Confluent Kafka Integration with Orkes Conductor
The Confluent Kafka configuration is deprecated. For new configurations, use Apache Kafka.
To use the Event task, Event Handler, or enable Change Data Capture (CDC) in Orkes Conductor, you must integrate your Conductor cluster with the necessary message brokers. This guide explains how to integrate Confluent Kafka with Orkes Conductor to publish and receive messages from topics. Here’s an overview:
- Get the required credentials from Confluent Kafka.
- Configure a new Confluent Kafka integration in Orkes Conductor.
- Set access limits to the message broker to govern which applications or groups can use it.
Step 1: Get the Confluent Kafka credentials
To integrate Confluent Kafka with Orkes Conductor, retrieve the following credentials from the Confluent Cloud portal:
- API keys
- Bootstrap server
- Schema registry URL (Only if integrating with a Schema registry for AVRO protocol)
- Consumer Group ID
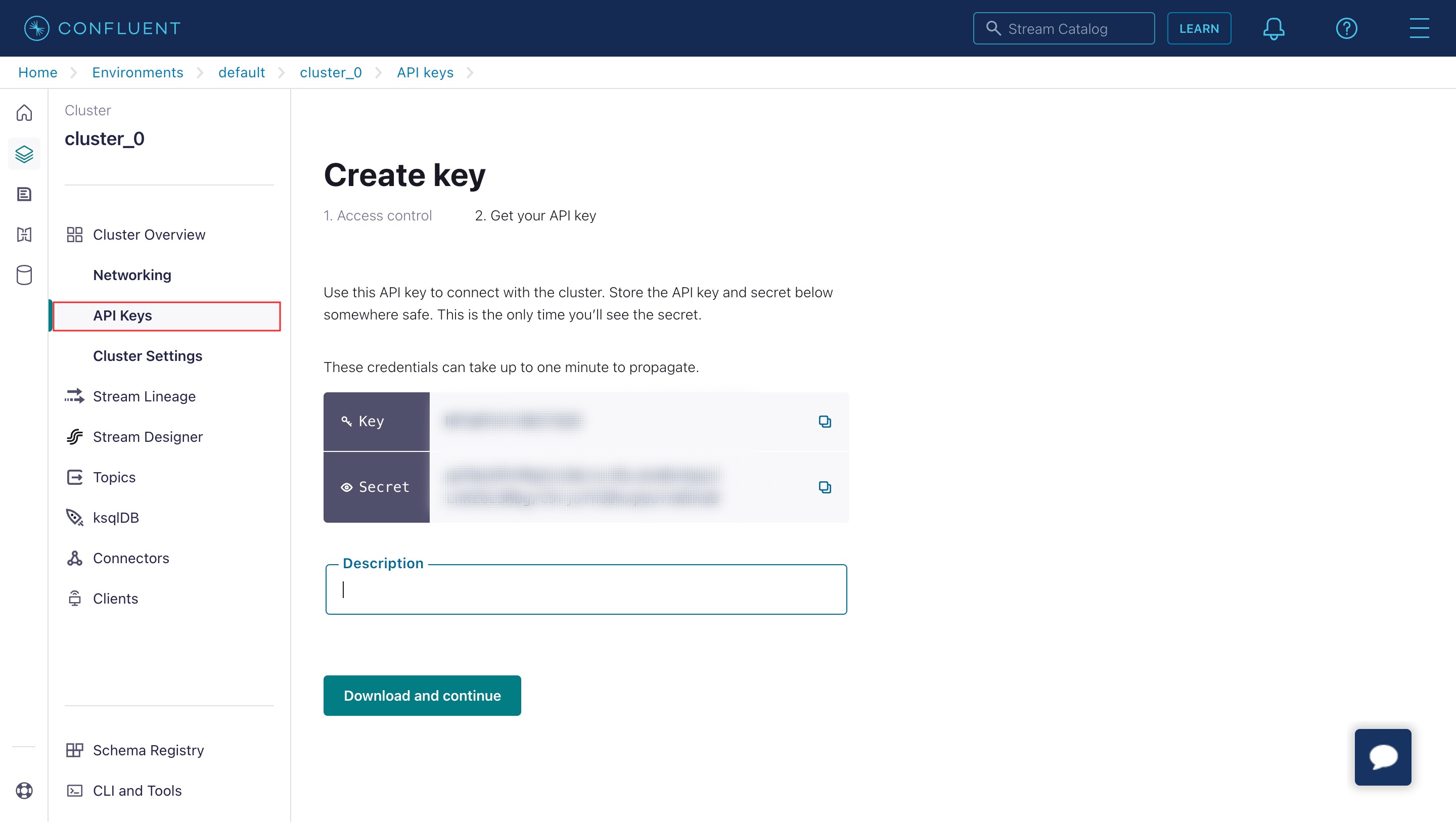
Get the API keys
To retrieve the API keys:
- Sign in to the Confluent Cloud portal.
