Event
The Event task is used to publish events into eventing systems. It supports various eventing models, including AMQP, Amazon MSK, AWS SQS, Azure Service Bus, Confluent Kafka, Apache Kafka, NATS Messaging, GCP Pub/Sub, and IBM MQ.
An Event task publishes a message to an event queue or topic. The specific eventing system used depends on the configured sink. The sink parameter defines the message broker type, integration name, and queue/topic name. The task execution payload is sent to this sink, and Conductor automatically appends additional system input parameters to the payload.
- Integrate the required message broker with Orkes Conductor.
Task parameters
Configure these parameters for the Event task.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| sink | The event queue sink in the format: message-broker-type:integration-name:topic/queue-name Where,
| Required. |
| inputParameters | The input parameters for the Event task, which can be passed as a variable or a fixed value. These parameters determine the payload sent to the event sink during task execution. | Optional. |
Additional system inputs to payload
Conductor automatically adds the following parameters to the payload. Ensure that these fields are not present in the payload, as they will be overwritten during execution.
- workflowInstanceId–Workflow ID from where this event was sent.
- workflowType–Name of the workflow definition.
- workflowVersion–Version of the workflow definition.
- correlationId–Correlation ID of the workflow execution.
Example
Given the following task definition:
{
"name": "event_task",
"taskReferenceName": "event_task_ref",
"type": "EVENT",
"sink": "kafka:integration-name:topic-name",
"inputParameters": {
"myKey": "myValue",
"myNumber": 100
}
}
The execution will produce the following input parameters:
{
"myKey": "myValue",
"myNumber": 100,
"workflowInstanceId": "967b19ae-10d1-4b23-b0e7-ae324524dac0",
"workflowType": "my-workflow-name",
"workflowVersion": "1",
"correlationId": "fbdcafd2-69c7-4b75-8dd1-653e33d48746"
}
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for an Event task.
{
"name": "event",
"taskReferenceName": "event_ref",
"type": "EVENT",
"sink": "messaging-type:integration-name:queue-or-topic-name",
"inputParameters": {}
}
Task output
The task output mirrors the payload sent during execution, including system-appended parameters.
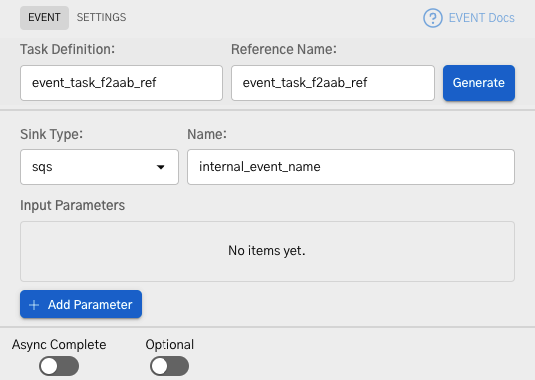
Adding an Event task in UI
To add an Event task:
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add an Event task.
- In Sink, select the required integration and append the topic/queue name. Failure to do so may result in execution errors, as the payload won't have a valid destination.
- (Optional) Add any additional input parameters.
Examples
Here are some examples for using the Event task.
Using Event task in a workflow
In this example, we’ll integrate Confluent Kafka with Orkes Conductor to publish messages to a Kafka topic.
- Integrate Confluent Kafka with Orkes Conductor.
- Create an Event Handler in Conductor.
- Create a Workflow with an Event task.
- Run Workflow.
