Dynamic Fork
The Dynamic Fork task is used to run tasks in parallel, with the forking behavior (such as the number of forks) determined at runtime. This contrasts with the Fork/Join task, where the forking behavior is defined at the time of workflow creation.
The Dynamic Fork task must be followed by a Join task that waits for the forked tasks to finish before moving to the next task. This Join task collects the outputs from each forked task.
Unlike the Fork/Join task, a Dynamic Fork task can only run one task per fork. To run multiple tasks per fork, you can use a Sub Workflow task inside the fork.
There are two ways to run the Dynamic Fork task:
- Each fork runs a different task—Use
dynamicForkTasksParamanddynamicForkTasksInputParamName. - All forks run the same task—Use
forkTaskNameandforkTaskInputsfor any task type, orforkTaskWorkflowandforkTaskInputsfor Sub Workflow tasks.
Task parameters
Configure these parameters for the Dynamic Fork task. The input payload for the forked tasks should correspond with their expected input. For example, if the forked tasks are HTTP tasks, the input should include the method and URI.
For the Fork task:
- For different tasks
- For the same task (any task type)
- For the same task (sub-workflows)
The dynamic fork executes each task in the array specified by dynamicForkTasksParam with its corresponding input specified by dynamicForkTasksInputParamName. The number of forks created at runtime corresponds with the array size.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| dynamicForkTasksParam | The input parameter key whose value will be used to schedule each task on a different fork. For example, "dynamicTasks", which will then be specified as an input parameter in the Dynamic Fork task. | Required. |
| inputParameters. dynamicTasks | An array of tasks that will run in parallel. Each array element is a task configuration that corresponds to a separate fork branch. It can be passed as a variable. | Required. |
| dynamicForkTasksInputParamName | The input parameter key whose value will be used to pass the required input parameters for each forked task. For example, "dynamicTasksInput", which will then be specified as an input parameter in the Dynamic Fork task. | Required. |
| inputParameters. dynamicTasksInput | A map where the keys are the task reference names for each fork and the values are the input parameters that will be passed into its matching task. It can be passed as a variable. | Required. |
Configure these parameters to execute any task type except Sub Workflow tasks.
The dynamic fork executes the task specified by forkTaskName for each element of forkTaskInputs. The number of forks created at runtime depends on the number of forkTaskInputs sent. Configure these parameters to execute any task type except Sub Workflow tasks.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| inputParameters. forkTaskName | The name of the task that will be executed in each fork. It can be passed as a variable. | Required. |
| inputParameters. forkTaskInputs | An array of JSON inputs for each forked branch. The number of array elements determines the number of branches in the dynamic fork. It can be passed as a variable. | Required. |
Configure these parameters to execute a Sub Workflow task.
The dynamic fork executes the workflow specified by forkTaskWorkflow and forkTaskWorkflowVersion for each element of forkTaskInputs. The number of forks created at runtime depends on the number of forkTaskInputs sent. Configure these parameters to execute a Sub Workflow task.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| inputParameters. forkTaskWorkflow | The name of the workflow that will be executed in each fork. It can be passed as a variable. | Required. |
| inputParameters. forkTaskWorkflowVersion | The version of the workflow to be executed. If unspecified, the latest version will be used. | Required. |
| inputParameters. forkTaskInputs | An array of JSON inputs for each forked branch. The number of array elements determines the number of branches in the dynamic fork. It can be passed as a variable. | Required. |
The Join task will run after the forked tasks and implicitly waits for all forked tasks to complete.
For the Join task:
For a Dynamic Fork, no specific configuration is required, but the Join task must still be included in the workflow to complete the fork-join operation.
Required Join task configuration
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"type": "JOIN",
"inputParameters": {},
"joinOn": []
}
The following are generic configuration parameters that can be applied to the task and are not specific to the Dynamic Fork task.
