API Gateway: Expose Workflows as APIs
Using Conductor’s API Gateway, you can expose workflows as APIs. Each endpoint is mapped to a Conductor workflow that can run synchronously, coordinate multiple services, apply business logic, and return an aggregated response, all within a single API call. This allows you to build API endpoints that extend beyond simple request routing.
Endpoints are defined as routes within a service. Each route is linked to a Conductor workflow. When a request is made to the route, Conductor executes the associated workflow and returns its output as the response. To secure access, you can configure authentication settings that define how clients are authorized to invoke each route.
Here’s an overview of how to expose workflows as APIs in Conductor:
- Create workflows to define the logic for each endpoint.
- Create an application with permission to execute the workflows. This acts as the service account layer.
- Configure authentication settings for the API service.
- Define an API service.
- Define and test routes.
Step 1: Create workflows to define the logic for each endpoint
API Gateway exposes workflows as APIs. Before configuring the endpoints, create the required workflows for each endpoint’s logic.
You can create workflows using Conductor UI, APIs, or SDKs.
Step 2: Create an application in Orkes Conductor
Applications in Orkes Conductor act as the service account layer that interacts with the Conductor server. Through this application, you assign the permissions required to execute workflows exposed as APIs.
To create an application:
- Go to Access Control > Applications, and select + Create application.
- Enter a name for the application.
- (Optional) Enable the required Application role based on how the service wants to interact with the application.
- In Permissions, select + Add permission.
- In the Workflow tab, select the workflow created in Step 1 and enable EXECUTE permission.
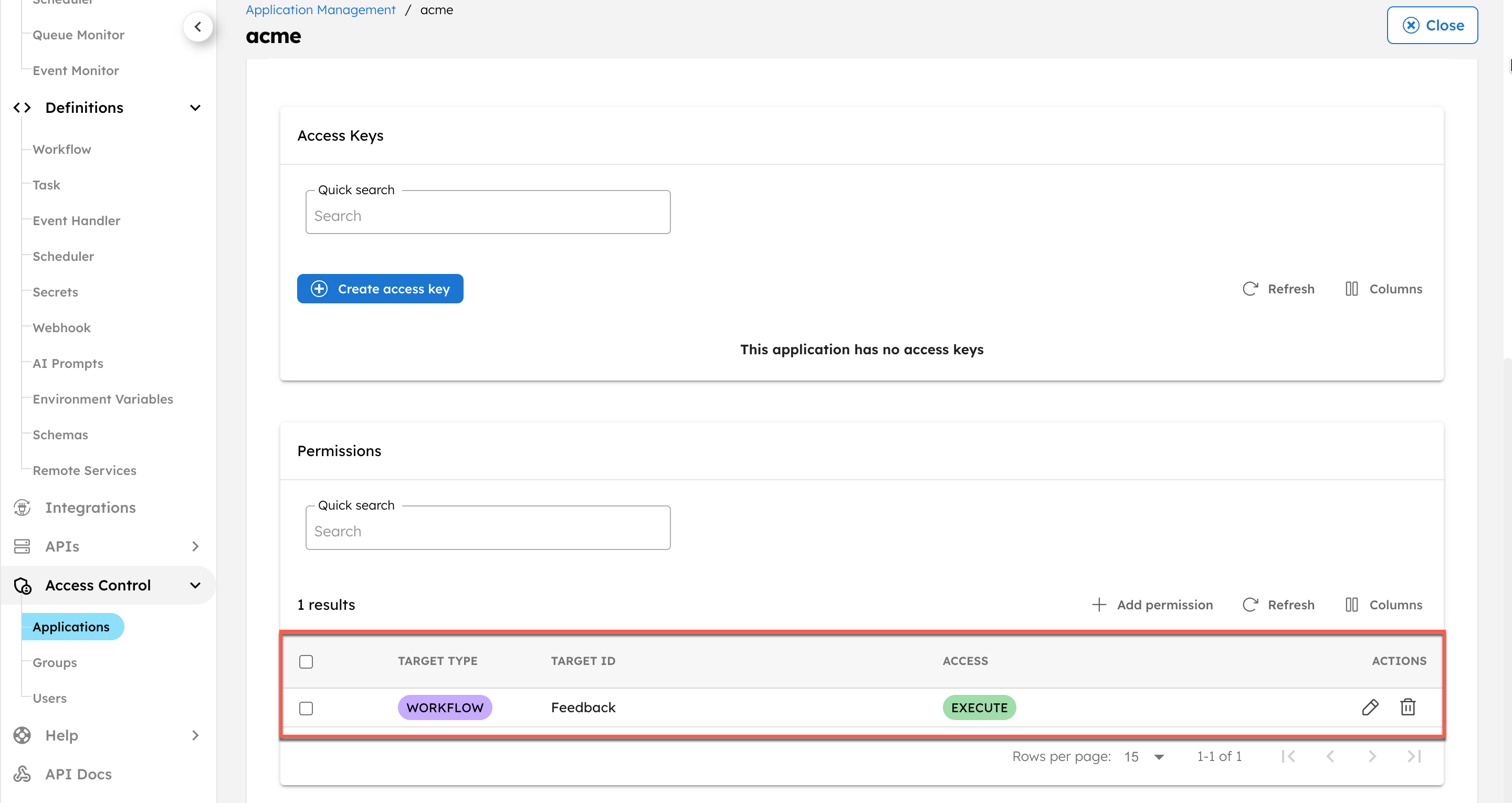
- Save the application.