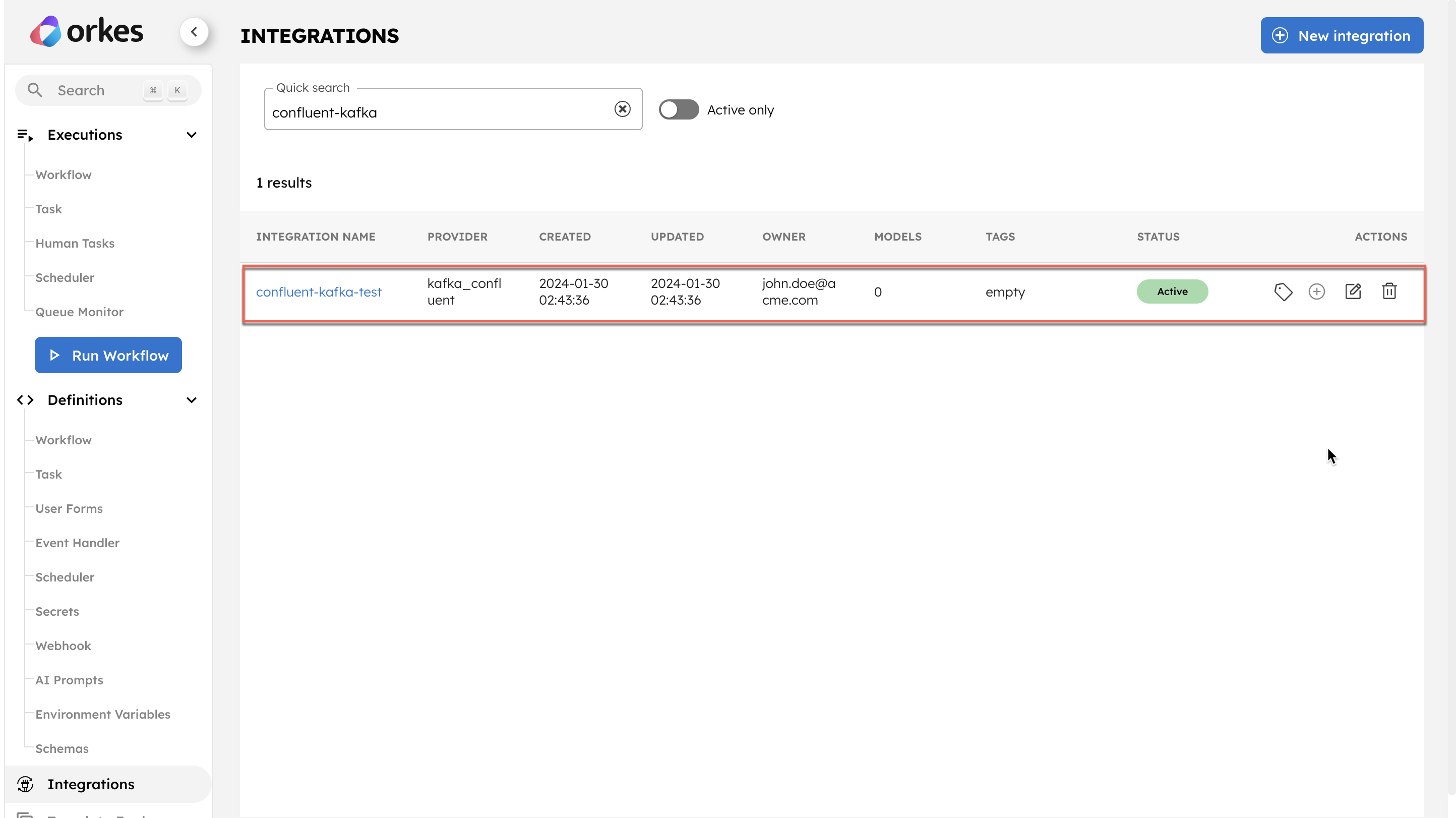
Step 1: Integrate Confluent Kafka with Orkes Conductor
Get the configuration credentials and integrate Kafka as a message broker in Conductor cluster.
