HTTP
The HTTP task is used to make calls to remote services exposed over HTTP/HTTPS. It supports various HTTP methods, headers, body content, and other configurations needed for interacting with APIs or remote services.
The HTTP task evaluates the parameters provided, constructs the HTTP request accordingly, and sends it to the specified URI. It handles the response by extracting useful information, such as the status code, headers, and body content, which can be used in subsequent tasks within the workflow.
Task parameters
Configure these parameters for the HTTP task.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| inputParameters.uri | The URI for the service. It can be a partial value when using vipAddress or it can be the server address. | Required. |
| inputParameters.method | The HTTP method. Supported methods:
| Required. |
| inputParameters.accept | The accept header required by the server. The default value is application/json. Supported types:
| Optional. |
| inputParameters.contentType | The content type for the server. The default value is application/json. Supported types:
| Optional. |
| inputParameters.hedgingConfig.maxAttempts | The maximum number of parallel requests to send. The system will use the response from the first successful attempt, helping reduce tail latencies in remote services. Note: Hedging makes parallel requests, so use it only for idempotent services. | Optional. |
| inputParameters.headers | A map of additional HTTP headers to be sent along with the request. Supported types:
| Optional. |
| inputParameters.body | The request body for POST, PUT, or PATCH methods. Can be text or parameters such as string, number, boolean, null, or object/array. | Required for POST, PUT, or PATCH. |
| inputParameters.encode | Determines whether the URI needs encoding. When set to true, the Conductor will automatically encode the query parameters before sending the HTTP request. Set this to false if the URI is already encoded. The default value is true. | Optional. |
The following are generic configuration parameters that can be applied to the task and are not specific to the HTTP task.
Caching parameters
You can cache the task outputs using the following parameters. Refer to Caching Task Outputs for a full guide.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| cacheConfig.ttlInSecond | The time to live in seconds, which is the duration for the output to be cached. | Required if using cacheConfig. |