- Select the Confluent cluster to integrate with Orkes Conductor.
- Go to Cluster Overview > API Keys from the left navigation menu.
- Select Create Key > + Add key.
- Choose either Global access or Granular access.
- Copy and store the Key and Secret.
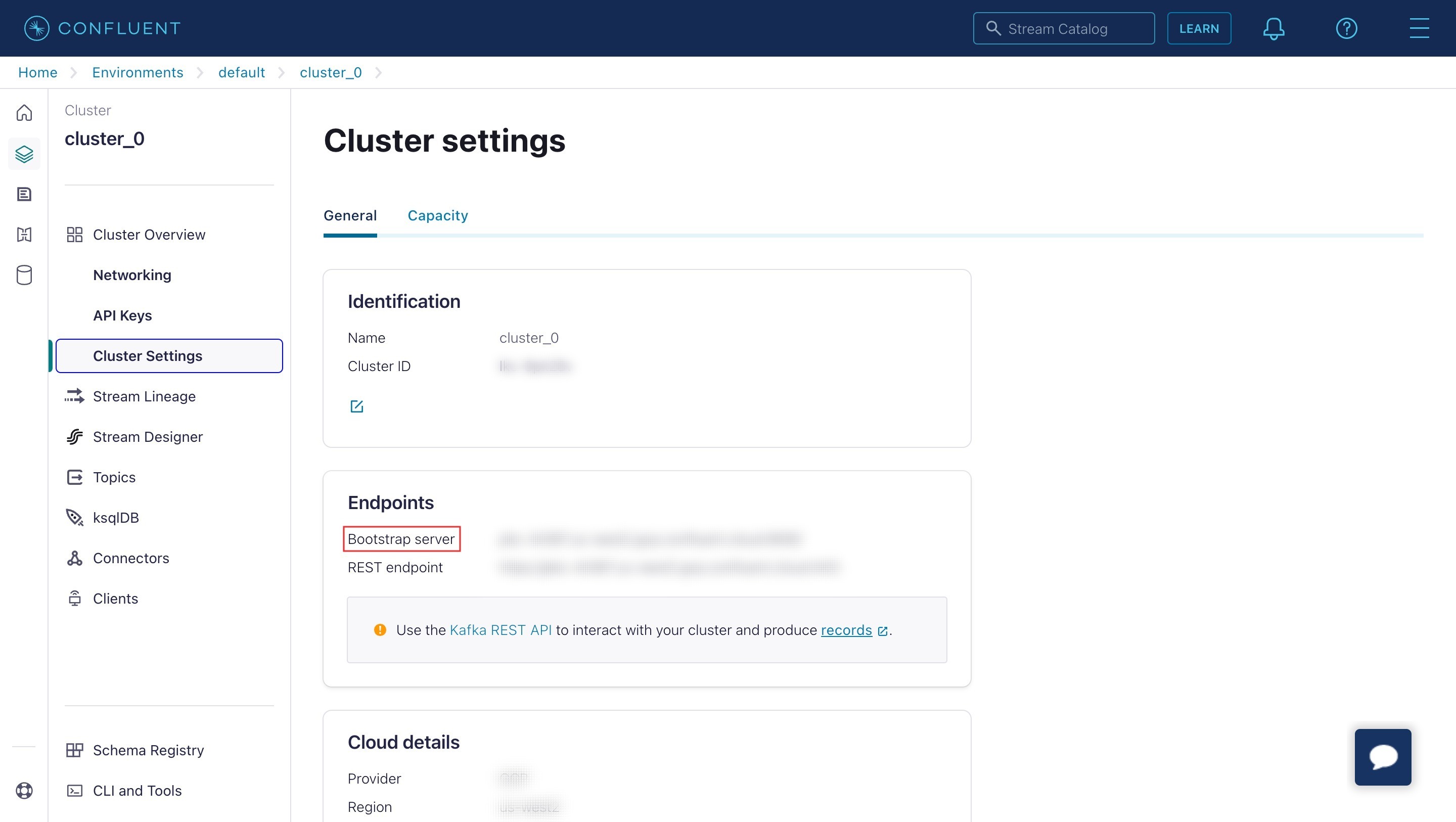
Get the Bootstrap server
To retrieve the Bootstrap server:
- Sign in to the Confluent Cloud portal.
