(function () {\n return {\n ticketId: 'TCK-' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 100000)\n };\n})();"
}
},
{
"name": "prepare_output",
"taskReferenceName": "prepare_output",
"type": "JSON_JQ_TRANSFORM",
"inputParameters": {
"source": {
"ticketId": "${generate_ticket_id.output.result.ticketId}"
},
"queryExpression": "{ \"ticketId\": .source.ticketId }"
}
}
],
"outputParameters": {
"ticketId": "${prepare_output.output.result.ticketId}"
}
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
Your workflow looks like this:

The workflow accepts ticket details as input, generates a mock ticket ID using an Inline task, and formats the output using a JSON JQ Transform task.
We are mocking the ticket ID creation process for demonstration purposes. However, you can modify the workflow to create an actual ticket in any of your ticketing systems.
The workflow is now ready. The next step is to define a schema that validates incoming MCP tool requests.
Step 2: Define input schema for the workflow
The input schema ensures that only valid requests from an AI agent can trigger the workflow.
To define an input schema:
- Go to Definitions > Schema from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + New schema.
- In the Code tab, paste the following schema:
{
"name": "CreateTicketSchema",
"version": 1,
"type": "JSON",
"data": {
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"issue": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Short description of the issue."
},
"priority": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"low",
"medium",
"high"
],
"description": "Urgency of the ticket."
},
"details": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Additional information or context for the issue."
},
"email": {
"type": "string",
"format": "email",
"description": "Email address of the requester."
},
"name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Name of the requester."
},
"source": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Where the request originated. For example: agent, chatbot, or web."
}
},
"required": [
"issue",
"priority",
"details",
"email",
"name",
"source"
]
}
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
The next step is to create an application with permission to execute the workflow.
Step 3: Create an application
Skip the step if you are using Orkes Developer Edition. If you are using Orkes Developer Edition, you do not need to create a separate application, as it has a Default Orkes Application, which is automatically available and has permission to execute workflows.
Applications act as service accounts that control which workflows the MCP Gateway can execute.
To create an application:
- Go to Access Control > Applications, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Create application.
- Enter a Name for the application.
- In Permissions, select + Add permission.
- In the Workflow tab, select the workflow created in Step 1.
- Enable the EXECUTE permission.
- Select Add permissions.
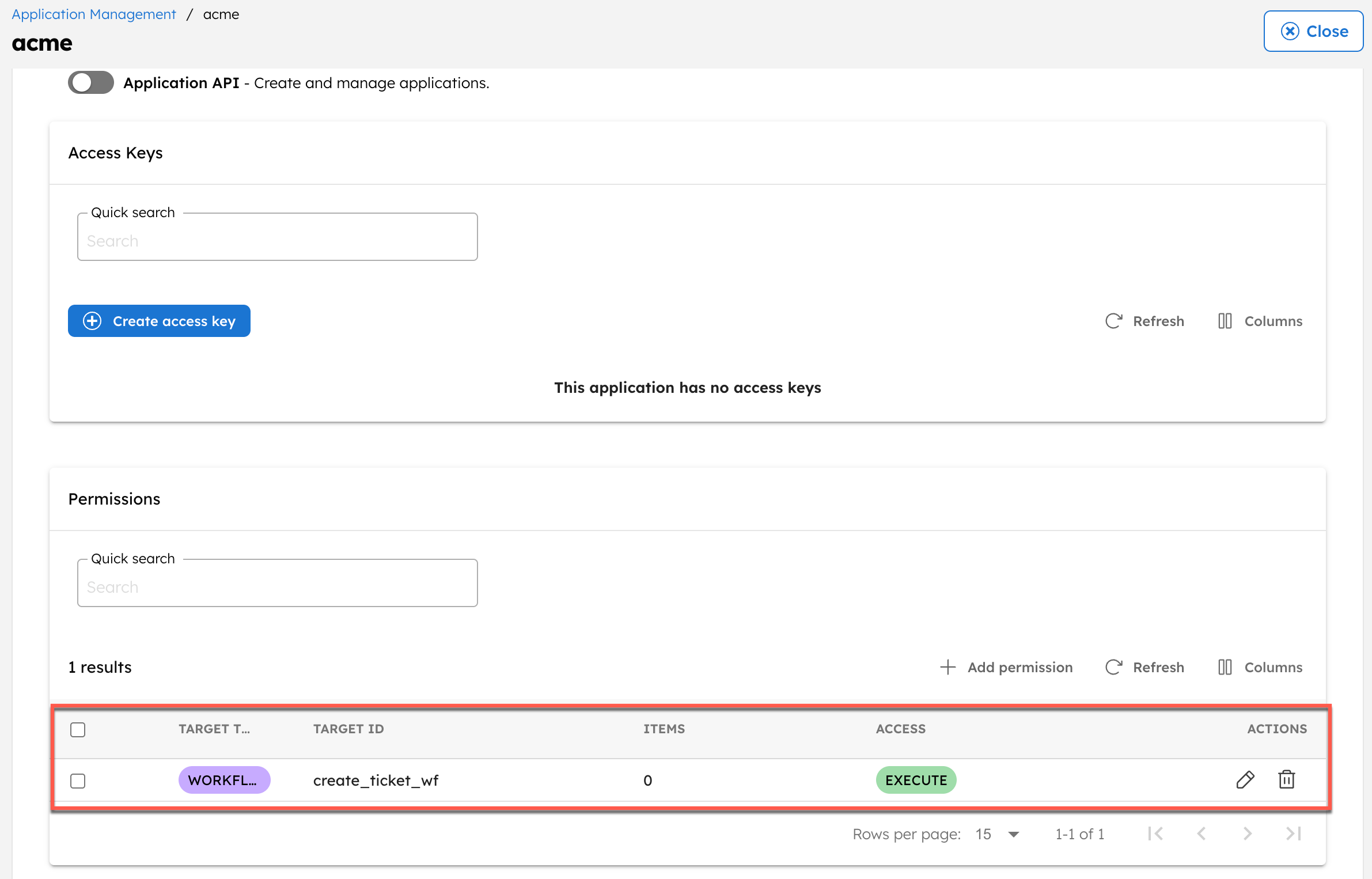
The application now has permission to execute the ticket workflow.
Step 4: Configure authentication settings
Authentication settings define how MCP clients are authorized to access the tool. In this example, the service uses no authentication.
To configure authentication settings:
- Go to APIs > Authentication, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + New authentication.
- Enter a unique name as the ID and select Authentication Type as No Authentication.
- In Application, select the application created in the previous step. If you are using Orkes Developer Edition, use the application Default Orkes Application here.
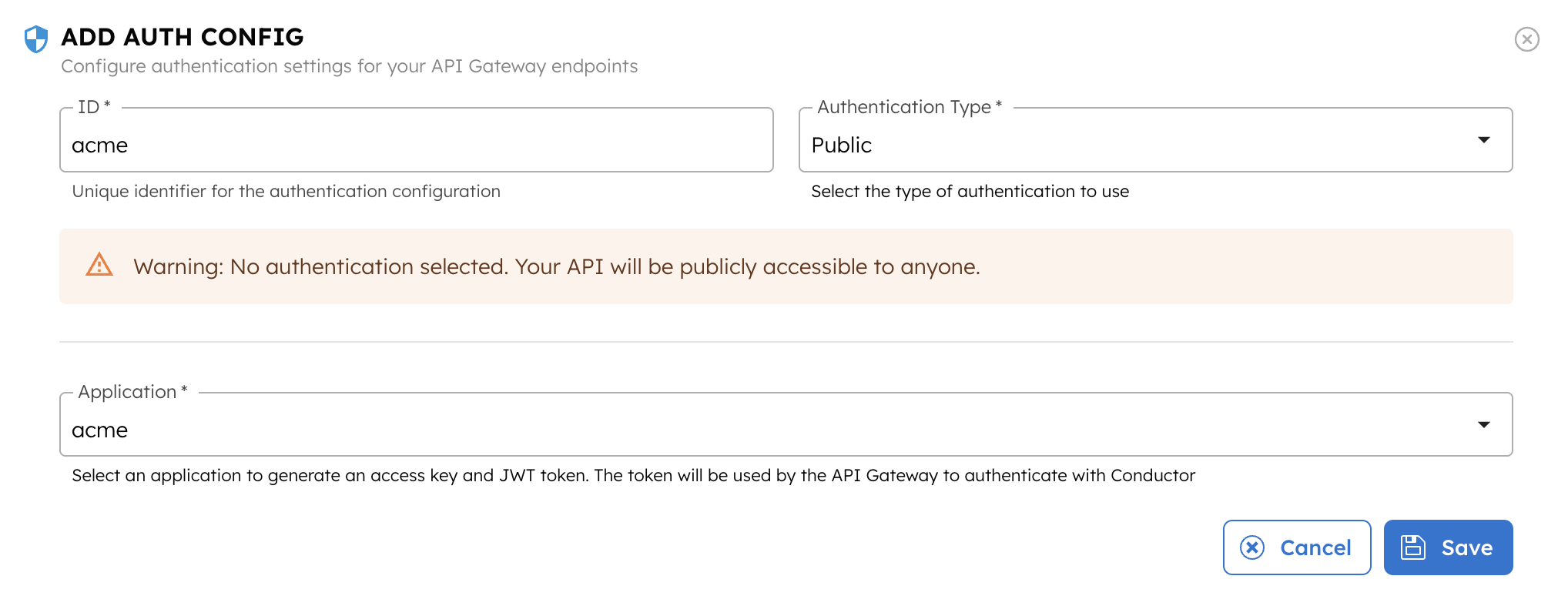
- Select Save.
Step 5: Create a ticket service
A service represents a logical grouping of MCP routes that share a common configuration.
To create a service:
- Go to APIs > Services, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + New service.
- In Service ID, enter ticket-tools.
- Enter the Display Name as Ticket Service.
- Enter the Base Path as /api/tickets.
- Set the Auth Config to the authentication setting created in the previous step.
- In CORS Configuration,
- Set Allowed Origins as *.
- Set Allowed Methods to Select All.
- Set Allowed Headers as *.
- Set an optional Description for the service.