| cacheConfig.key | The cache key is a unique identifier for the cached output and must be constructed exclusively from the task’s input parameters. It can be a string concatenation that contains the task’s input keys, such as ${uri}-${method} or re_${uri}_${method}. | Required if using cacheConfig. |
Other generic parameters
Here are other parameters for configuring the task behavior.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| optional | Whether the task is optional. If set to true, any task failure is ignored, and the workflow continues with the task status updated to COMPLETED_WITH_ERRORS. However, the task must reach a terminal state. If the task remains incomplete, the workflow waits until it reaches a terminal state before proceeding. | Optional. |
| asyncComplete | Whether the task is completed asynchronously. The default value is false.
| Optional. |
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for an HTTP task.
{
"name": "http",
"taskReferenceName": "http_ref",
"type": "HTTP",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true,
"hedgingConfig": {
"maxAttempts": 4
},
"headers": {
"header-1": "${workflow.input.header-1}"
}
}
}
Task output
The HTTP task will return the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| response | A JSON object representing the response, if present. |
| headers | An object containing the metadata about the response. |
| statusCode | The HTTP status code indicating success or failure of the request. |
| reasonPhrase | The reason phrase associated with the HTTP status code. |
| body | The response body containing the data returned by the API. |
Adding an HTTP task in UI
An HTTP task can be configured manually through the UI or automatically populated using registered service definitions.
- Using registered services
- Manually configuring an HTTP tasks
To add an HTTP task using registered services:
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add an HTTP task.
- Select Populate from remote services.
- In Service, select the registered HTTP service.
- In Host, select the required host for the service.
- In Service method, select the required endpoint.
- Select Populate.
- (Optional) In Hedging Config > Maximum attempts, enter a value for parallel hedged requests to reduce latency.