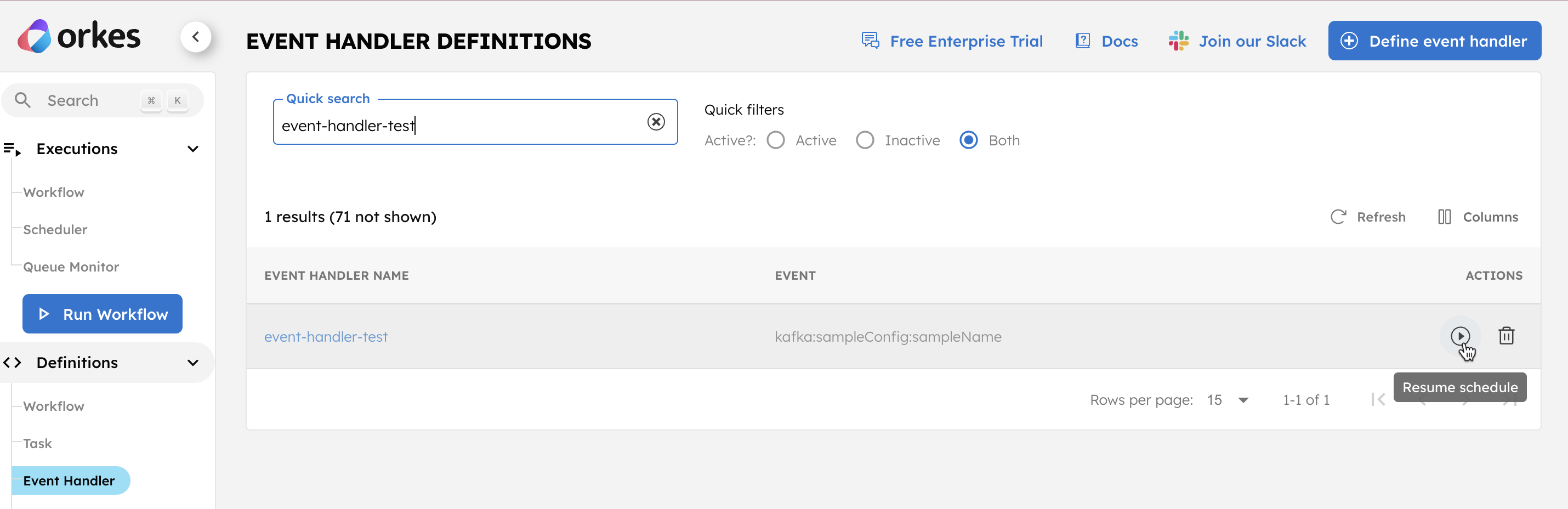
Step 2: Create an Event Handler in Orkes Conductor
Next, create an event handler for the added integration.
To create an event handler:
- Go to Definitions > Event Handlers, from the left menu in the Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define event handler and configure the parameters.
- In the
eventfield, specify the integration in the following format.
message-broker-type:integration-name:topic/queue-name
For Confluent Kafka:
- Set the
message-broker-typetokafka_confluent(default). integration-nameis the name of the integration created in the previous step.topic/queue-nameis the Kafka topic for publishing messages.
Sample Event Handler JSON
{
"name": "event-handler-name",
"event": "kafka_confluent:confluent-kafka-test:topic_0",
"condition": "",
"actions": [
{
"action": "start_workflow",
"start_workflow": {
"name": "http-sample-test",
"version": 1,
"correlationId": "",
"input": {}
},
"expandInlineJSON": false
}
],
"active": true,
"evaluatorType": "javascript"
}