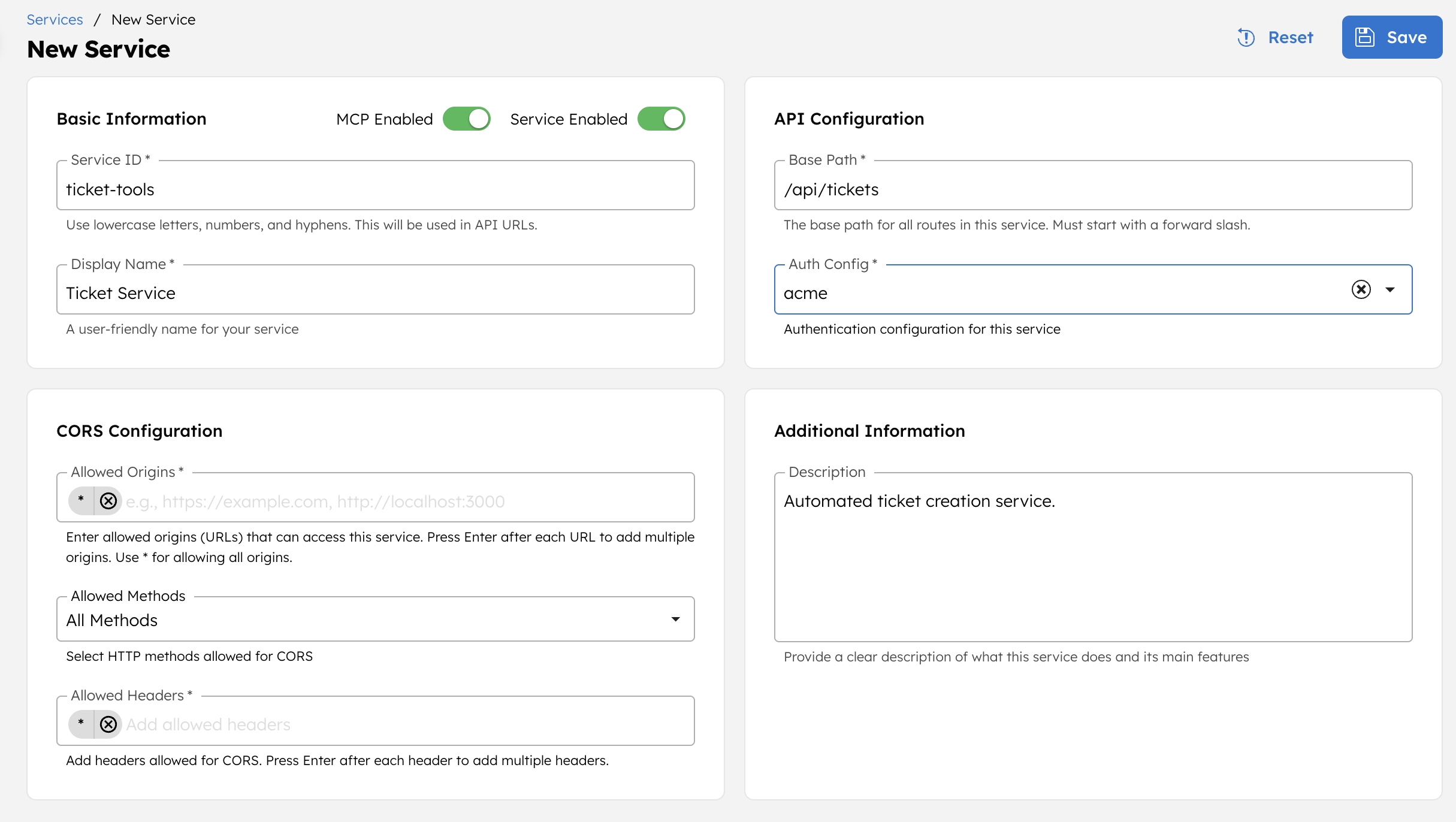
- Select Save.
The service is now ready. Next, create a route to connect it to the workflow.
Step 6: Create a route
Routes define MCP tool endpoints and map them to workflows.
To create a route:
- Go to the Services and select the + button next to the service created.
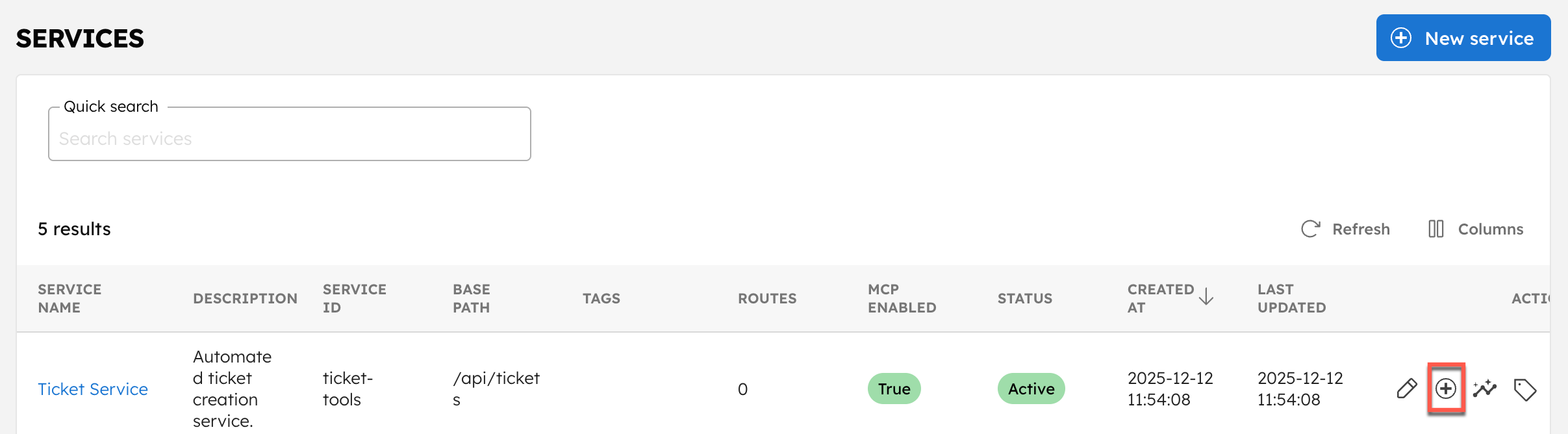
- In Route Definition, set:
- HTTP Method to POST.
- Path to
/create.
- In Workflow Configuration, set the Workflow Name to the one created in Step 1.
- In Schema, set the Input Schema to the schema created in Step 2.
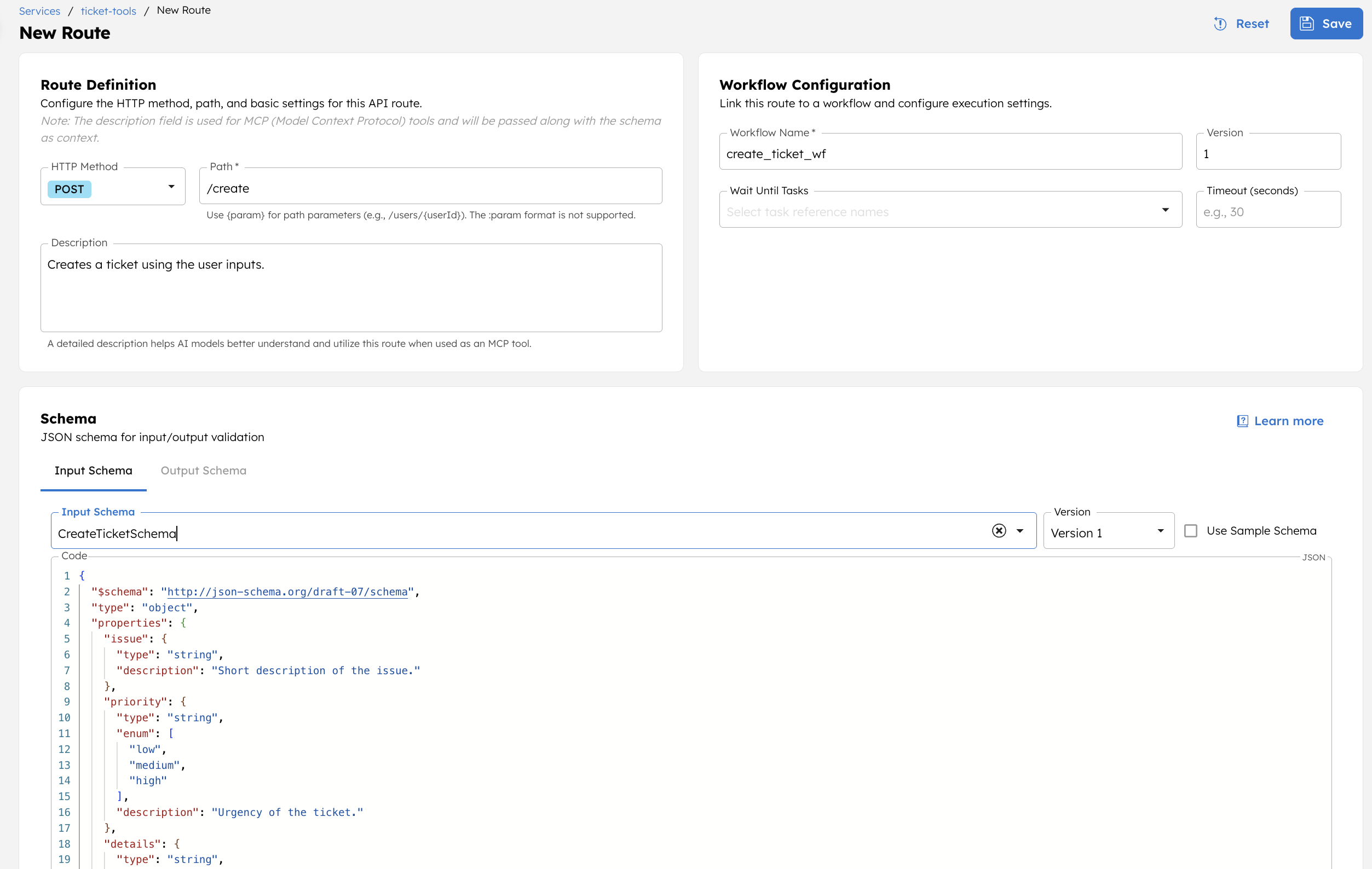
- Select Save.