Other generic parameters
Here are other parameters for configuring the task behavior.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| optional | Whether the task is optional. If set to true, any task failure is ignored, and the workflow continues with the task status updated to COMPLETED_WITH_ERRORS. However, the task must reach a terminal state. If the task remains incomplete, the workflow waits until it reaches a terminal state before proceeding. | Optional. |
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for a Dynamic Fork task.
- Run different tasks
- Run the same task (any task type)
- Run the same task (sub-workflows)
// JSON schema for the Dynamic Fork task
{
"name": "fork_join_dynamic",
"taskReferenceName": "fork_join_dynamic_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"dynamicTasks": [ // name of the tasks to execute
{
"name": "http",
"taskReferenceName": "http_ref",
"type": "HTTP",
"inputParameters": {}
},
{ // another task configuration }
],
"dynamicTasksInput": { // inputs for the tasks
"taskReferenceName" : {
"key": "value",
"key": "value"
},
"anotherTaskReferenceName" : {
"key": "value",
"key": "value"
}
}
},
"type": "FORK_JOIN_DYNAMIC",
"dynamicForkTasksParam": "dynamicTasks", // input parameter key that will hold the task names to execute
"dynamicForkTasksInputParamName": "dynamicTasksInput" // input parameter key that will hold the input parameters for each task
}
// JSON schema for the Join task
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": []
}
// JSON schema for the Dynamic Fork task
{
"name": "fork_join_dynamic",
"taskReferenceName": "fork_join_dynamic_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"forkTaskName": "",