- Go to Cluster Overview > Cluster Settings > Endpoints.
- Copy the Bootstrap server.
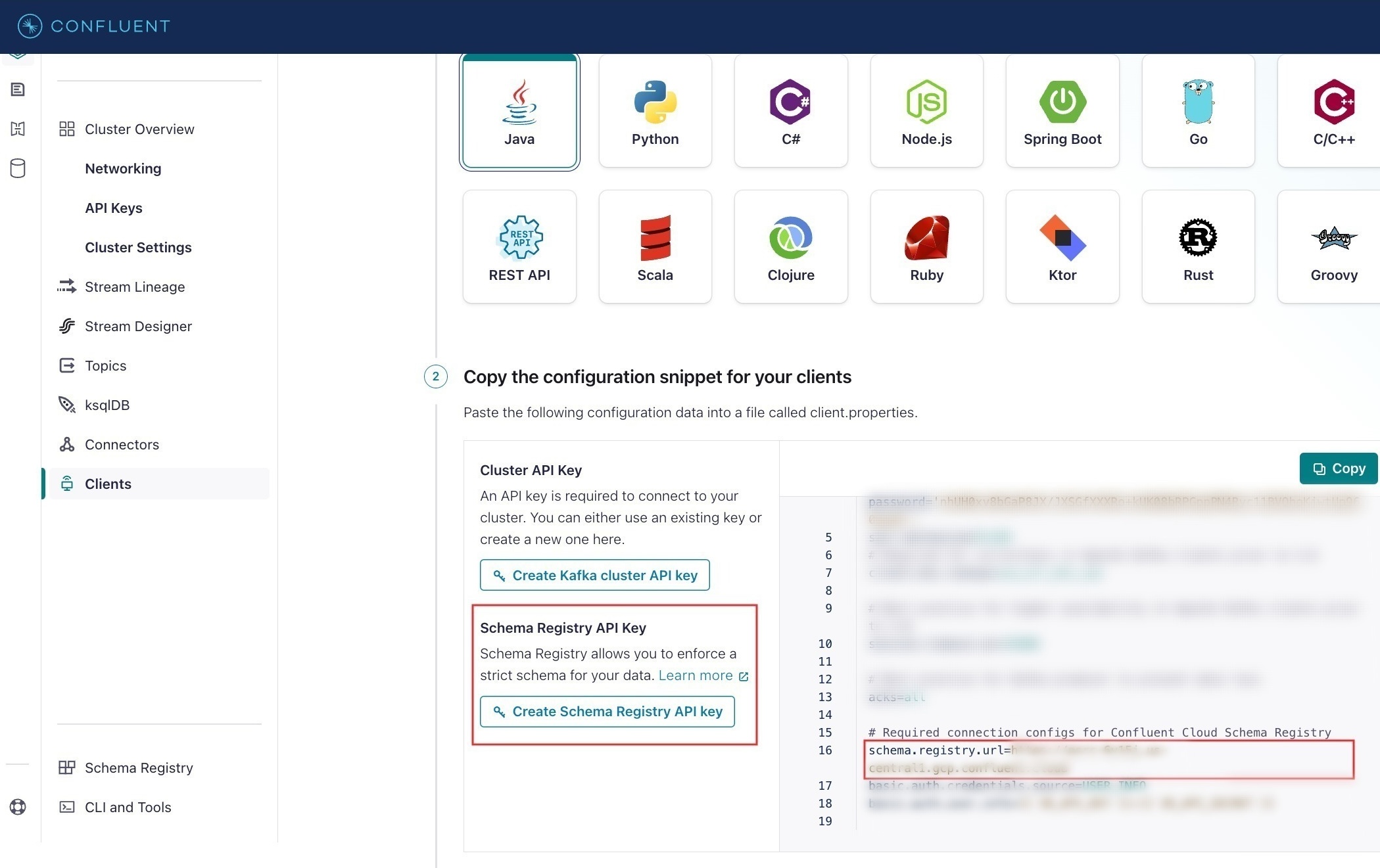
Get the Schema registry server
The Schema registry server, API key, and secret are only required if you are integrating with a schema registry (for AVRO protocol).
To get the Schema registry server and API keys:
- Sign in to the Confluent Cloud portal.
- Go to Clients > Add new client.
- In Copy the configuration snippet for your clients > schema.registry.url, copy the URL.
- Select Create Schema Registry API key to download the file. The downloaded file will have the Schema Registry API key and secret.
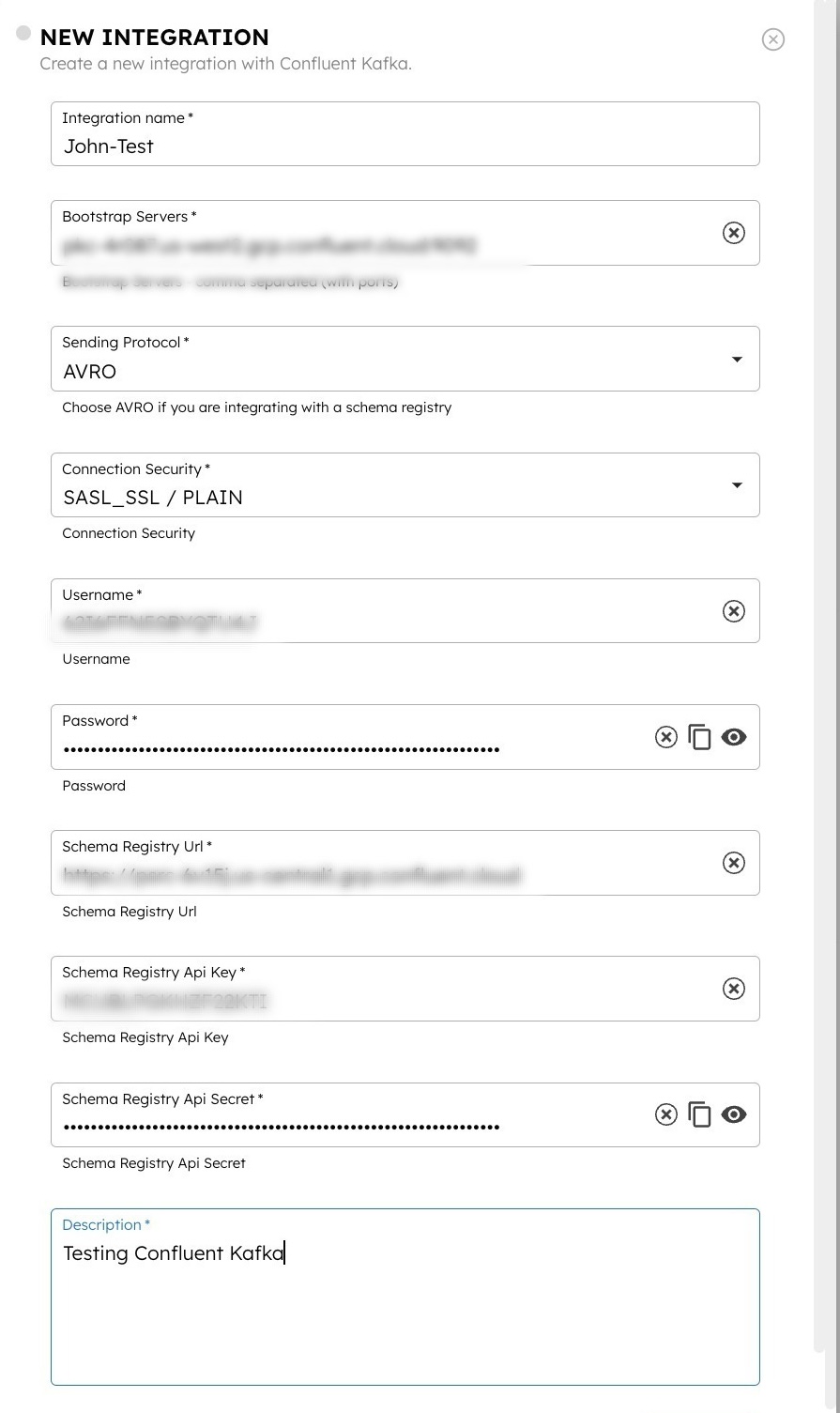
Step 2: Add an integration for Confluent Kafka
After obtaining the credentials, add a Confluent Kafka integration to your Conductor cluster.
To create a Confluent Kafka integration:
- Go to Integrations from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + New integration.
- In the Message Broker section, choose Confluent Kafka.
- Select + Add and enter the following parameters:
| Paremeters | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| Integration name | A name for the integration. | Required. |