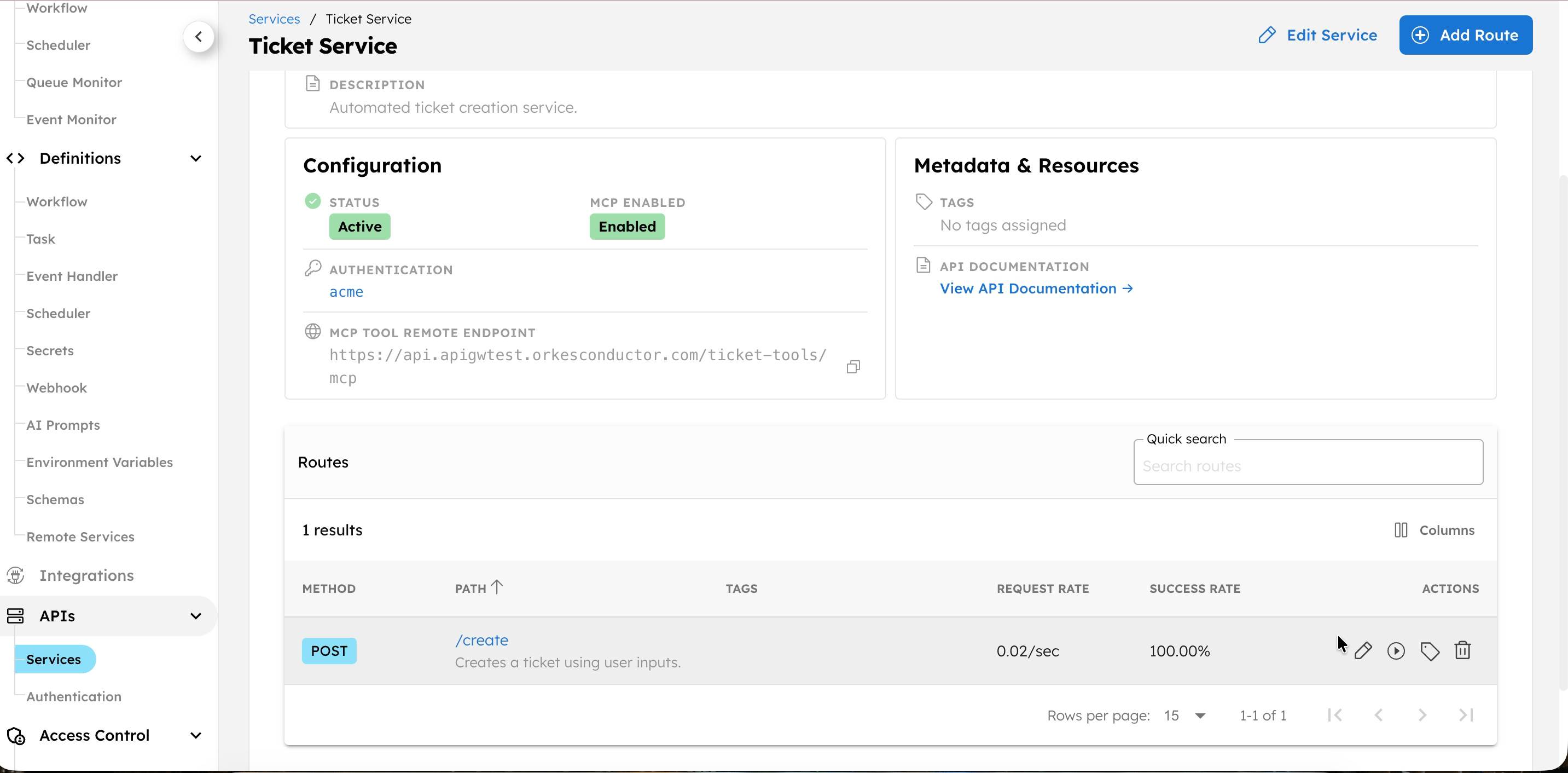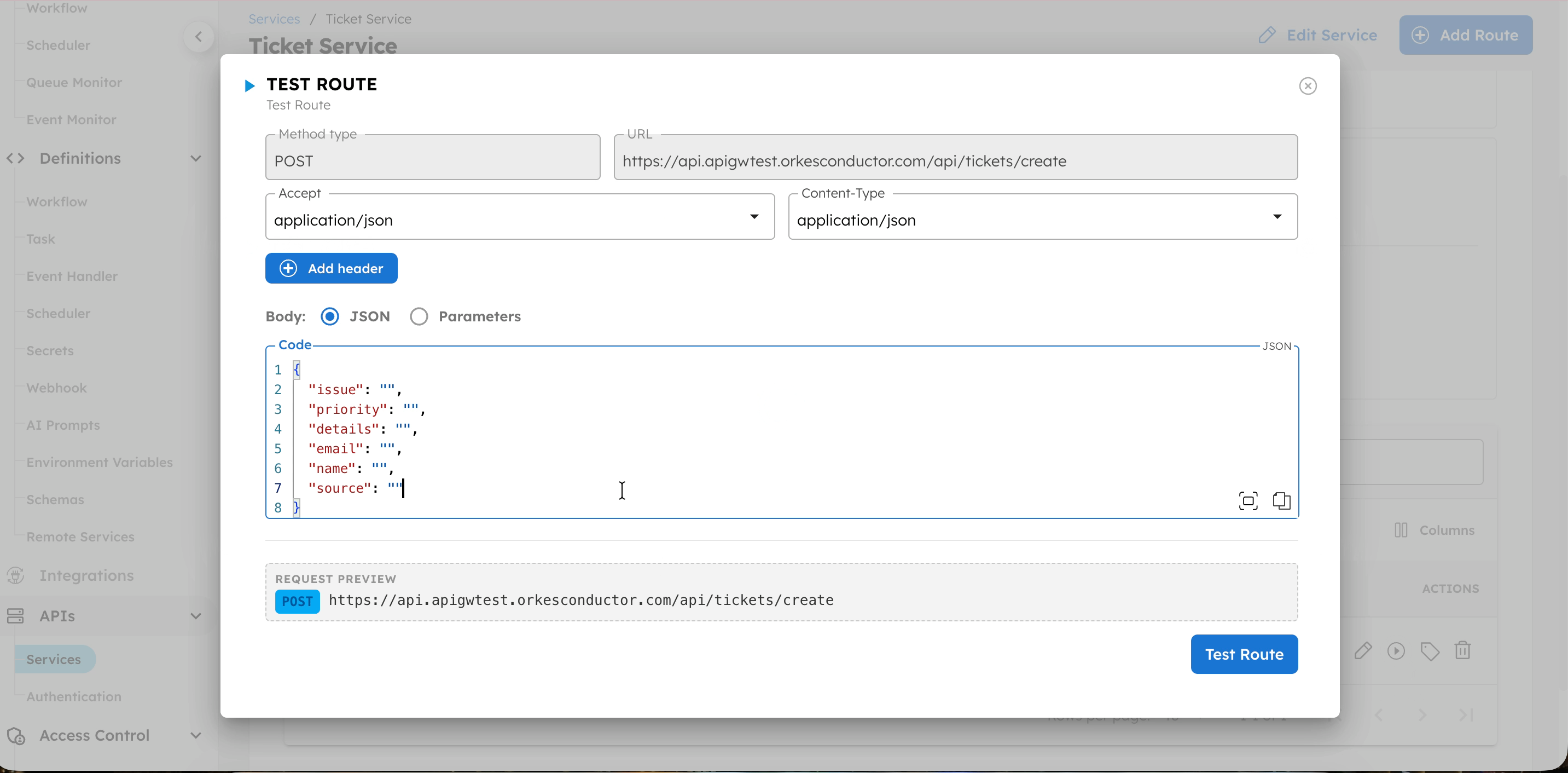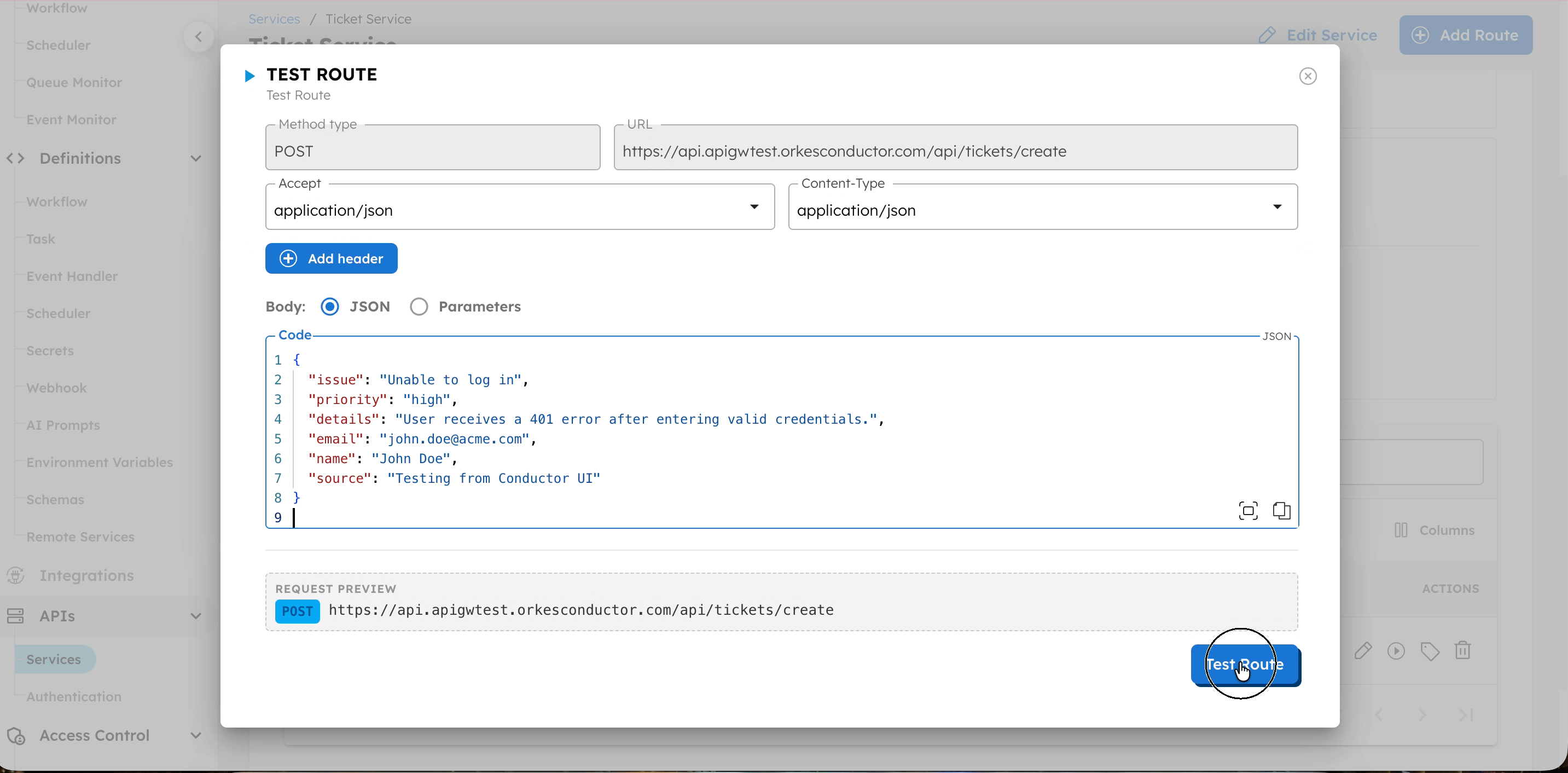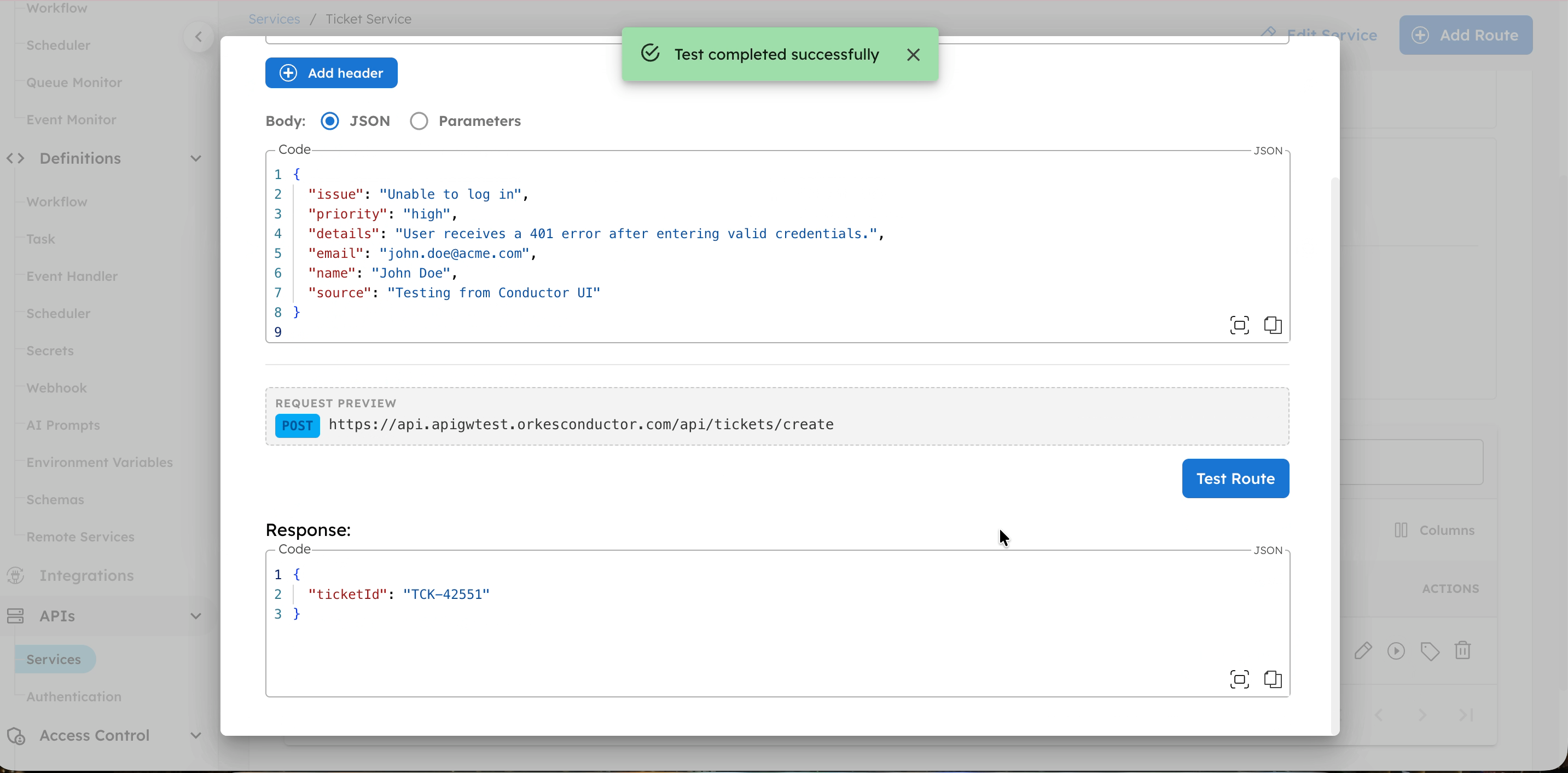
Step 7: Test the endpoint
You can test the route directly from the Conductor UI.
Test endpoint from Conductor UI
To test a route:
- Go to the APIs > Services, and select the service.
- In Routes, select the play icon next to the route to test.
- In Body, enter the request payload as defined in the workflow. For example:
{
"issue": "Unable to log in",
"priority": "high",