If creating the event handler in the Conductor UI, the drop-down selection in the Event field only lists integrations added to the cluster. Select the required integration and ensure to append the topic name.
Save the definition, and select the play button to run it.
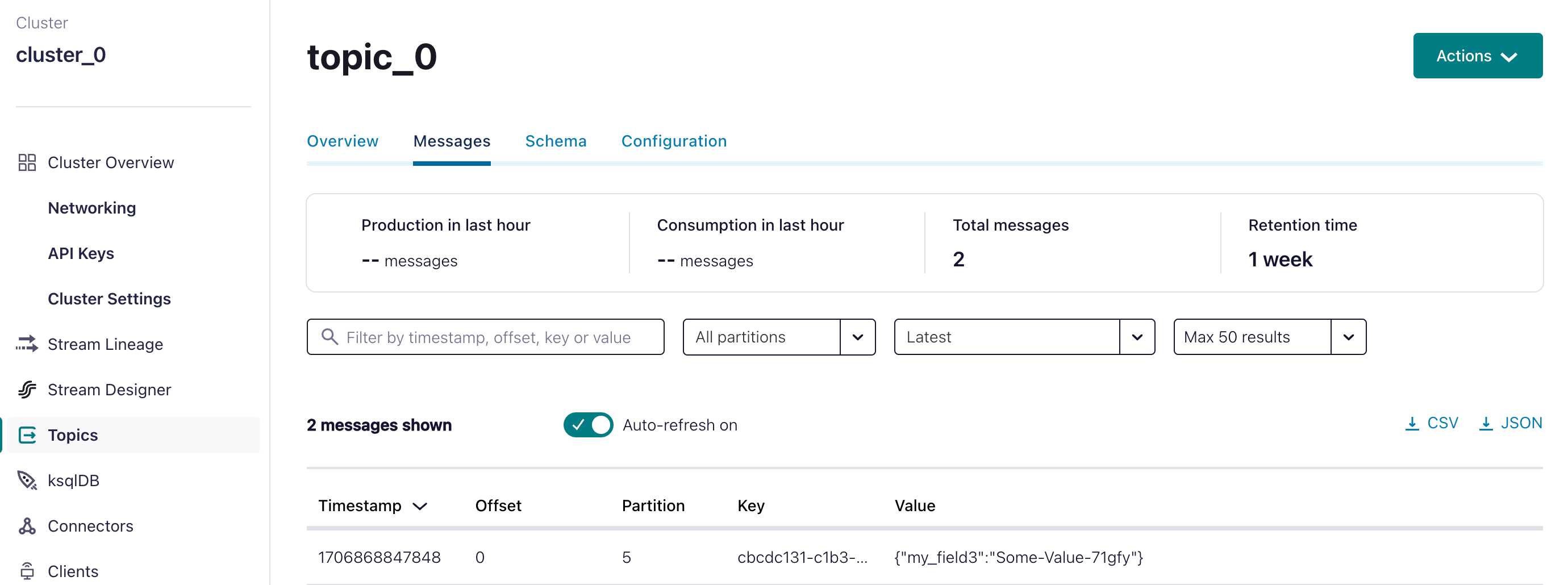
Step 3: Create a Workflow with an Event task
This step involves creating a workflow with an Event task. Here, we utilize the Kafka topic as a sink for the event.
For testing purposes, we can quickly build a workflow using Conductor UI.
To create a workflow:
-
Go to Definitions > Workflow, and select + Define Workflow.
-
Add an Event task with the Sink
kafka_confluent:confluent-kafka-test:topic_0. -
In Input parameters, add the following parameters:
-
_schema—Set it to the topic name, including the schema subject.
To locate the schema subject name from Confluent console:- Go to Home > Environment > [Choose your environment].
- Under Schema Registry, find the subject name.
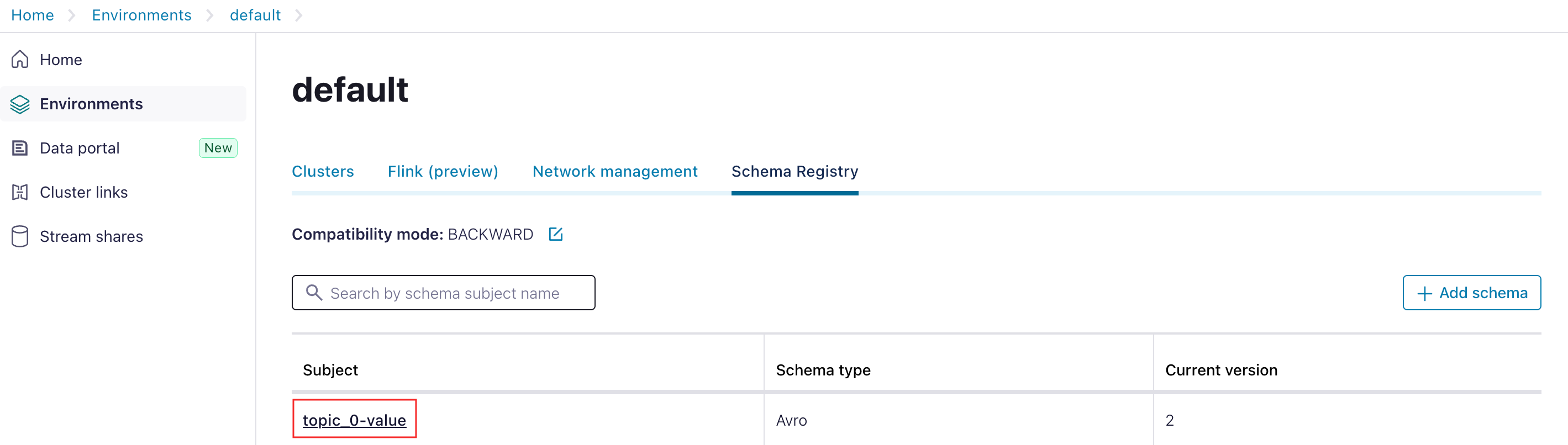
- Add this subject name as the input parameter:
"_schema": "topic_0-value"
-
Add all fields in the topic’s schema as the input parameters as well.