"forkTaskInputs": []
},
"type": "FORK_JOIN_DYNAMIC"
}
// JSON schema for the Join task
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": []
}
// JSON schema for the Dynamic Fork task
{
"name": "fork_join_dynamic",
"taskReferenceName": "fork_join_dynamic_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"forkTaskWorkflow": "",
"forkTaskWorkflowVersion": "",
"forkTaskInputs": []
},
"type": "FORK_JOIN_DYNAMIC"
}
// JSON schema for the Join task
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": []
}
forkTaskName and forkTaskInputs will take precedence even if dynamicForkTasksParam and dynamicForkTasksInputParamName are present in the task definition.
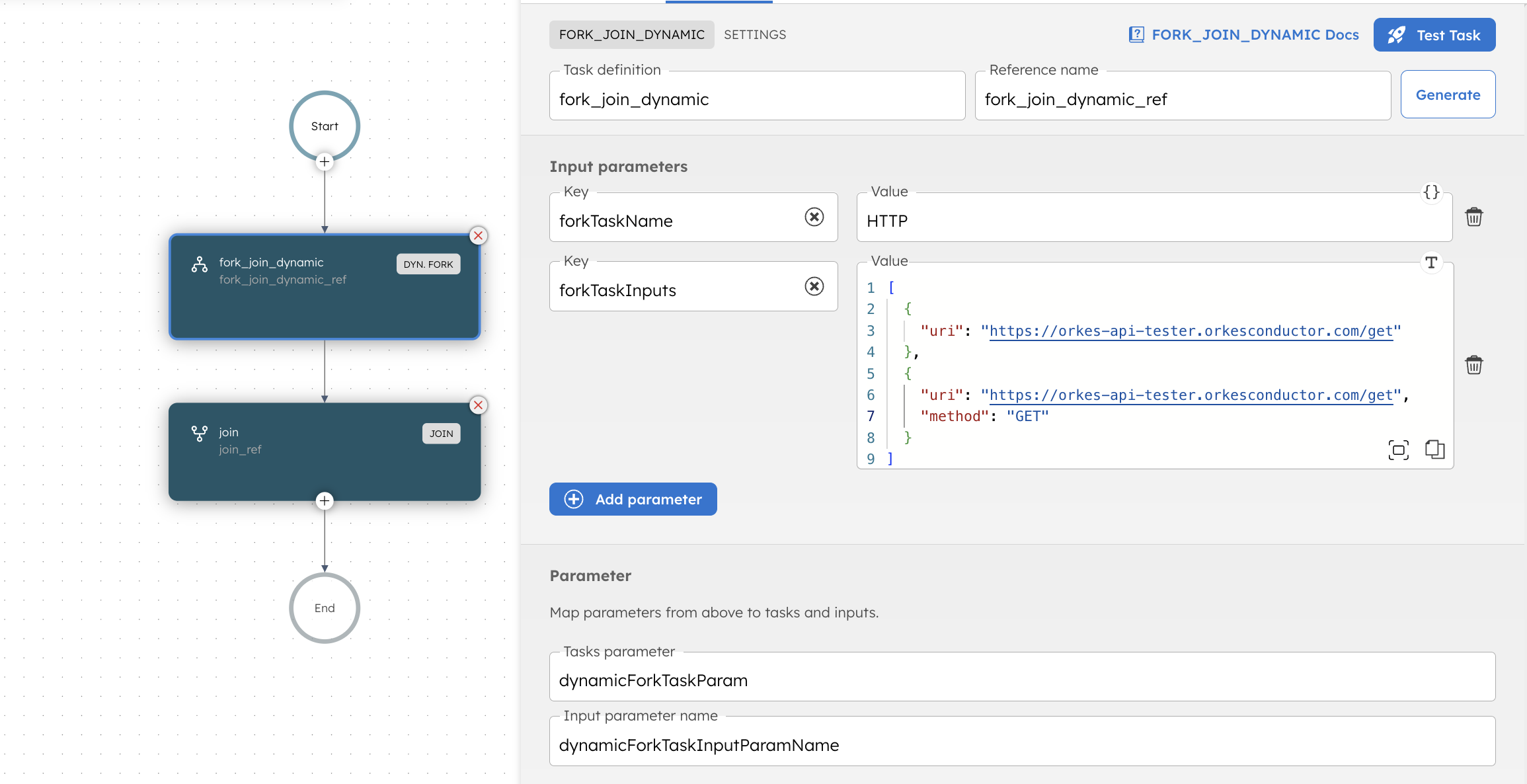
Adding a Dynamic Fork task in UI
To add a Dynamic Fork task:
- For different tasks
- For the same task
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add a **Dynamic Fork **task.
- In Input parameters, configure the
dynamicTaskparameter as an array of task configurations. - In Input parameters, configure the
dynamicTasksInputparameter as a map of input parameters for each task. - Include the Join task to complete the fork/join operation.
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add a Dynamic Fork task.
- In Input parameters, remove all current parameters and add the following parameters and its values:
forkTaskWorkflow,forkTaskWorkflowVersion, andforkTaskInputsfor Sub Workflow tasks.forkTaskNameandforkTaskInputsfor all other task types.
- Include the Join task to complete the fork/join operation.
Examples
Here are some examples for using the Dynamic Fork task.