"details": "User receives a 401 error after entering valid credentials.",
"email": "john.doe@acme.com",
"name": "John Doe",
"source": "Testing from Conductor UI"
}
- Select Test Route.
- Review the Response to verify the route works as expected.
Verify workflow execution
To confirm that the workflow was triggered:
- Go to Executions > Workflow.
- Select the latest execution of the create_ticket_wf workflow.
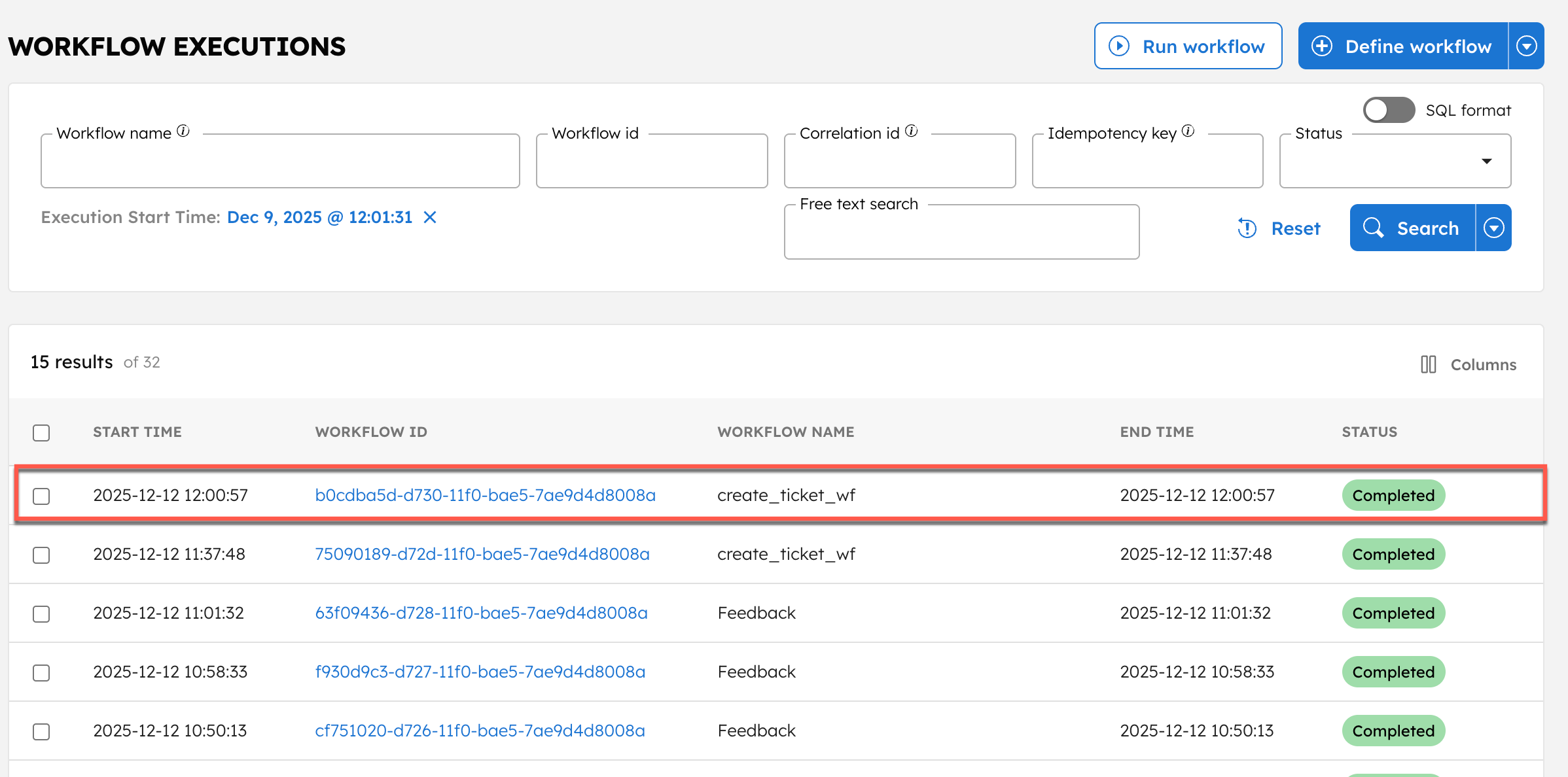
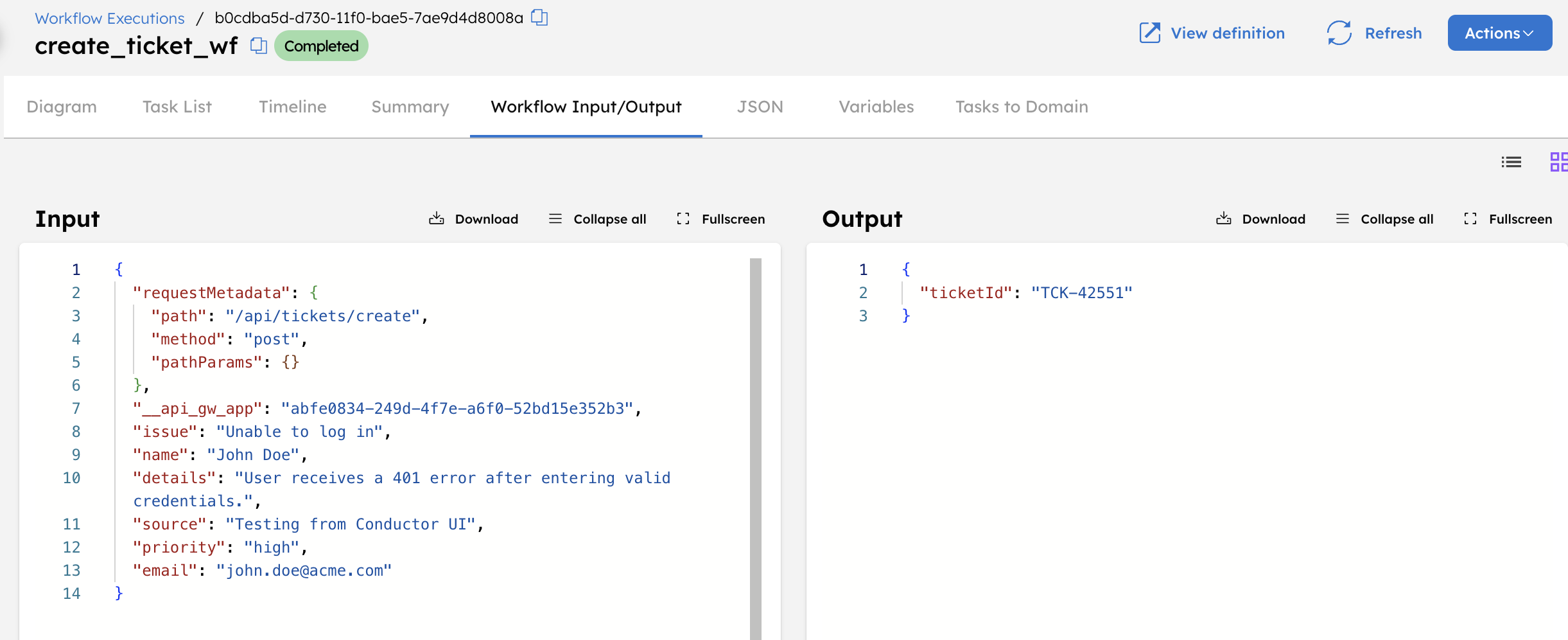
- Select the Workflow ID to view the execution details.