The next step is to create an authentication setting for the API service.
Step 3: Configure authentication settings
Authentication settings control how clients are authorized to access a service. You can create authentication settings globally in your Conductor cluster and reuse them across services.
To configure authentication settings:
- Go to APIs > Authentication from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + New authentication.
- Configure the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| ID | A unique identifier for the authentication configuration. This cannot be renamed once saved. | Required. |
| Authentication Type | The type of authentication to use. Supported values:
| Required. |
| API Key | The API key for authentication. A random key is generated by default. You can also select Generate to create one instantly. Copy and store the key securely for future authentication. | Required if Authentication Type is API Key. |
| Application | Select the application created in Step 2, which generates an access key and JWT token. The API Gateway will use this token to authenticate with the Conductor. The service using this authentication will inherit the application’s permissions. | Required. |
- Select Save.
Step 4: Define an API service
A service represents a logical grouping of API endpoints (called routes) that share common settings such as base path, authentication, and CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) policies. Each route within a service maps to a specific workflow. You must create a service before adding individual routes.
To define a service:
- Go to APIs > Services from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + New service.
- Configure the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| Basic information | ||
| Service ID | A unique identifier for the service. Use lowercase letters and hyphens, as this value is used in the API URLs. This cannot be renamed once saved. | Required. |
| Display Name | A user-friendly name for the service. | Required. |
| Service Enabled | Determines whether the service is active. Enabled by default. Switch it off if you do not want to activate the service immediately. | Required. |
| MCP Enabled | Determines whether the MCP is active for this service. Enabled by default. Switch it off, since we are using this as an API gateway. | Required. |
| API Configuration | ||
| Base Path | The base path for all routes in the service. The path must start with a forward slash (for example, | Required. |
| Auth Config | The authentication configuration to use for this service. Select the configuration created in the previous step, or select + Create New Auth Config from the dropdown, and configure the authentication settings. | Required. |
| CORS Configuration | ||
| Allowed Origins | The origins (URLs) that can access this service. Press Enter after each URL to add multiple origins. Use * to allow all origins. | Required. |
| Allowed Methods | The HTTP methods that can be used in cross-origin requests. Supported values:
| Required. |
| Allowed Headers | The HTTP headers that can be sent in requests from allowed origins. Press Enter after each header to add multiple headers. Use * to allow all headers. | Required. |
| Additional Information | ||
| Description | A description of the service. | Optional. |
- Select Save.
Step 5: Define and test a route
Each endpoint in a service must be defined as a route, which is mapped to the Conductor workflow that executes the logic.
To create a route within a service:
- Go to the Services and select the + button next to the service created.
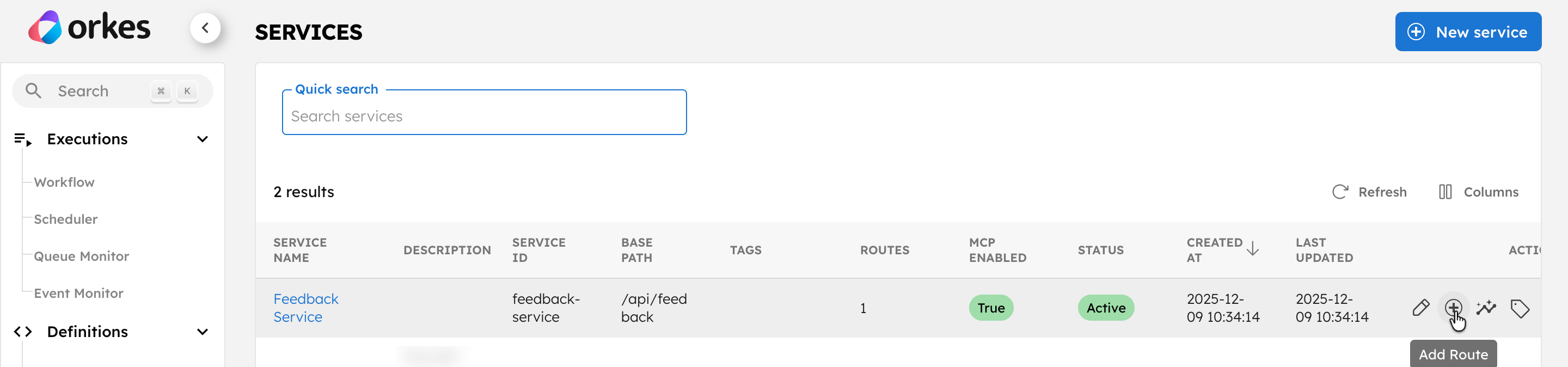
- Configure the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| Route Definition | ||
| HTTP Method | The HTTP method for the route. Supported methods:
| Required. |
| Path | The path for the request.