| Bootstrap Server | The bootstrap server of the Confluent Kafka cluster. | Required. |
| Sending Protocol | The sending protocol for the integration. Supported values:
| Required. |
| Connection Security | The security mechanism for connecting to the Kafka cluster. Supported values:
| Required. |
| Choose Trust Store file | Upload the Java JKS trust store file with CAs. | Required if Connection Security is SASL_SSL / SCRAM-SHA-256 / JKS. |
| Trust Store Password | The password for the trust store file. | Required if Connection Security is SASL_SSL / SCRAM-SHA-256 / JKS. |
| Username | The username to authenticate with the Kafka cluster. Note: For AVRO configuration, use the previously-copied API key as the username. | Required. |
| Password | The password associated with the username. Note: For AVRO configuration, use the previously-copied API secret as the password. | Required. |
| Schema Registry URL | The Schema Registry URL copied from the Confluent Kafka console. | Required if Sending Protocol is AVRO. |
| Schema Registry Auth Type | The authentication mechanism for connecting to the schema registry. Supported values:
| Required if Sending Protocol is AVRO. |
| Schema Registry API Key | The schema registry API key obtained from the schema registry server. | Required if
|
| Schema Registry API Secret | The schema registry API secret obtained from the schema registry server. | Required if
|
| Value Subject Name Strategy | The strategy for constructing the subject name under which the AVRO schema will be registered in the schema registry. Supported values:
| Required if Sending Protocol is AVRO. |
| Consumer Group ID | The Consumer Group ID from Kafka. This unique identifier helps manage message processing, load balancing, and fault tolerance within consumer groups. | Required. |
| Description | A description of the integration. | Required. |
- (Optional) Toggle the Active button off if you don’t want to activate the integration instantly.
- Select Save.
Step 3: Set access limits to integration
Once the integration is configured, set access controls to manage which applications or groups can use the message broker.
To provide access to an application or group:
- Go to Access Control > Applications or Groups from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Create a new group/application or select an existing one.
- In the Permissions section, select + Add Permission.
- In the Integration tab, select the required message broker and toggle the necessary permissions.