- In the Workflow Input/Output tab, verify that the metadata was passed correctly.
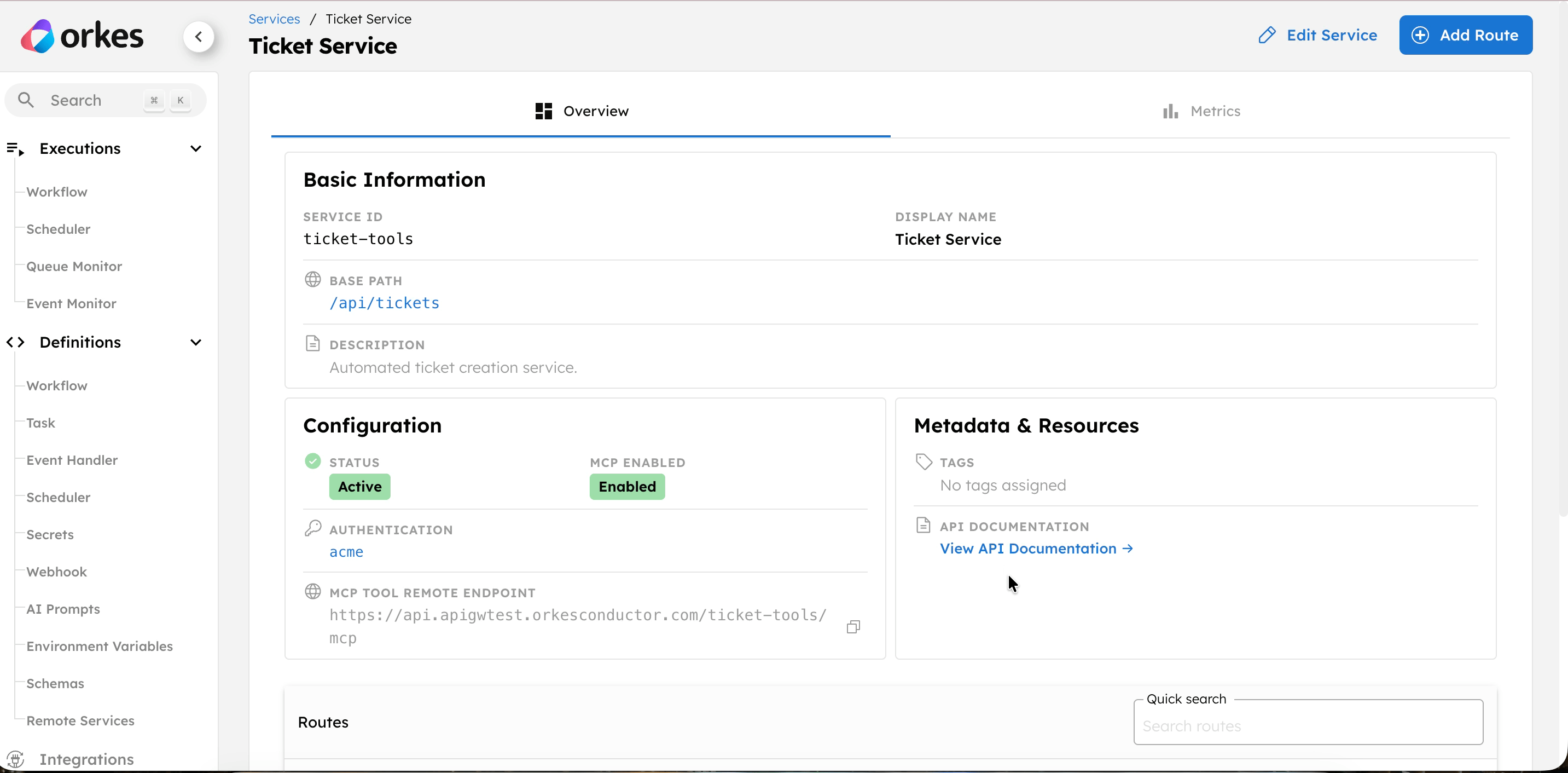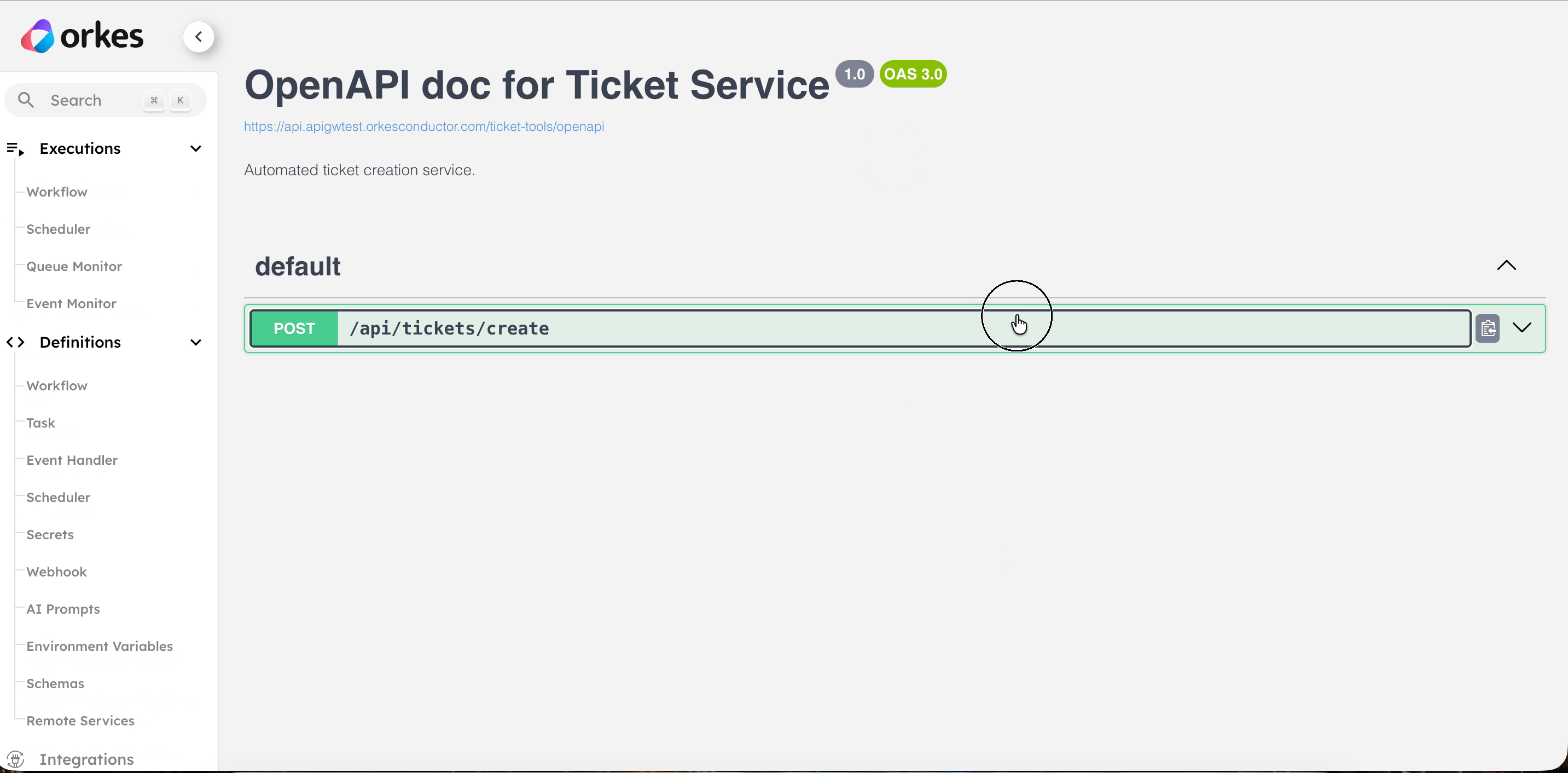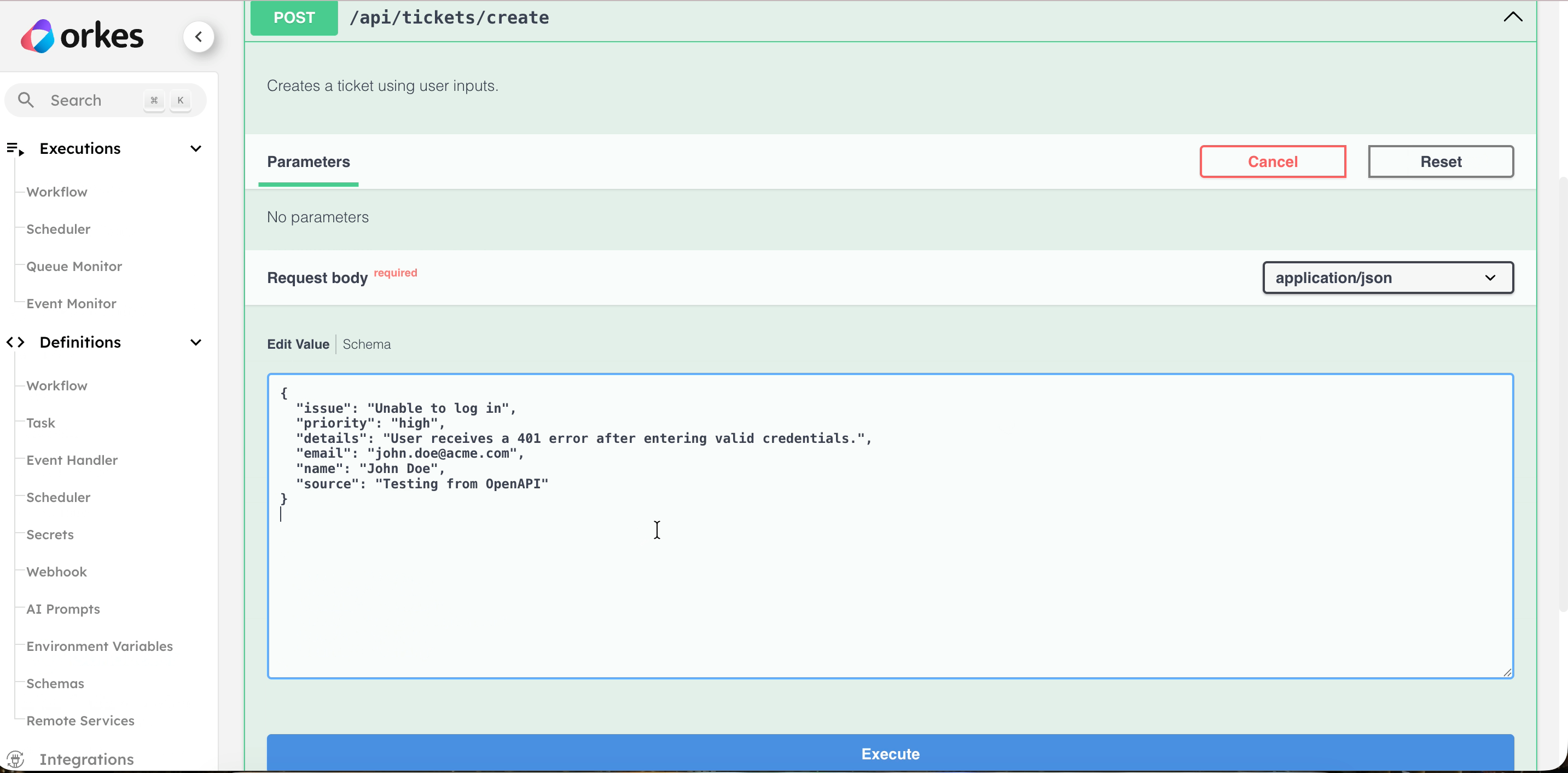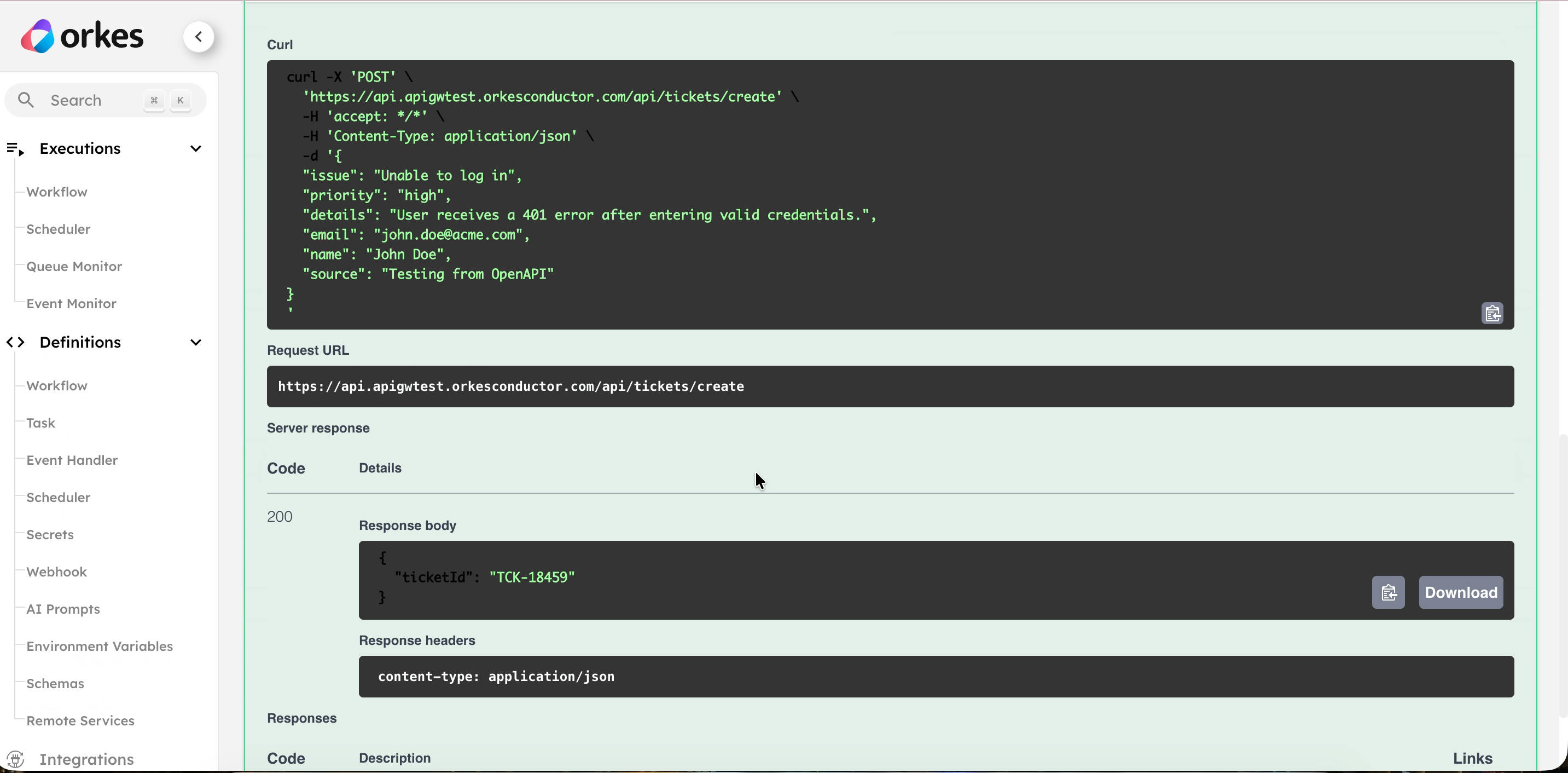
Access the endpoint details
To view the endpoint details and supporting resources:
- Go to APIs > Services, and select your service.
- Select a route to open its details.
- You can get the cURL command for the actual endpoint here.

You can also get the OpenAPI documentation for the service. Go to APIs > Services, and select your service. In Metadata & Resources, select View API Documentation.
Step 8: Verify using Orkes MCP Workbench
Next, you can connect this MCP service to your preferred AI tool as an MCP tool. You need the MCP endpoint URL for this.
To get the MCP tool endpoint:
- Go to APIs > Services, and select the service.
- In Configuration, copy the MCP Tool Remote Endpoint.