| Required. |
| Description | A description of the route. | Optional. |
| Workflow Configuration | ||
| Workflow Name | The workflow to be triggered by the route. | Required. |
| Version | The version of the workflow to use. If unspecified, the latest version will be used. | Required. |
| Wait Until Tasks | The task to wait for before returning a response. The API will return the output of this task, instead of the workflow output. This is useful if the workflow contains tasks that take a long time to complete, but a response from the API is required before the connection times out. | Optional. |
| Timeout (seconds) | The duration in seconds to wait before returning a response. | Optional. |
| Schema | ||
| Input Schema | The input schema for the request.
| Optional. |
| Output Schema | The output schema for the request.
| Optional. |
| Query Parameters | ||
| Parameter Name | The query parameter that can be accepted by the endpoint. Can contain only letters, numbers, underscores, and hyphens. Enable Required if the parameters are mandatory. | Optional. |
| Transformation Scripts | ||
| Pre-request Script | A JavaScript function to transform the incoming request payload before passing it to the workflow. The returned object becomes the workflow input. Use Example | Optional. |
| Test Pre-request Script | Test the input processing script. To test the payload:
| N/A |
| Post-response Script | A JavaScript function to transform the final workflow output before it is returned in the API response. The returned object is sent as the API response. Use Example | Optional. |
| Test Post-response Script | Test the output processing script. To test the payload:
| N/A |
| Cache Configuration | ||
| Cache Key | Enables caching for a route. When caching is enabled, Conductor stores responses for repeated requests and returns the cached result for matching inputs until the entry expires. | Optional. |
| TTL (Time To Live) in Seconds | Set how long the cached value remains valid. | Optional. |
| Rate Limit Configuration | ||
| Rate Limit Key | Key used to identify the rate limit scope for this route. Can be passed as a variable. | Optional. |
| Concurrent Execution Limit | Maximum number of concurrent executions allowed for this route. | Optional. |
- Select Save.
Test a route
You can test route behavior directly from the Conductor UI before exposing it as an API.
Run a test request
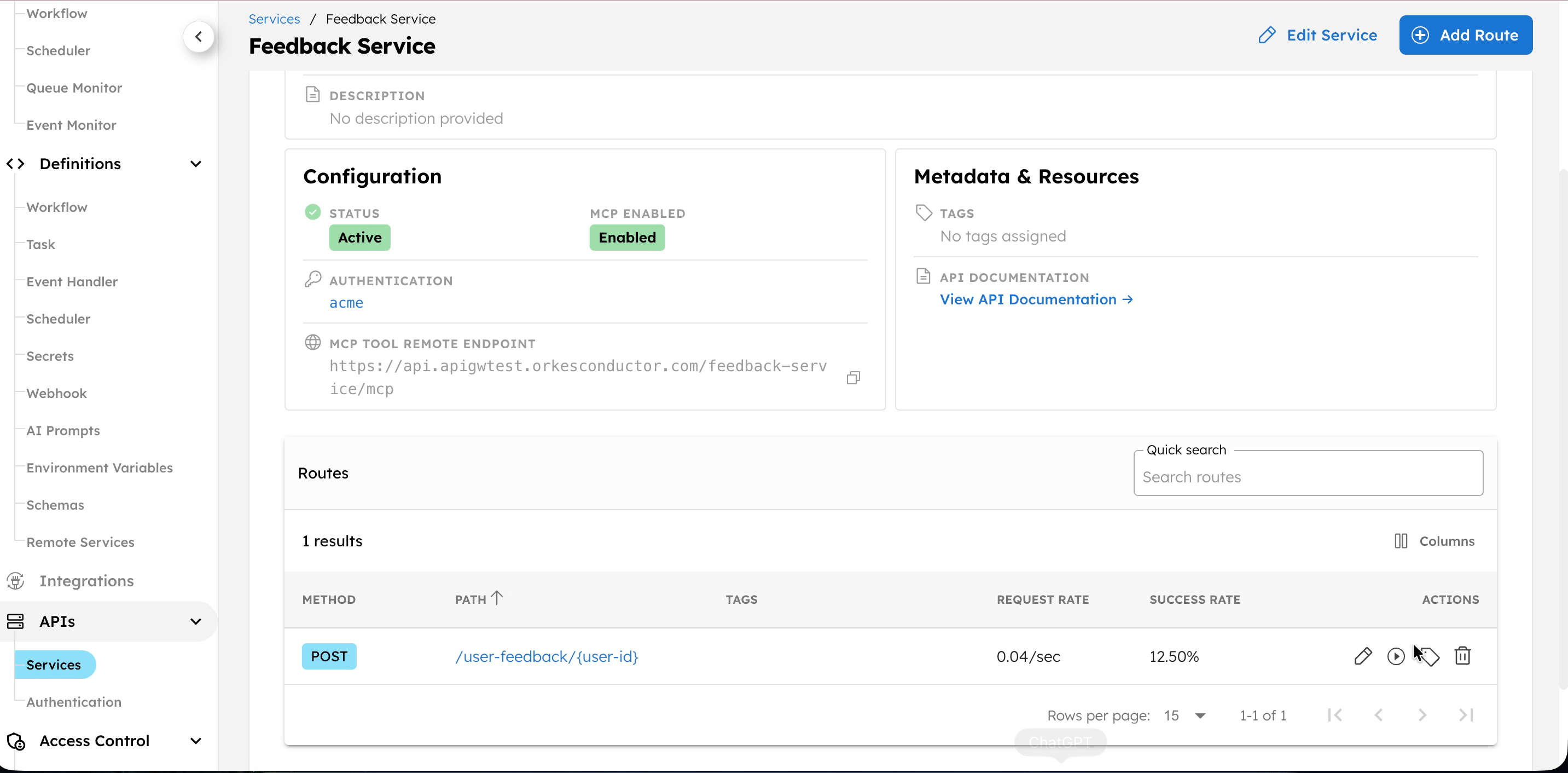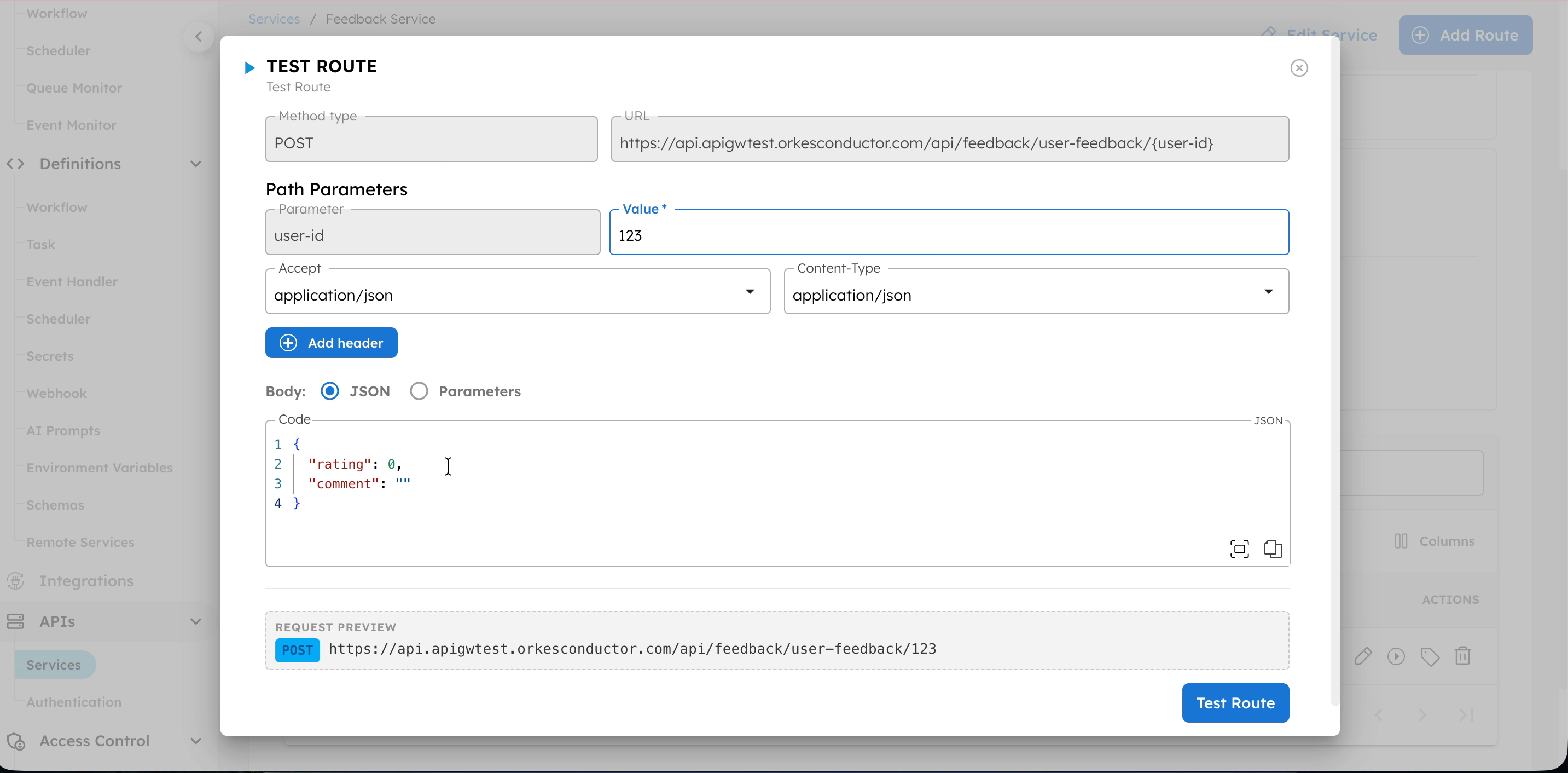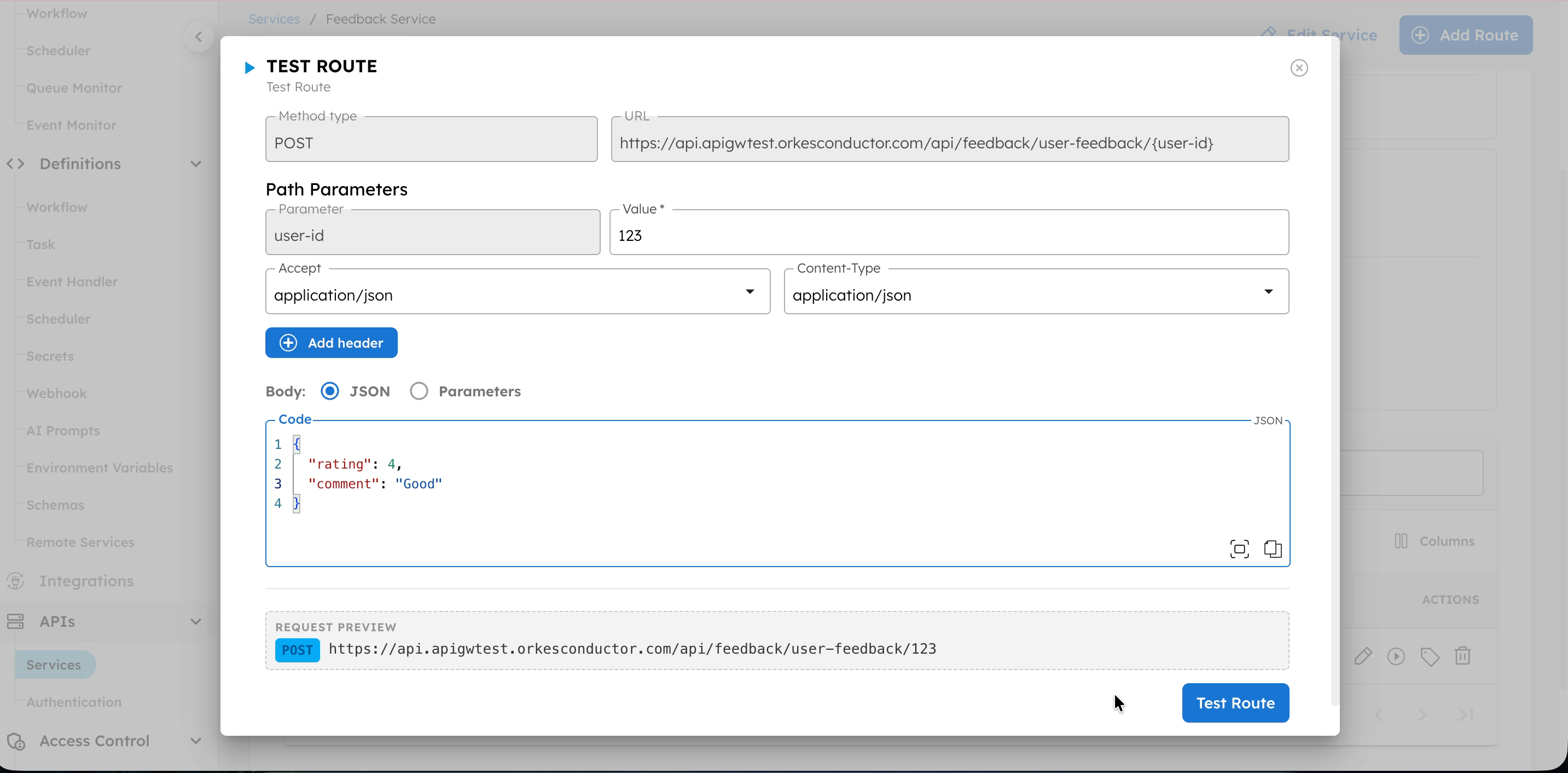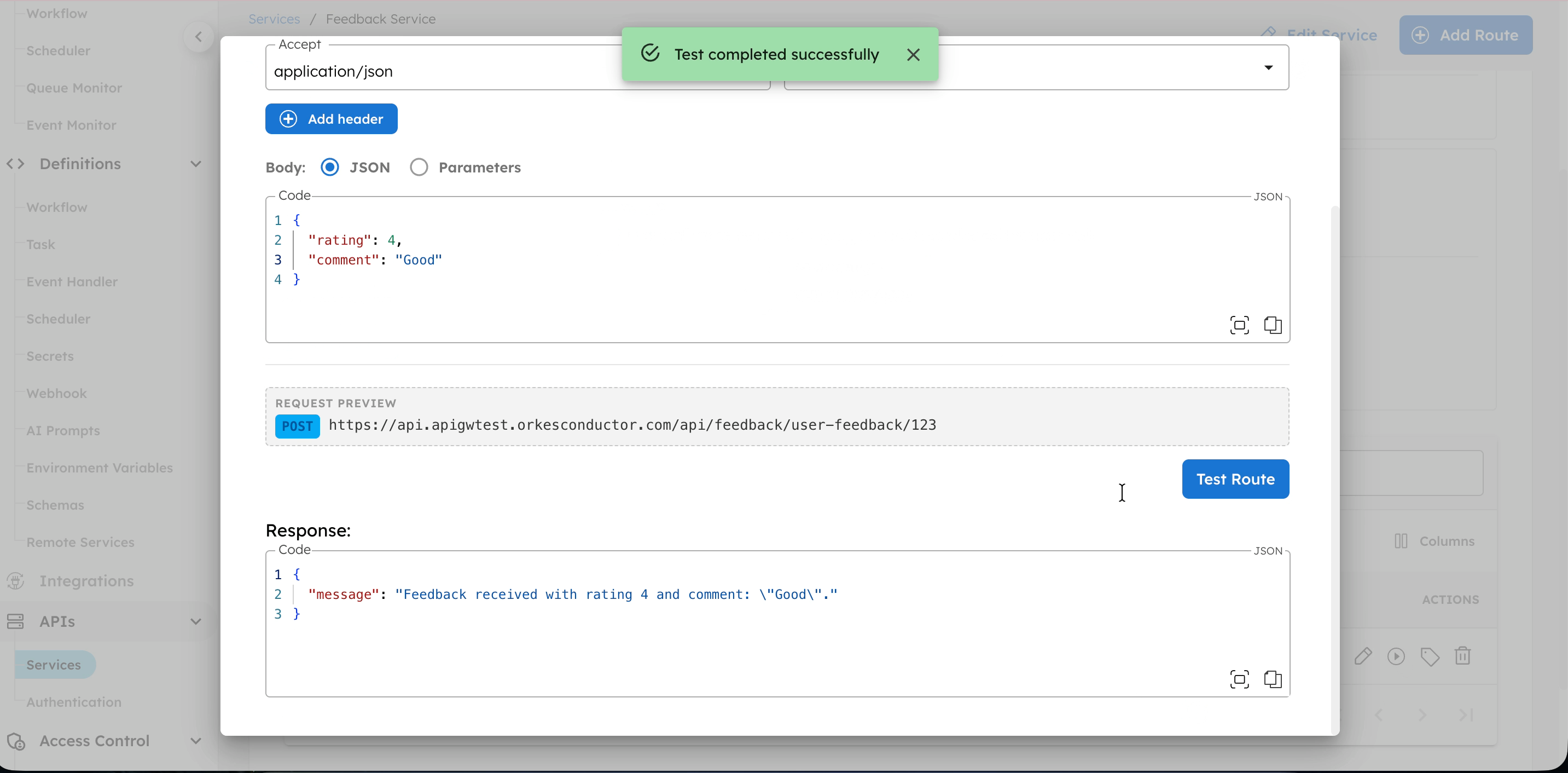