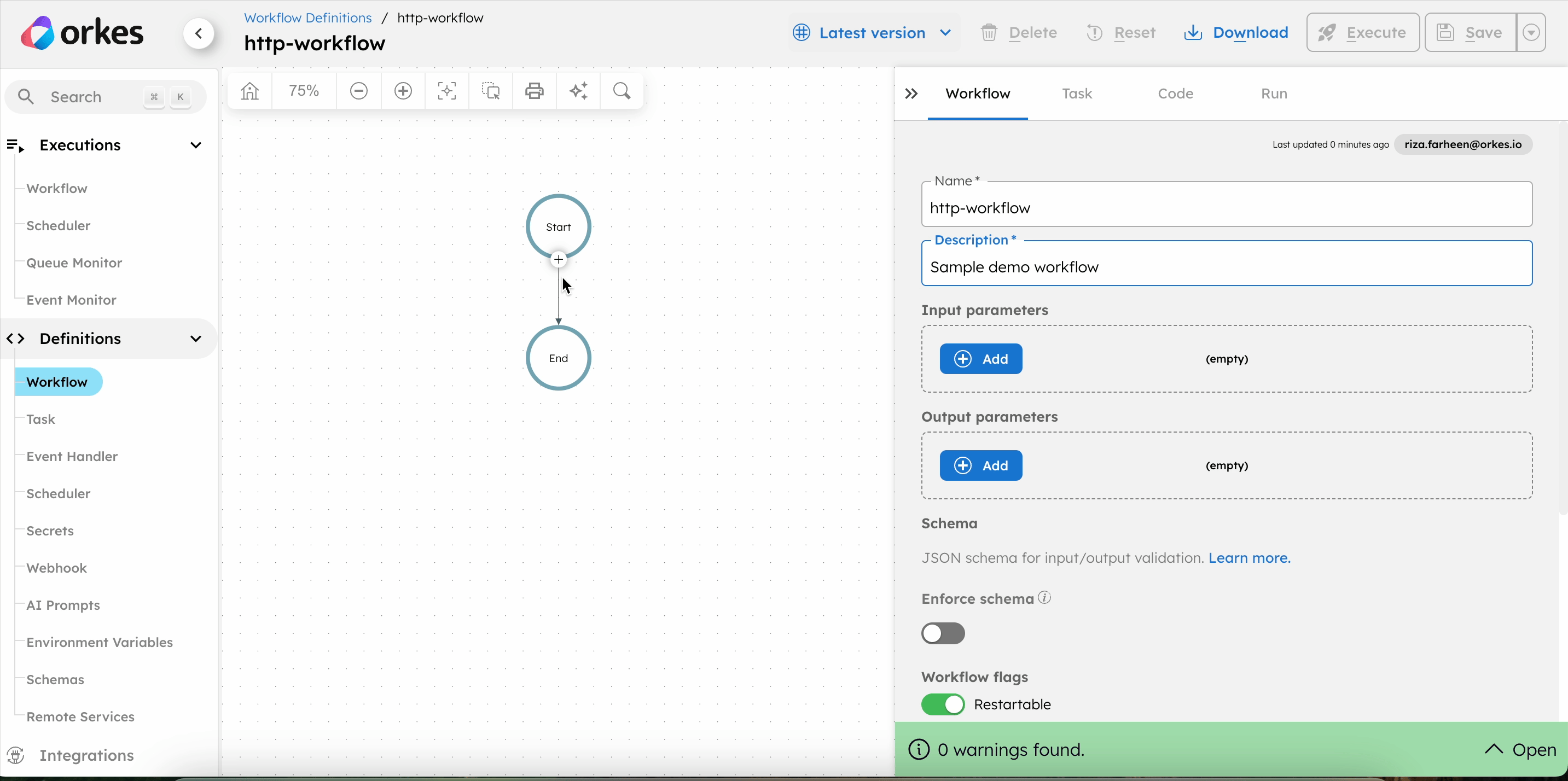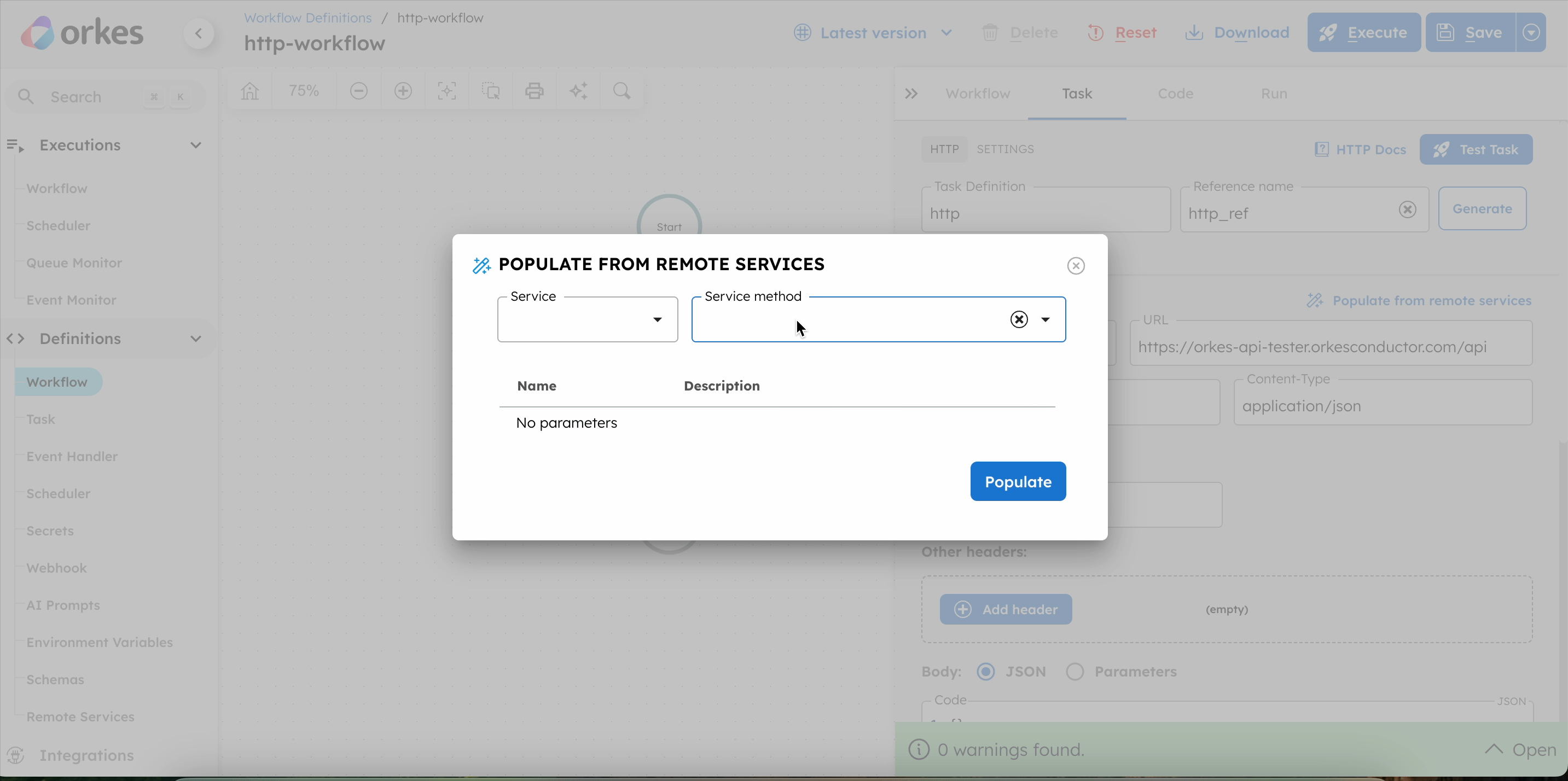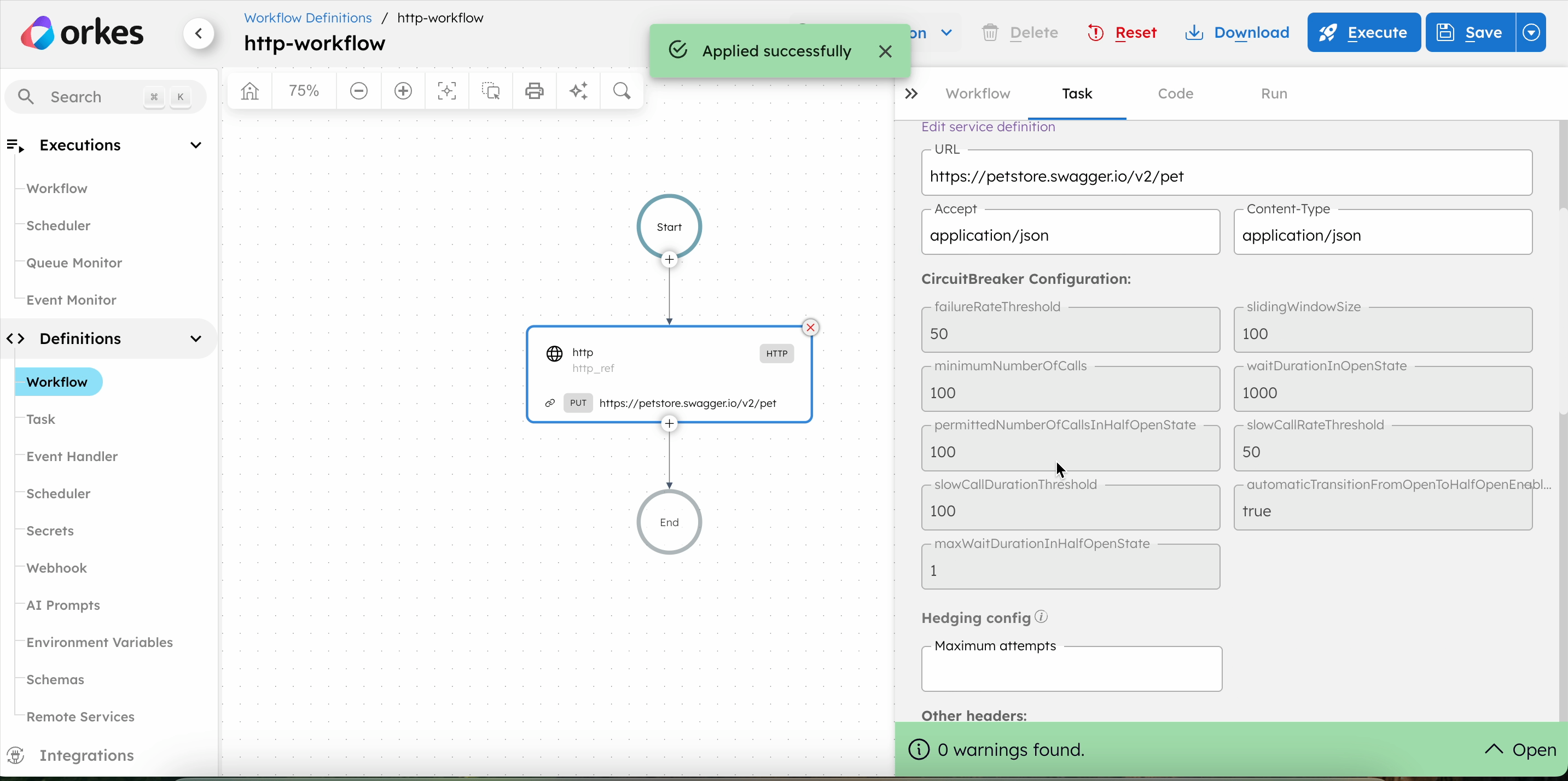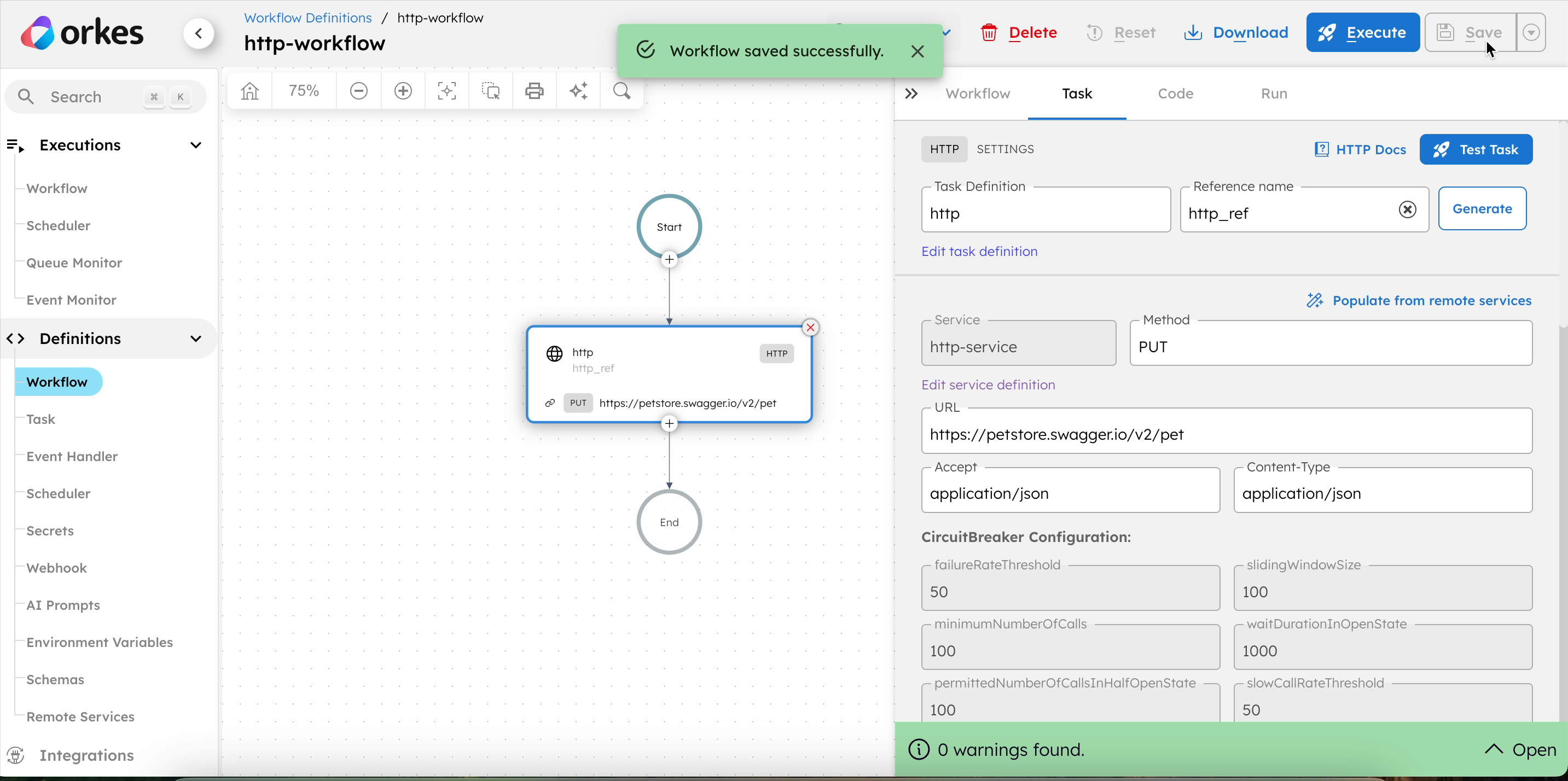
This method automatically fills in the HTTP task parameters based on the selected service. It is recommended if you have already registered your HTTP services in Orkes Conductor.
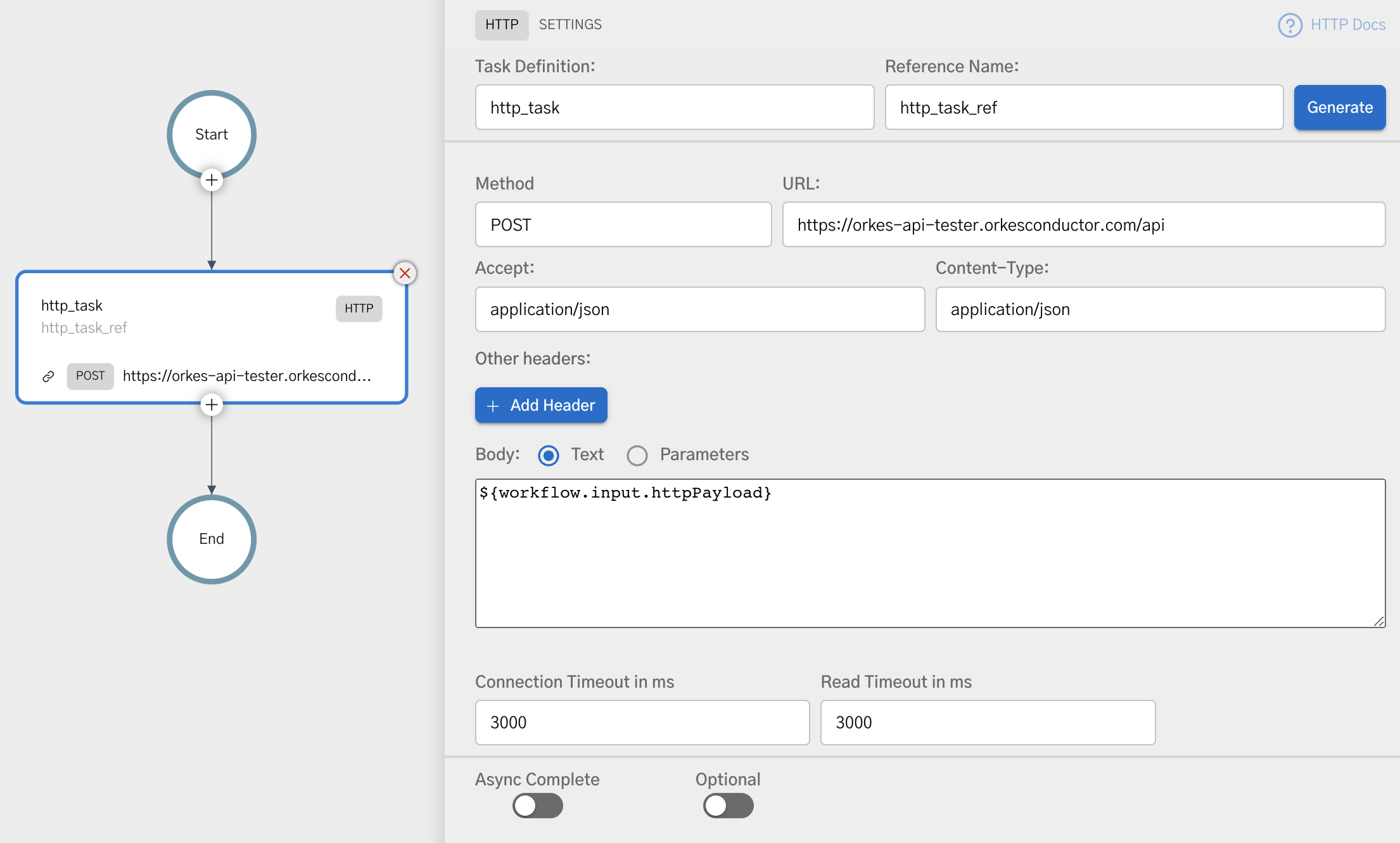
To add an HTTP task:
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add an HTTP task.
- Choose the HTTP method for sending requests from the Method drop-down.
- In URL, add the URI to be called by the HTTP task.
- In Accept, select the accept header as required by the server.
- In Content-Type, select the content type for the server.
- (Optional) Enable or disable Encode to specify if the URI needs to be encoded.
- (Optional) In Hedging Config > Maximum attempts, enter a value for parallel hedged requests to reduce latency.
- (Optional) In Additional headers, add any additional HTTP headers to be sent along with the request.
- In Body, add the request body when using PUT, POST, or PATCH method.
- (Optional) Set Async complete to true if the task is to be completed asynchronously.
Examples