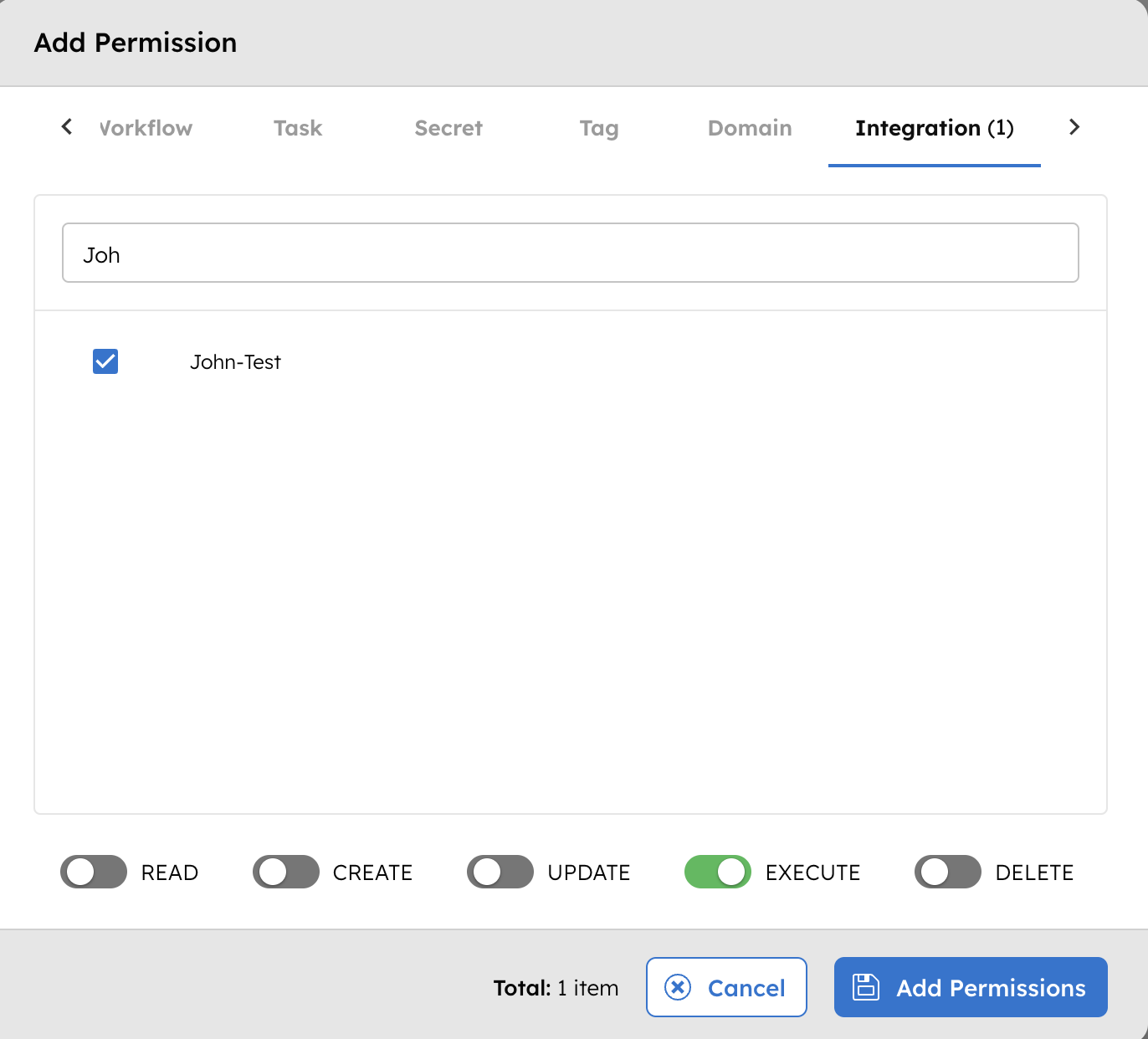
The group or application can now access the message broker according to the configured permissions.
Next steps
With the integration in place, you can now:
- Create Event Handlers.
- Configure Event tasks.
- Enable Change Data Capture (CDC) to send workflow state changes to message brokers.