Running different tasks
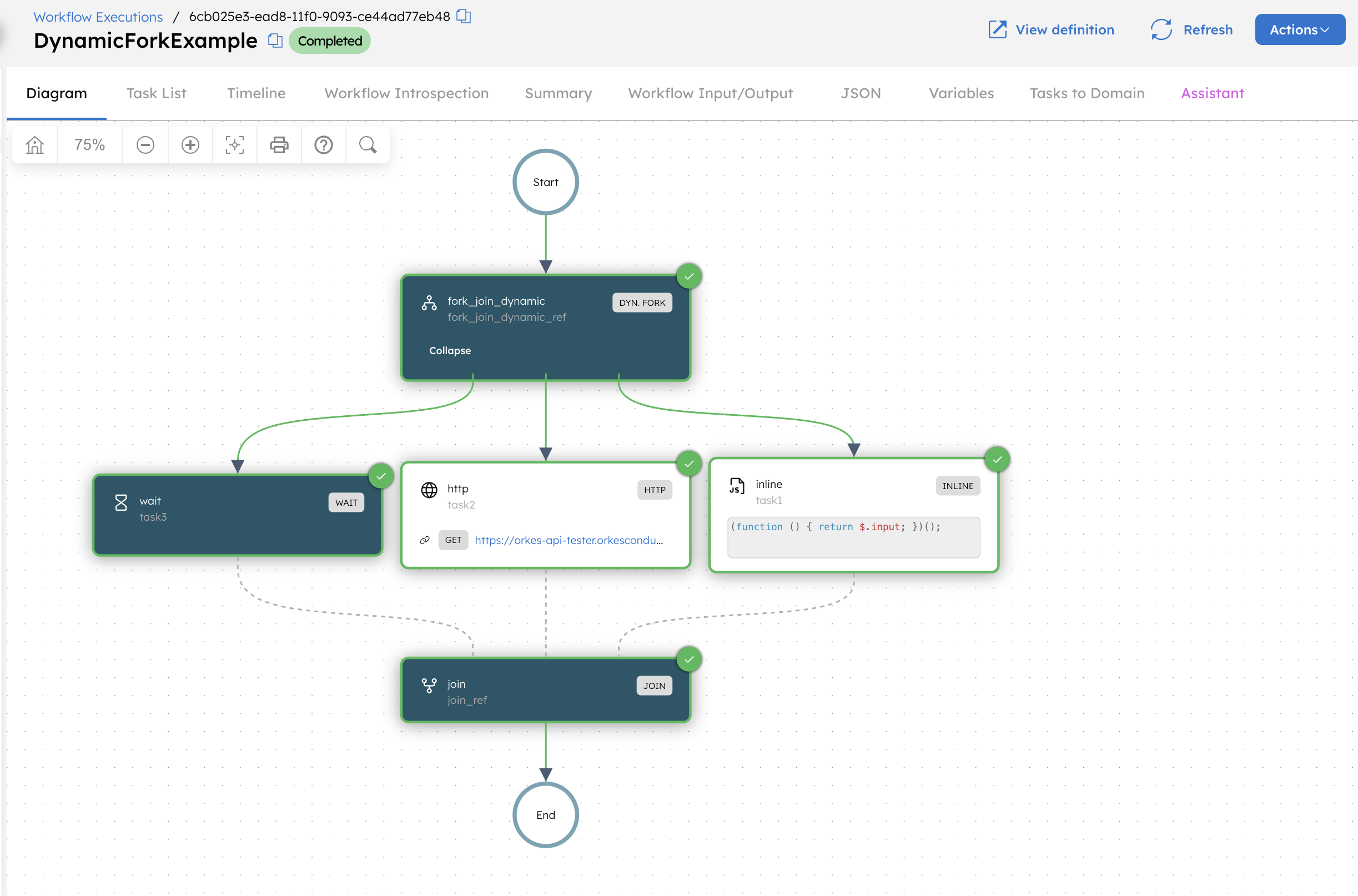
A Dynamic Fork task can be used to run multiple tasks in parallel when the set of tasks is determined at runtime. This example builds a workflow that dynamically forks into three parallel branches, each running a different task type, and then waits for all branches to complete before continuing.
To run a different task per fork in a dynamic fork, you must use dynamicForkTasksParam and dynamicForkTasksInputParamName. Here is an example workflow definition of a Dynamic Fork task running different tasks.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "DynamicForkExample",
"description": "This workflow runs different tasks in a dynamic fork.",
"version": 1,
"schemaVersion": 2,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "fork_join_dynamic",
"taskReferenceName": "fork_join_dynamic_ref",
"type": "FORK_JOIN_DYNAMIC",
"inputParameters": {
"dynamicTasks": [
{
"name": "inline",
"taskReferenceName": "task1",
"type": "INLINE",
"inputParameters": {
"expression": "(function () { return $.input; })();",
"evaluatorType": "graaljs"
}
},
{
"name": "http",
"taskReferenceName": "task2",
"type": "HTTP",
"inputParameters": {
"method": "GET",
"connectionTimeOut": 3000,
"readTimeOut": 3000,
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
}
},
{
"name": "wait",
"taskReferenceName": "task3",
"type": "WAIT",
"inputParameters": {
"duration": "5 seconds"
}
}
],
"dynamicTasksInput": {
"task1": {
"input": "one"
},
"task2": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api"
},
"task3": {
"duration": "5 seconds"
}
}
},
"dynamicForkTasksParam": "dynamicTasks",
"dynamicForkTasksInputParamName": "dynamicTasksInput"
},
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"type": "JOIN",
"inputParameters": {},
"joinOn": []
}
]
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
To run the workflow:
- Go to the Run tab.