Here are some examples for using the HTTP task.
Sending an HTTP POST request
This example creates a workflow that sends an HTTP POST request to a public test API and returns the created resource in the task output.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "http_post_end_to_end_example",
"description": "Sends an HTTP POST request and returns the response body",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "http",
"taskReferenceName": "post_request",
"type": "HTTP",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts",
"method": "POST",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"headers": {
"x-source": "orkes-conductor"
},
"body": {
"title": "Sample post created by Conductor",
"body": "This payload was sent by an HTTP task.",
"userId": 1
}
}
}
],
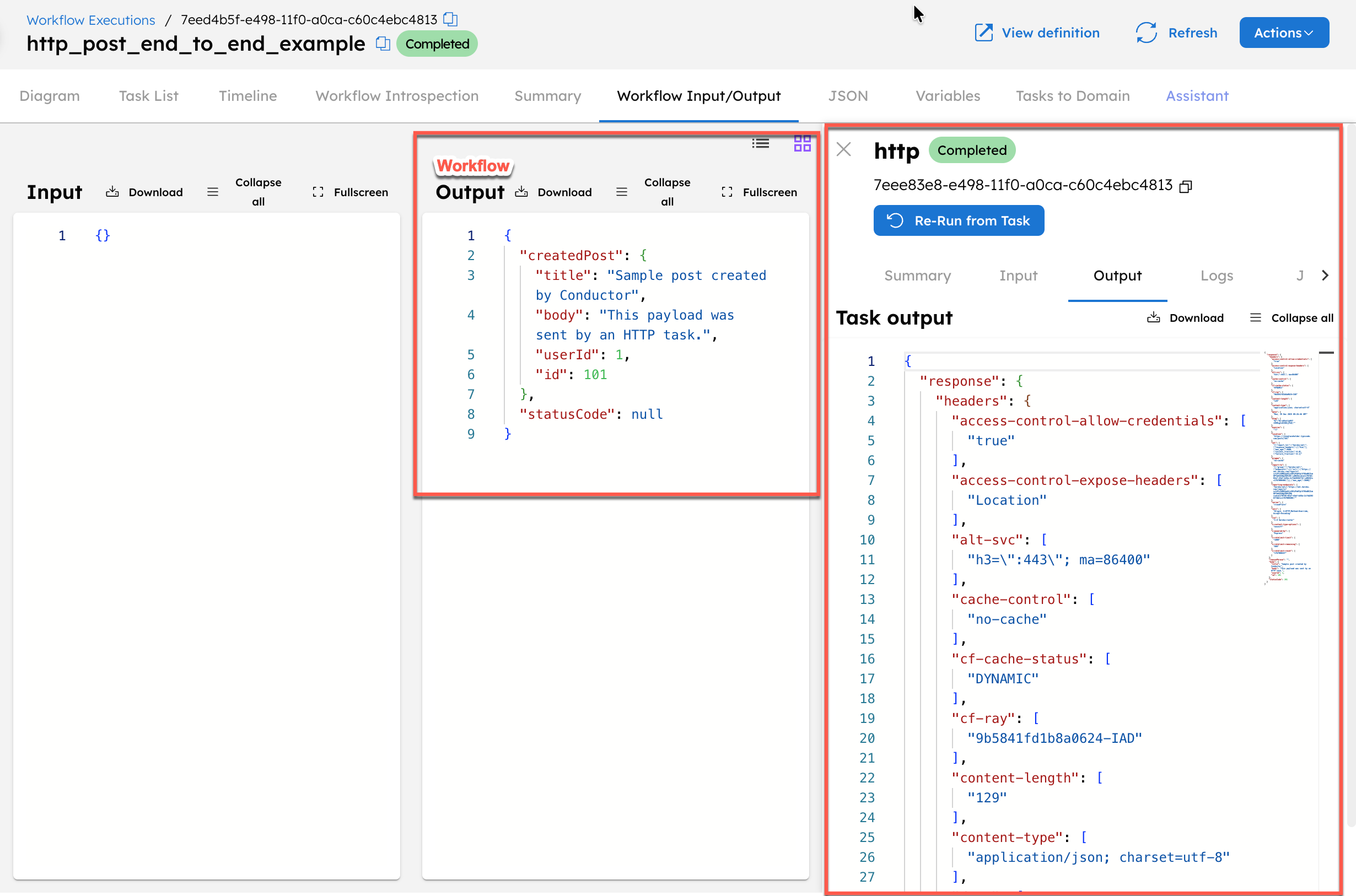
"outputParameters": {
"createdPost": "${post_request.output.response.body}",
"statusCode": "${post_request.output.statusCode}"
},
"schemaVersion": 2
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
- Select Execute to run the workflow.
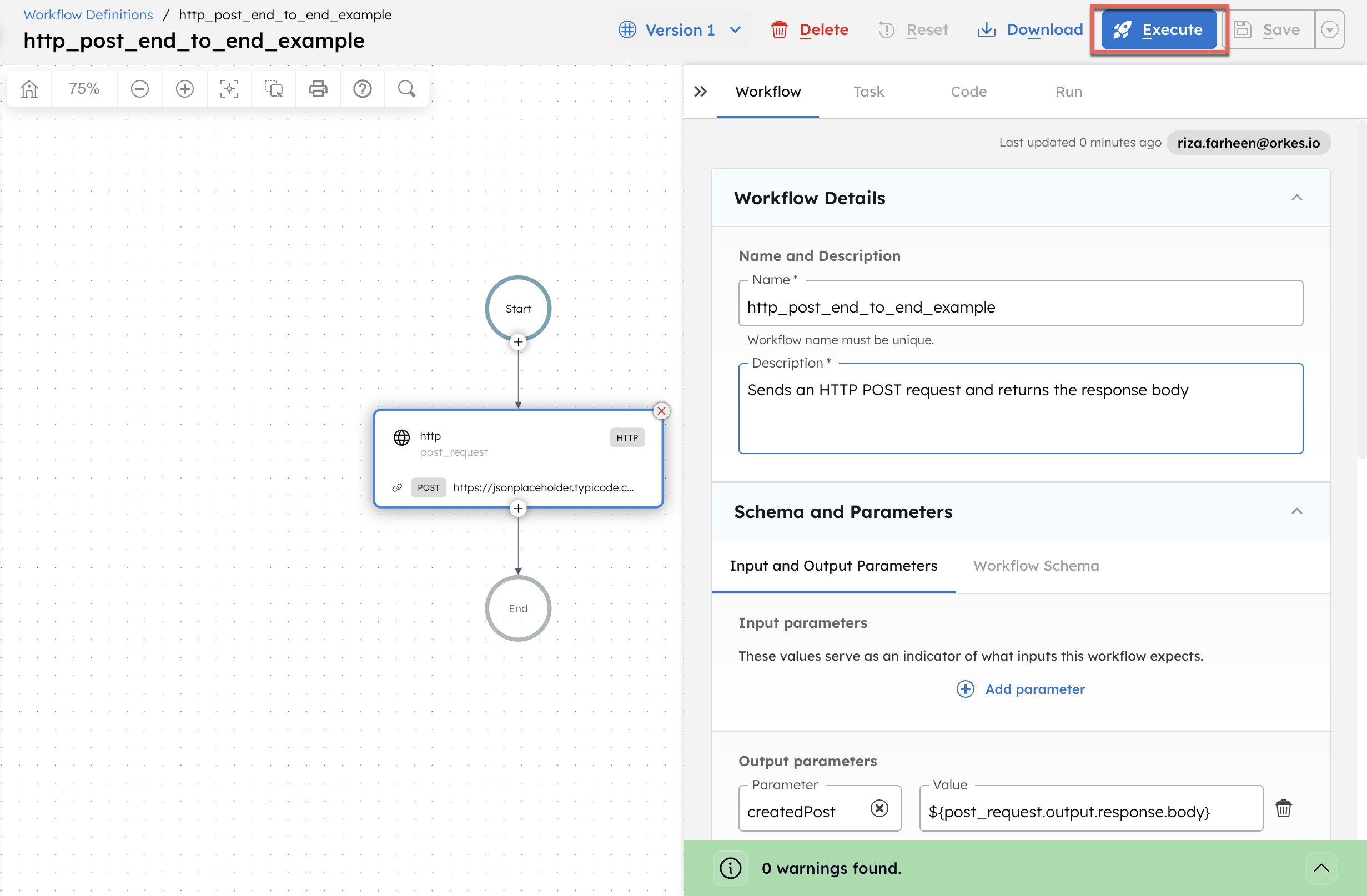
This takes you to the workflow execution page, where you can inspect the task output and workflow output.