To test a route:
- Go to the APIs > Services, and select the service.
- In Routes, select the play icon next to the route to test.
- In Path Parameters, enter any required parameters for the endpoint.
- (If Authentication is using an API key) Replace *** with the API key copied in Step 3.
- In Body, enter the request payload as expected by the workflow.
- Select Test Route.
- Review the Response to verify the route works as expected.
Verify workflow execution
To confirm that the route triggered the workflow:
- Go to Executions > Workflow in your Conductor cluster and verify that the workflow is completed successfully.
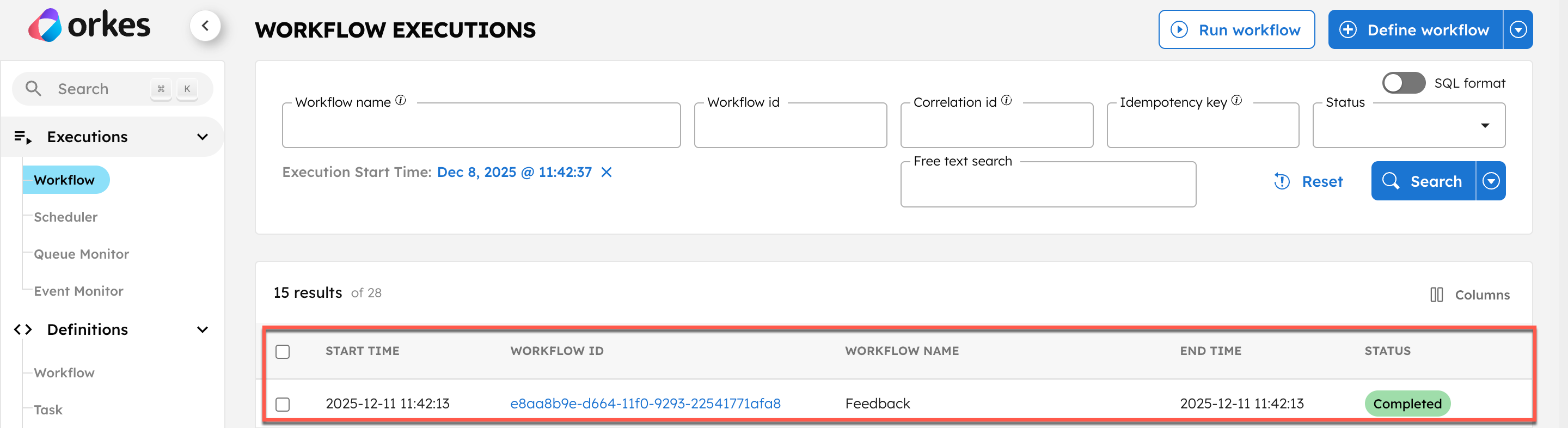
- Select the Workflow ID to view the complete execution, including the workflow input and output.