- Select Execute.
This takes you to the workflow execution page.
- The Dynamic Fork task creates three parallel branches at runtime.
- Each branch executes a different task:
- An Inline task that echoes the input value.
- An HTTP task that calls the API tester endpoint.
- A Wait task that pauses execution for five seconds.
- The Join task waits for all forked tasks to complete before finishing the workflow.
You can verify the execution by inspecting the completed tasks and their outputs on the workflow execution page.
Running the same task: HTTP task
In this example, the dynamic fork runs HTTP tasks in parallel. The provided input in forkTaskInputs contains the typical payload expected in an HTTP task.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "dynamic_workflow_array_http",
"description": "Runs HTTP tasks in parallel using a Dynamic Fork task.",
"version": 1,
"schemaVersion": 2,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "dynamic_fork_http",
"taskReferenceName": "dynamic_fork_http_ref",
"type": "FORK_JOIN_DYNAMIC",
"inputParameters": {
"forkTaskName": "HTTP",
"forkTaskInputs": [
{
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
},
{
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
}
]
}
},
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"type": "JOIN",
"inputParameters": {},
"joinOn": []
}
]
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
To run the workflow:
- Go to the Run tab.
- Select Execute.
This takes you to the workflow execution page.
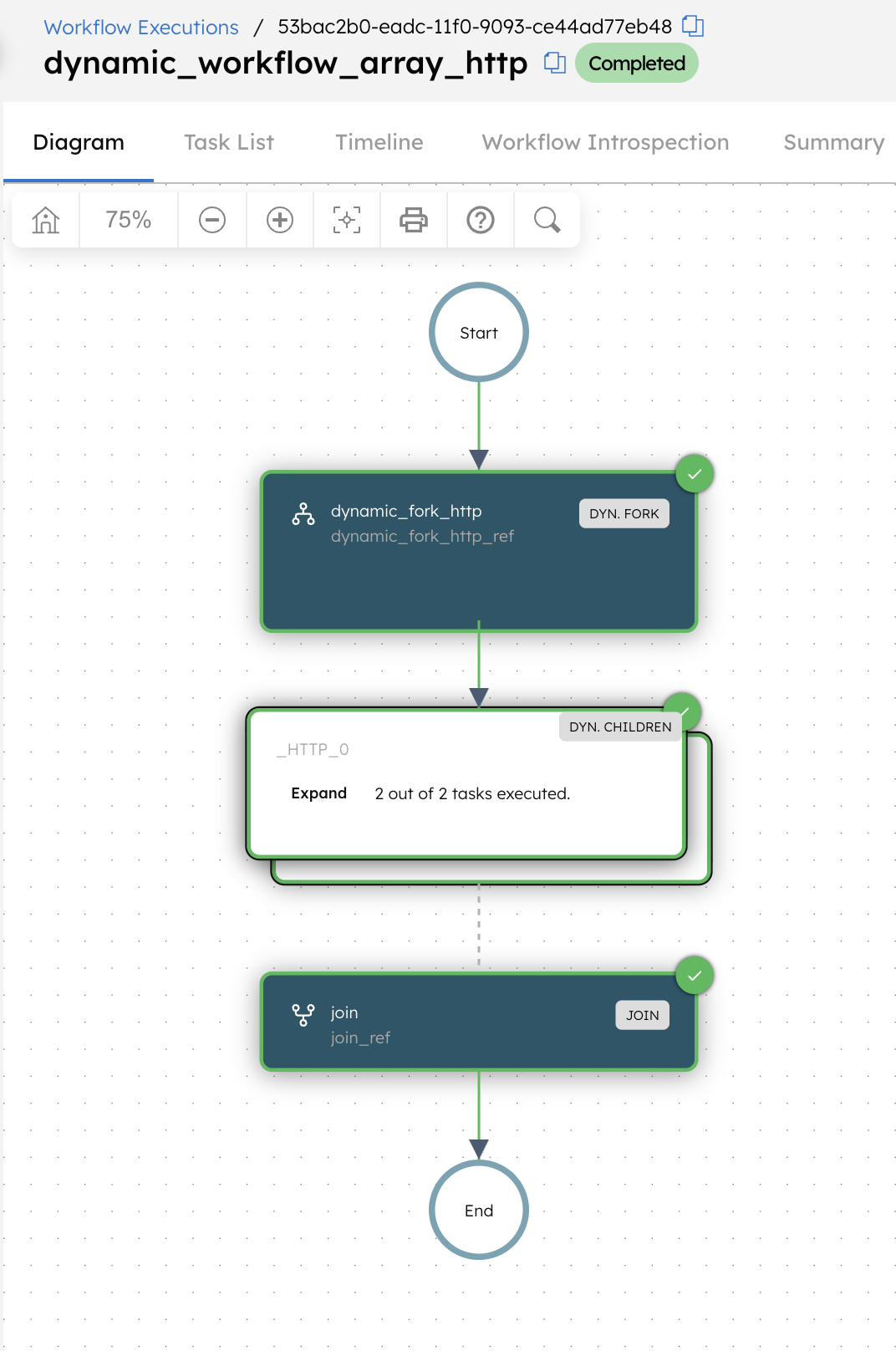
- The Dynamic Fork task creates one fork per element in
forkTaskInputs. - Each fork executes the HTTP system task using the corresponding input payload.
- The Join task completes after all forked HTTP tasks complete.
To verify, open the forked HTTP task instances under the Dynamic Fork task and confirm that each task completed successfully and returned a response.
Running the same task: Worker task
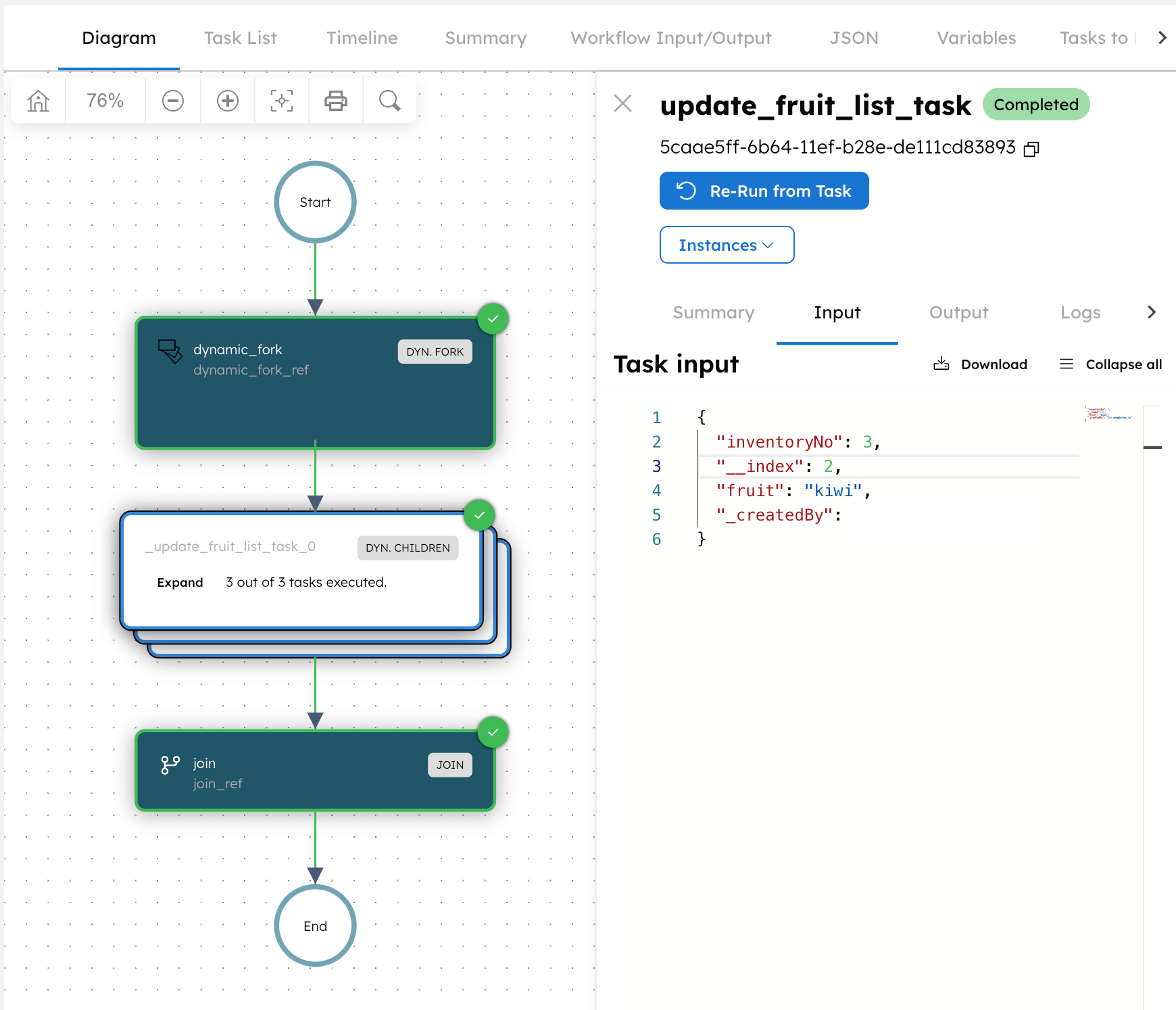
In this example workflow, the Dynamic Fork task runs a worker task named update_fruit_list_task in parallel. The task input is taken from the workflow input parameter fruits, which is an array. Each array element results in one forked task execution.
{
"name": "dynamic_workflow_array_simple",
"description": "Update fruit list",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "fork_join_dynamic",
"taskReferenceName": "fork_join_dynamic_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"forkTaskName": "update_fruit_list_task",
"forkTaskInputs": "${workflow.input.fruits}"
},
"type": "FORK_JOIN_DYNAMIC"
},
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": []
}
],
"inputParameters": [
"fruits"
],
"outputParameters": {},
"schemaVersion": 2
}
Here, forkTaskInputs is an array input that determines how many forks are created at runtime. For example, if fruits contains three objects, the Dynamic Fork task creates three parallel executions of the task.
// workflow input payload
{
"fruits": [
{
"inventoryNo": 5,
"fruit": "apple"
},
{
"inventoryNo": 20,
"fruit": "orange"
},
{
"inventoryNo": 3,
"fruit": "kiwi"
}
]
}
During execution, Conductor inserts an additional parameter called __index into each JSON object, which represents its array index.
// one input instance for the Dynamic Fork task at run-time
{
"fruit": "kiwi",
"inventoryNo": 3,
"__index": 2 // index of the element in the source array
}
If forkTaskInputs contains simple values (for example, ["apple", "orange", "kiwi"]), Conductor will set each array element in a parameter called input, and still adds __index:
// one input instance for the Dynamic Fork task at run-time
{
"input": "apple", // input value
"__index": 0 // index of the element in the source array
}