Use asyncComplete to complete an HTTP task asynchronously
The asyncComplete parameter allows an HTTP task to be completed asynchronously. When enabled, the task remains in progress until an external signal marks it as completed.
This example shows how to pause a workflow after an HTTP task starts and resume it later using asynchronous completion.
In this example, you’ll build a workflow that:
- Executes an HTTP request
- Pauses execution using
asyncComplete - Resumes only when an external signal marks the task as completed
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "async_complete_example",
"description": "Edit or extend this sample workflow. Set the workflow name to get started",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "http_task_85tf2",
"taskReferenceName": "http_task_85tf2_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"connectionTimeOut": 3000,
"readTimeOut": "3000",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json"
},
"type": "HTTP",
"asyncComplete": true
}
],
"schemaVersion": 2
}
- Save the workflow.
- Select Execute to run the workflow.
Upon execution, the HTTP task remains “In Progress” instead of completing immediately, allowing for asynchronous completion. The task can be completed using various methods:
- Method 1: Complete the task using API
- Method 2: Complete the task using API Conductor UI
- From the workflow execution page, copy the workflow ID and task reference name.
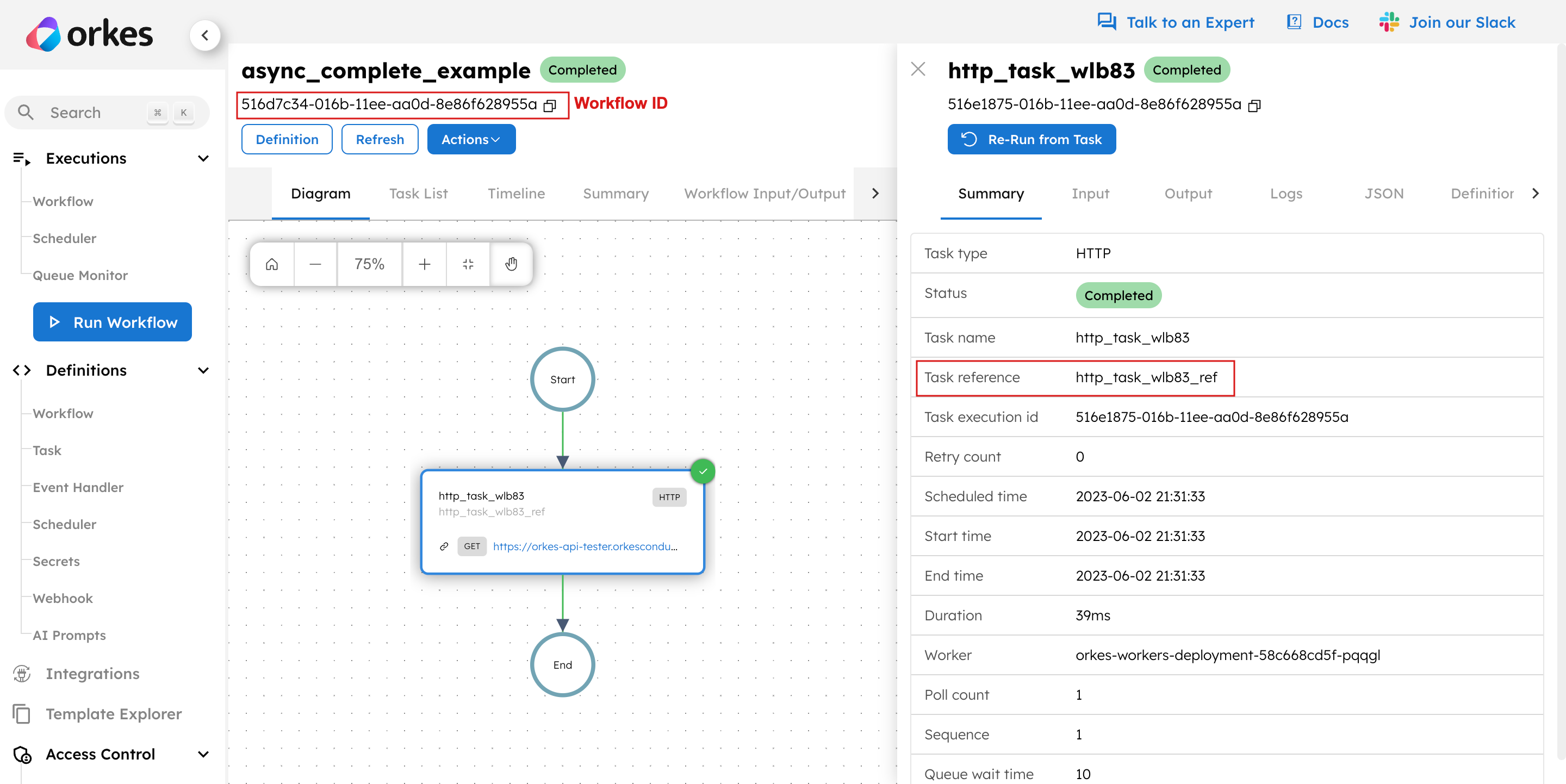
- Use this
workflowIdalong with thetaskRefNameto complete the task using the Update Task Status in a Workflow API.