- Locate the schema for your topic by navigating to the Schema sub-tab from your topic and selecting Evolve schema.
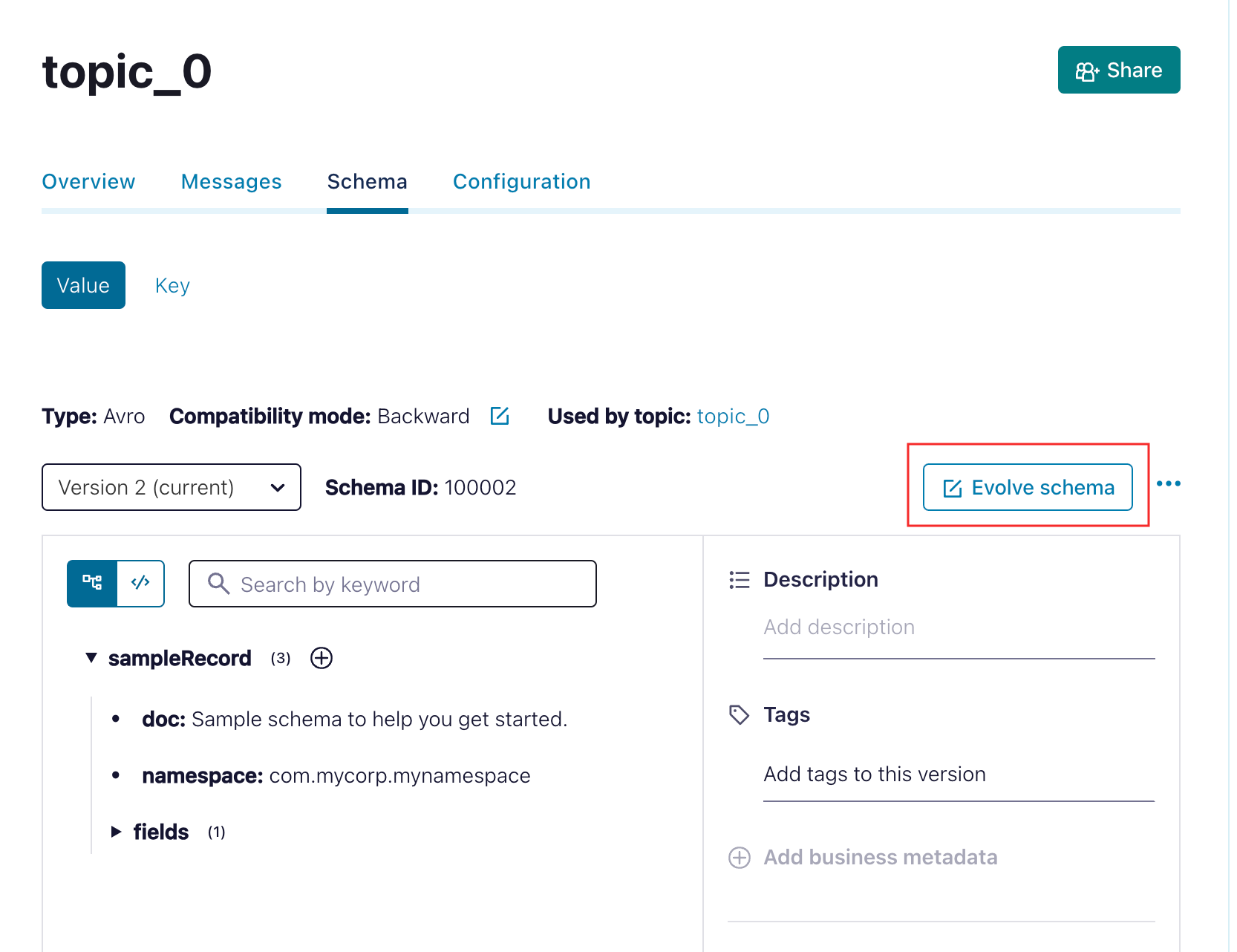
For example, The topic here is
topic_0, which has the following schema:{
"doc": "Sample schema to help you get started.",
"fields": [
{
"doc": "The string is a unicode character sequence.",
"name": "my_field3",
"type": "string"
}
],
"name": "sampleRecord",
"namespace": "com.mycorp.mynamespace", //Use a unique `name` and `namespace` to avoid any conflicts.