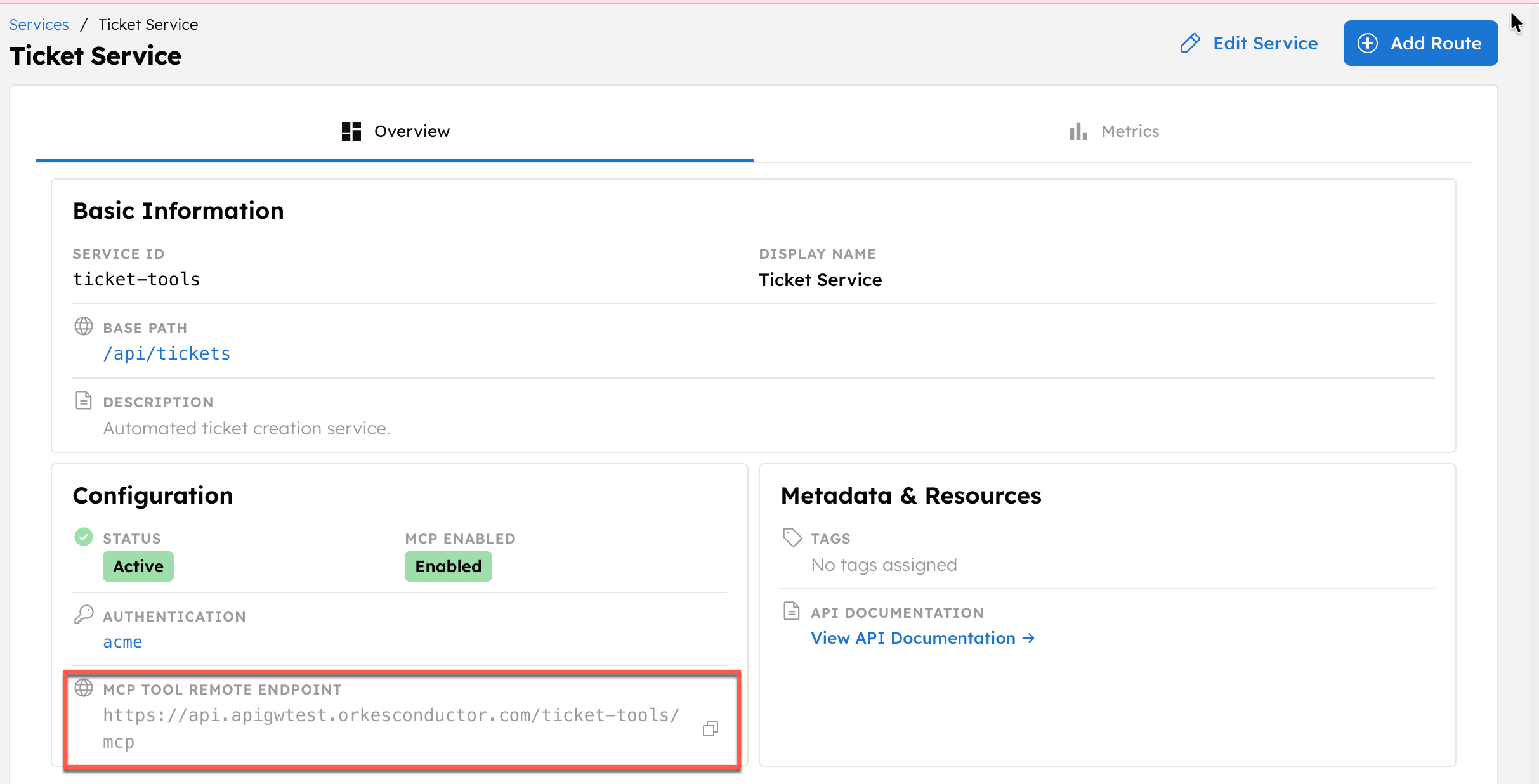
Use this as the MCP server endpoint when you configure your AI tool. Let’s verify this using Orkes MCP Workbench before plugging into an AI agent.
To test the MCP tool:
- Access Orkes MCP Workbench.
- In Connections, select + Add.
- In URL, enter the MCP Tool Remote Endpoint copied from Conductor.
- In Type, select Streamable HTTP (Stateless).
- Select Save, and then select Connect.
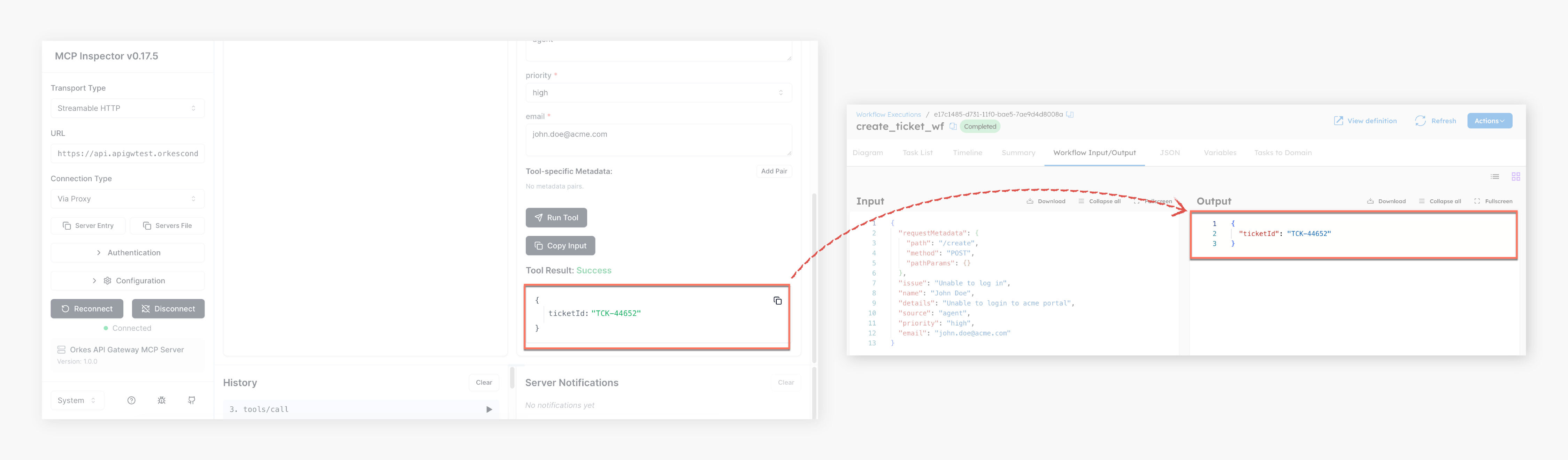
- Once the connection is successful, select POST_create from Select Tool, and enter the required parameters.
- Select Run Tool.