POST /api/tasks/{workflowId}/{taskRefName}/{status}
Example Request
curl -X 'POST' \
'https://developer.orkescloud.com/api/tasks/0cc5dd20-e49d-11f0-a0ca-c60c4ebc4813/http_task_85tf2_ref/COMPLETED' \
-H 'accept: text/plain' \
-H 'X-Authorization: <TOKEN>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{}'
Example Response
0cc73cb9-e49d-11f0-a0ca-c60c4ebc4813
This API call marks the task as completed, allowing the workflow to finish its execution.
Alternatively, you can complete the task manually using Conductor UI.
- Open the workflow execution.
- Select the HTTP task.
- Update the status to
COMPLETED.
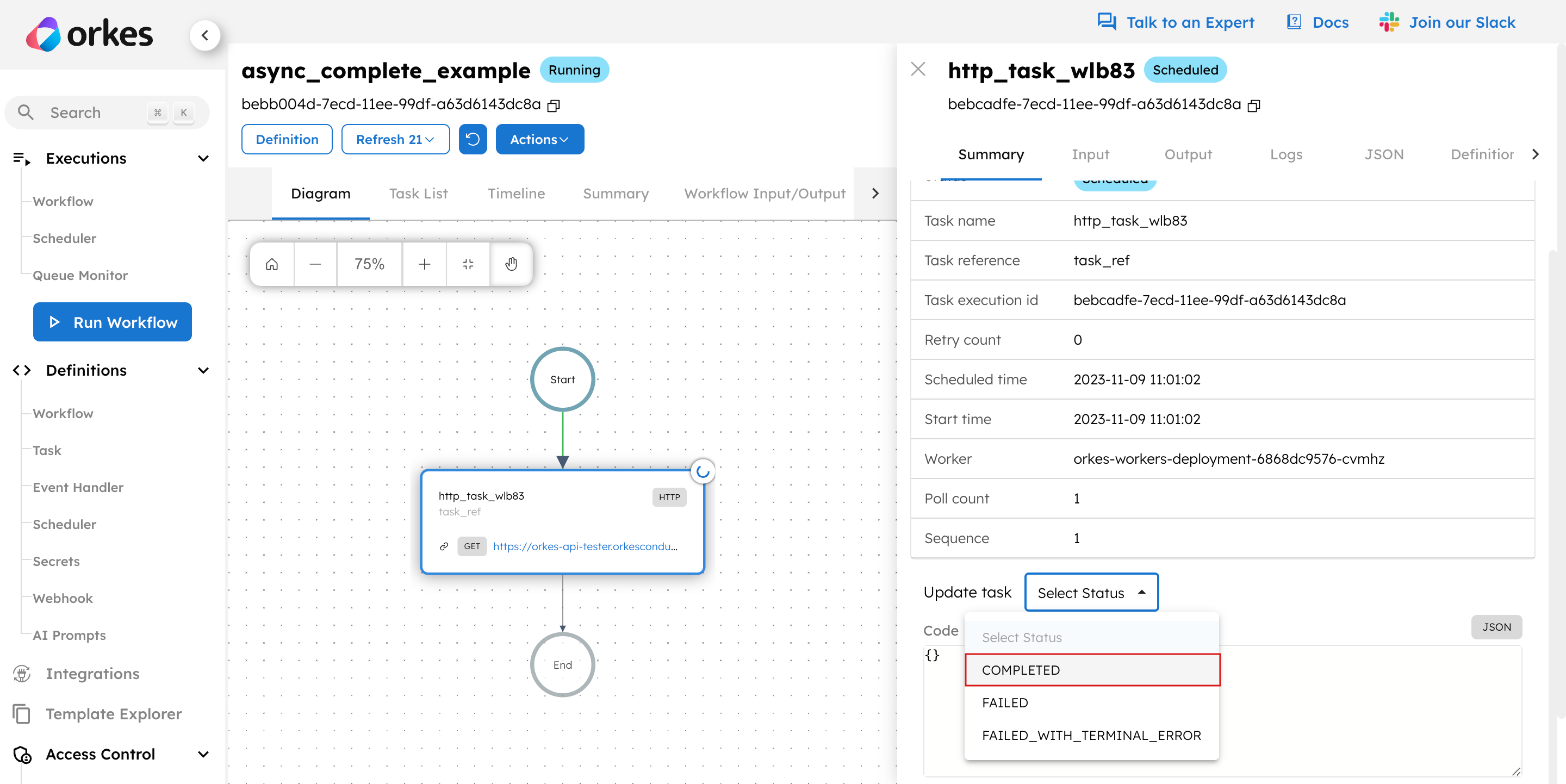
These methods allow you to asynchronously complete your workflow, which is beneficial when pausing the workflow for external interventions.
Orchestrating long-running APIs
Explore the full tutorial on orchestrating long-running APIs.