"type": "record"
}Ensure that each field in the schema is mapped as input parameters in the Event task.
So, in this example, the input parameters (including the schema fields and schema subject name) are as follows :
"inputParameters": {
"_schema": "topic_0-value",
"my_field3": "Some-Value-71gfy"
},
-
Here’s the complete workflow definition JSON:
{
"name": "Confluent-Kafka-workflow",
"description": "Sample Workflow for Confluent Kafka Integration",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "event",
"taskReferenceName": "event_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"_schema": "topic_0-value",
"my_field3": "Some-Value-71gfy"
},
"type": "EVENT",
"sink": "kafka_confluent:confluent-kafka-test:topic_name"
}
],
"schemaVersion": 2,
"ownerEmail": "john.doe@acme.com"
}
- Save the workflow.
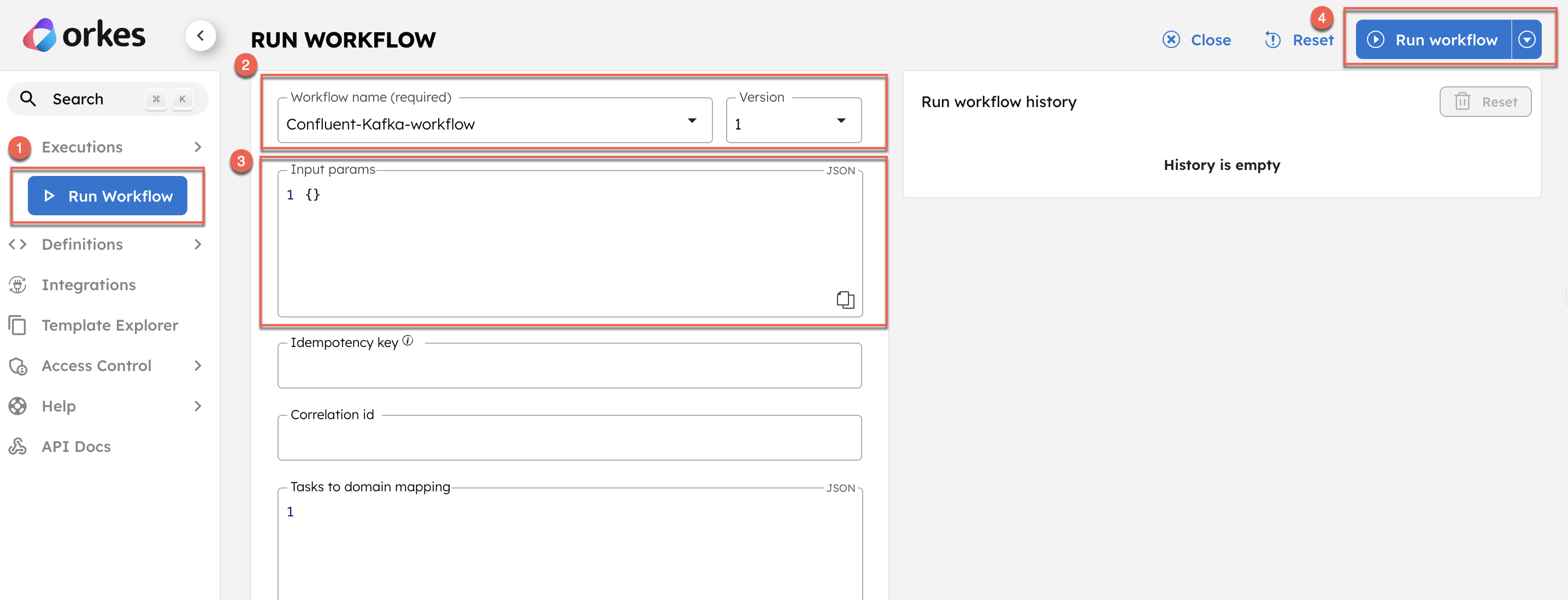
Step 4: Run Workflow
- Go to Run Workflow from the left menu on the Conductor cluster.
- Select the Workflow name and Version.
- Enter the input parameters.
- Click Run Workflow.
Once started, you can track execution progress in Executions > Workflow in the Conductor UI.
After successful execution, verify the message's delivery in the Confluent portal.
- From your cluster details page, navigate to Topics in the left menu.
- In the Messages tab, verify that the message is consumed successfully.