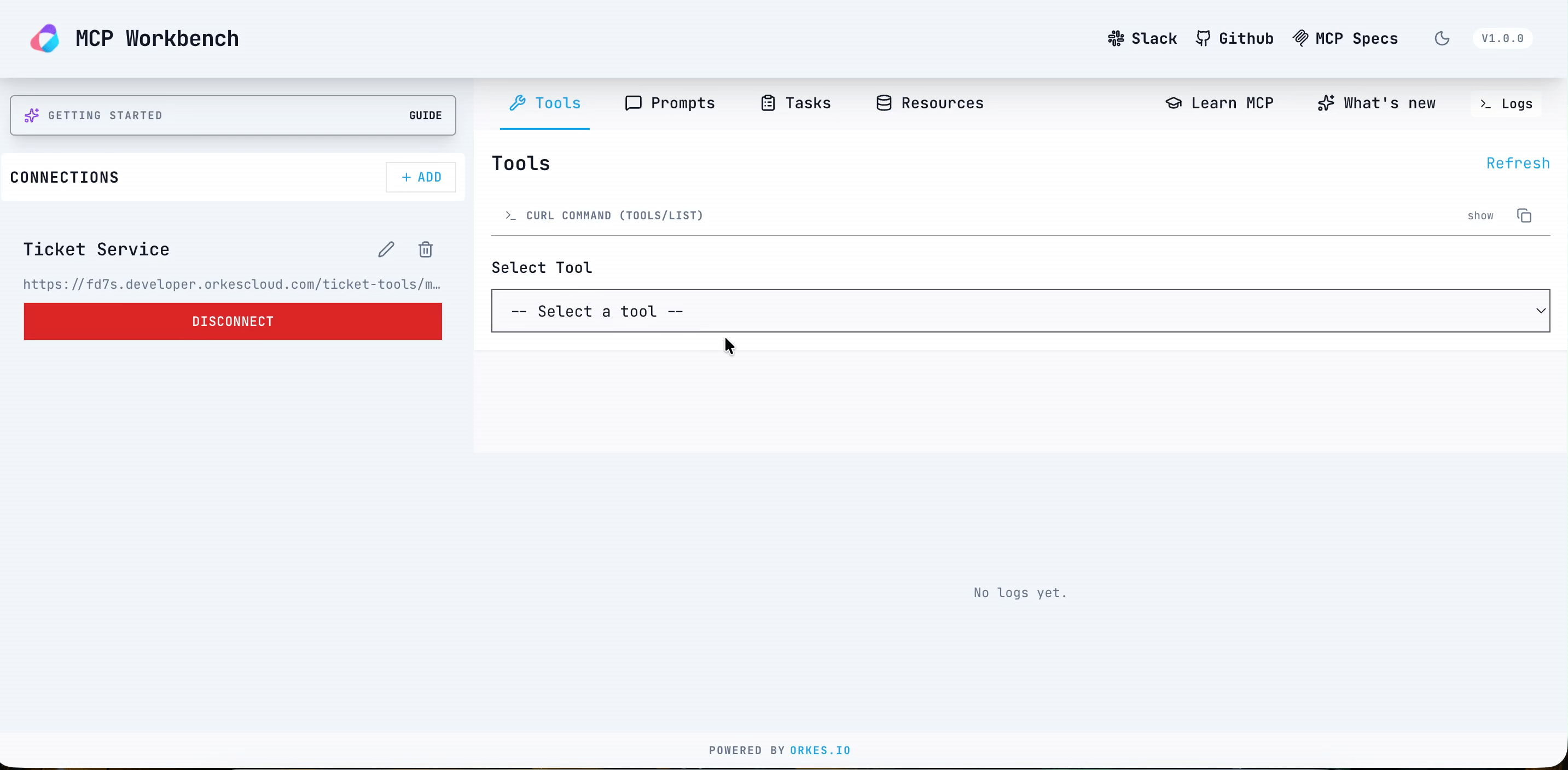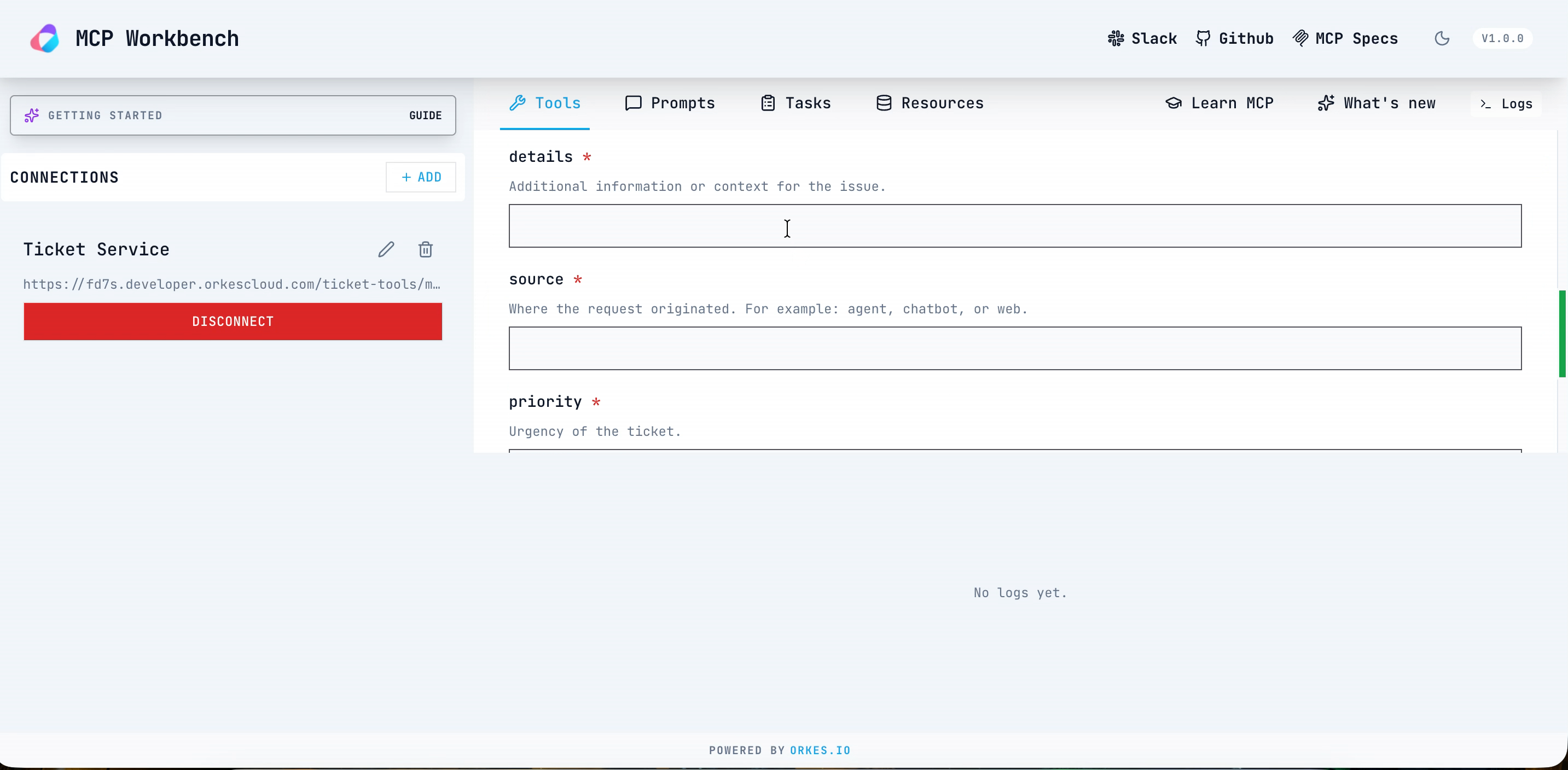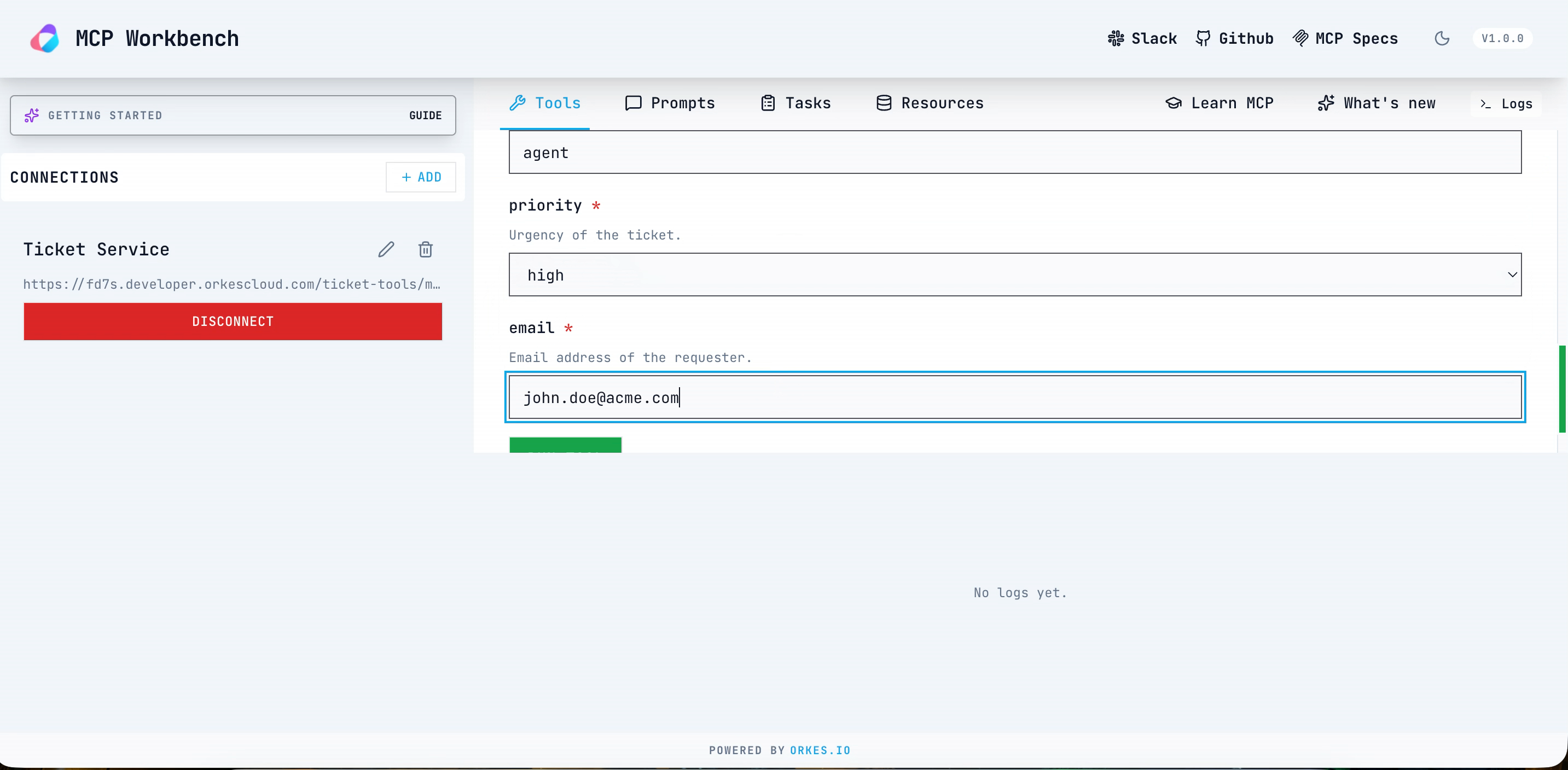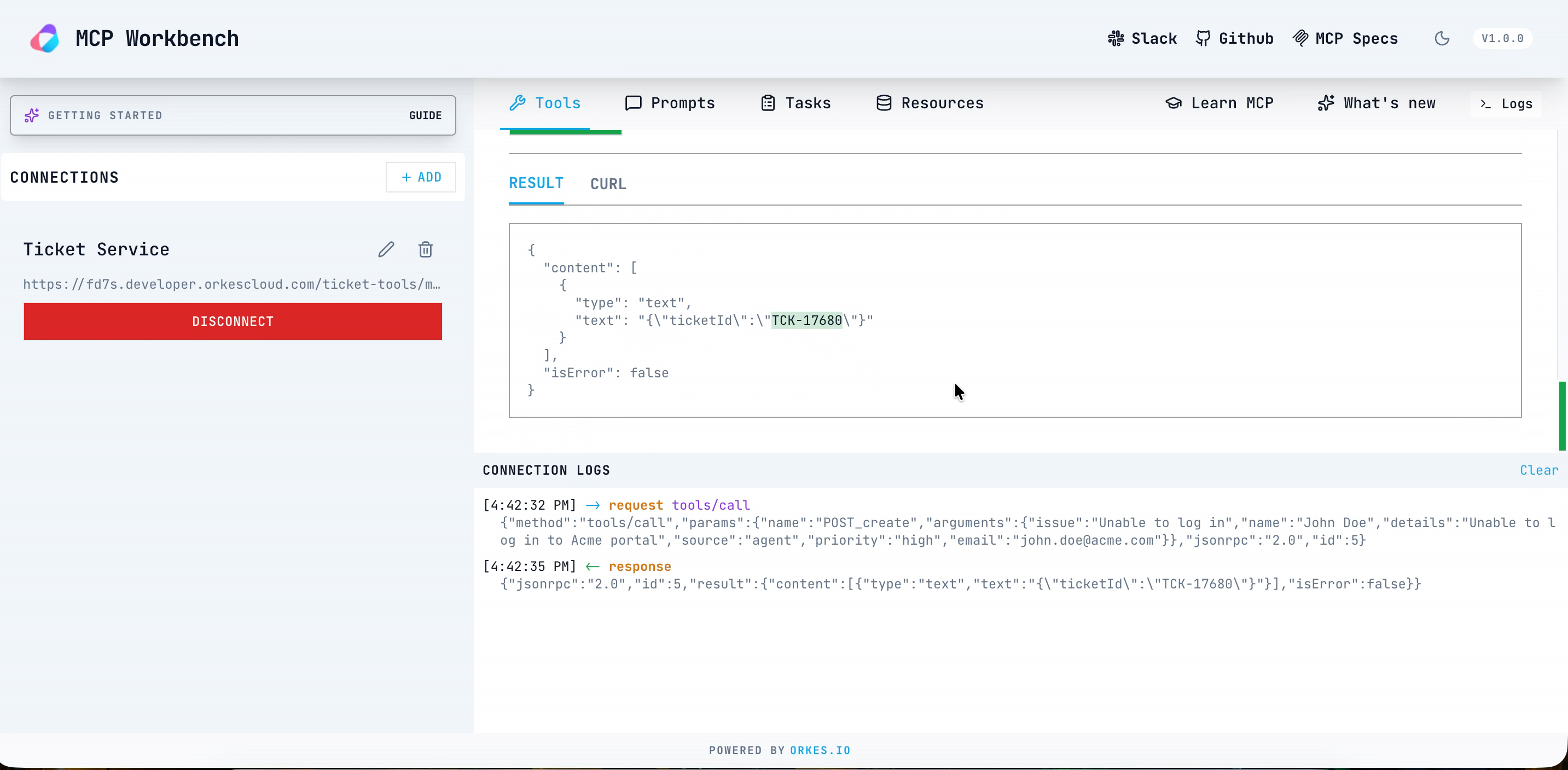
This returns the tool result status as success and returns the ticket ID. To verify the workflow execution in Conductor, go to Executions > Workflow. Open the latest run of create_ticket_wf, and review the Input/Output tab to confirm the ticket ID.
That’s it. Next, you can connect this with any AI agent that needs to invoke the MCP tool. When the MCP tool is invoked, the workflow runs automatically.
You can extend this workflow to integrate with real ticketing systems, trigger notifications, or support downstream automation.