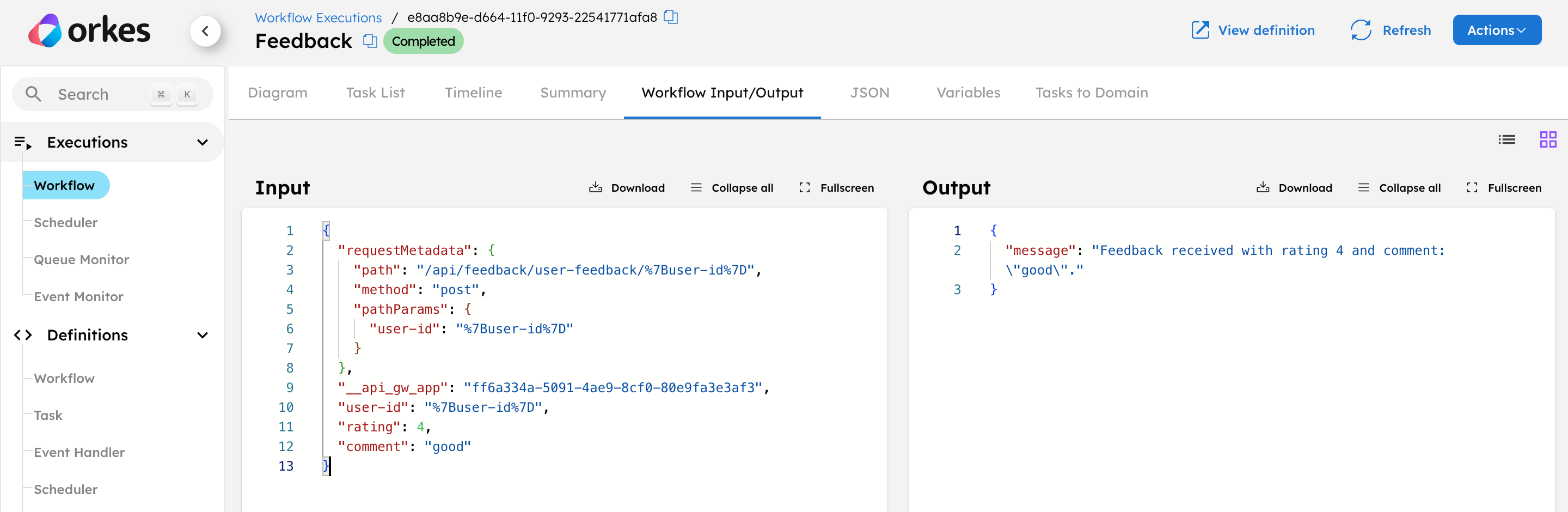
View endpoint details
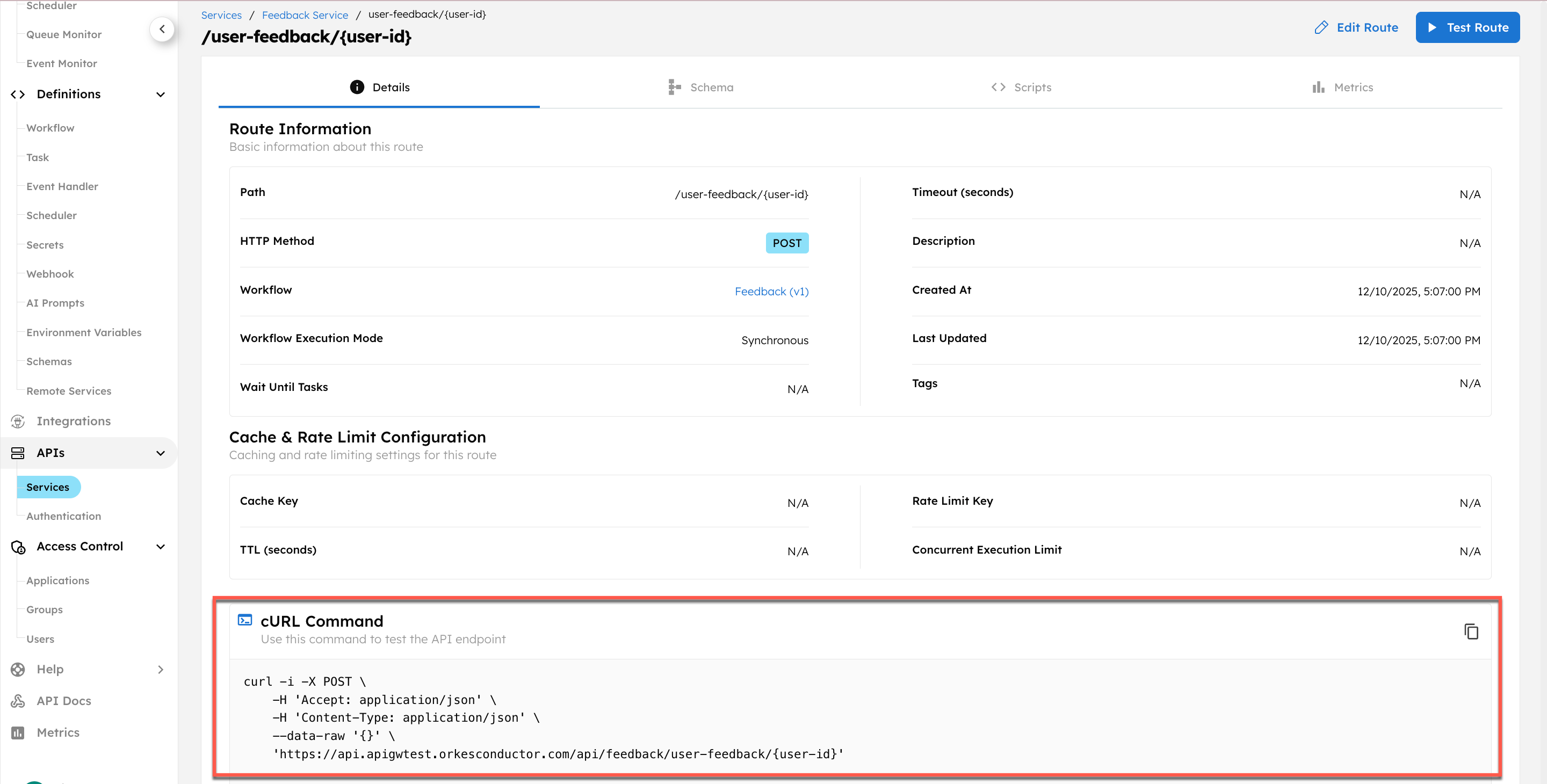
To get the cURL command:
- Go to APIs > Services, and select your service.
- Select a route to open its details.
- You can get the cURL command for the actual endpoint here.
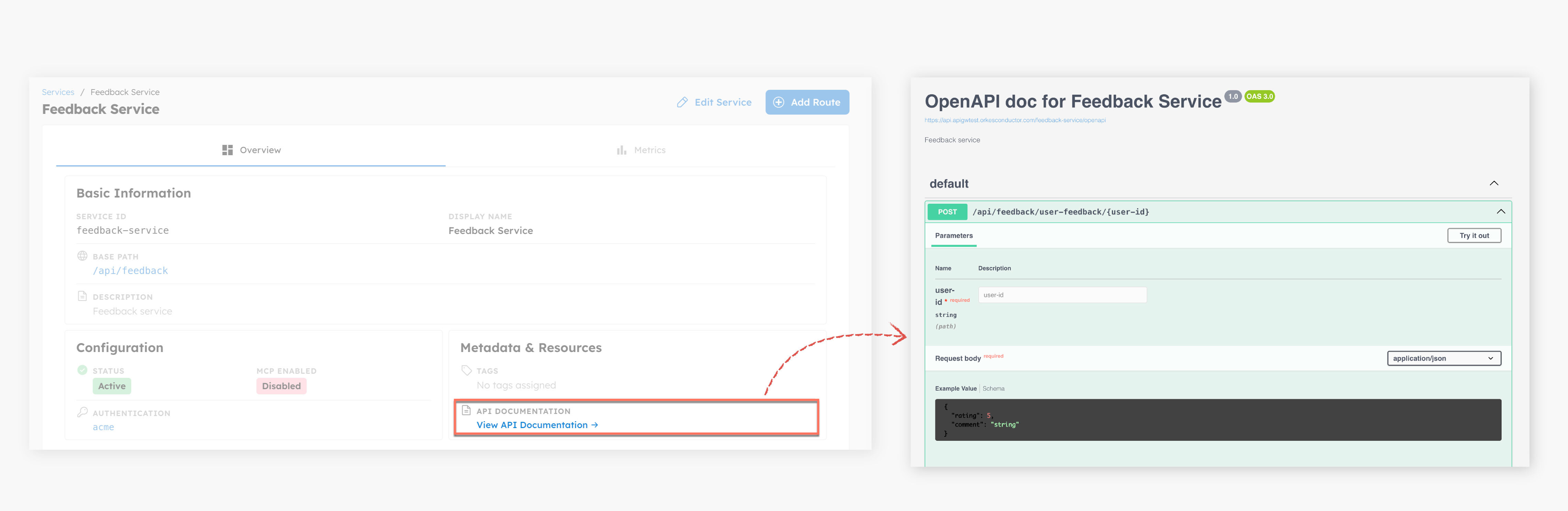
To view the OpenAPI documentation for the endpoint:
- Go to APIs > Services, and select the service.
- In Metadata & Resources, select View API documentation.
Examples
See an example of a feedback service exposing a feedback workflow as a public API.
Next steps
To learn how to monitor service and route performance, see Gateway Metrics.