Do While
The Do While task executes a sequence of tasks repeatedly as long as a condition evaluates to true. The looped tasks are executed at least once, and the condition is evaluated after each iteration, similar to a do..while statement in programming.
Task parameters
Configure these parameters for the Do While task.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| evaluatorType | The type of evaluator used. Supported types:
| Required. |
| loopCondition | The condition that is evaluated by the Do While task after every iteration. The expression format depends on the evaluator type:
| Required, unless iterating over a list of items. |
| loopOver | The list of tasks to be executed as long as the condition is true. | Required. |
| inputParameters. items | An array of items, which will be iterated over in the loop. The number of iterations is equal to the list size. You can use this to iterate without a condition. Refer to Examples for more information on how to use the items parameter. | Optional. |
| inputParameters. keepLastN | The number of iterations of execution data to retain. If enabled, the default value is 2. Use keepLastN if the number of iterations is expected to be large and not all execution data needs to be retained. Refer to the Execution data for more information. | Optional. |
The following are generic configuration parameters that can be applied to the task and are not specific to the Do While task.
Other generic parameters
Here are other parameters for configuring the task behavior.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| optional | Whether the task is optional. If set to true, any task failure is ignored, and the workflow continues with the task status updated to COMPLETED_WITH_ERRORS. However, the task must reach a terminal state. If the task remains incomplete, the workflow waits until it reaches a terminal state before proceeding. | Optional. |
Script expression
When using the graaljs evaluator, the JavaScript function should be formatted using the following syntax:
(function () {
// statements
})();
Or
(() => {
// statements
})();
The function should return a boolean value. To dynamically reference other input parameters in the script, it is recommended to use bracket notation (for example, $.do_while_ref['iteration']).
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for a Do While task.
{
"name": "do_while",
"taskReferenceName": "do_while_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "DO_WHILE",
"loopCondition": "", // Condition
"evaluatorType": "value-param",
"loopOver": [ // List of tasks to be executed in the loop
{// task configuration},
{// task configuration}
]
}
Task output
The Do While task will return the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| iteration | The number of iterations. If the Do While task is in progress, iteration will show the current iteration number. When completed, iteration will show the final number of iterations. |
| item | (If items is used as an input parameter) Contains the value of the last item specified in the items array. |
Additionally, an object will be created for each iteration, keyed by its iteration number (e.g., 1, 2, 3), and will contain the task outputs for all loopOver tasks. If keepLastN is specified, only outputs for the last n iterations will be stored.
Example output
{
"1": {
"taskA_ref": {
"response": {
"headers": {},
"body": {},
"statusCode": 200
}
},
"taskB_ref": {
// taskBOutput
}
},
"2": {
"taskA_ref": {
"response": {
"headers": {},
"body": {},
"statusCode": 200
}
},
"taskB_ref": {
// taskBOutput
}
},
"iteration": 2
}
Accessing the Do While task output
Each time a task in the do while loop is completed, the output is saved and indexed by the iteration value. This makes it possible for the condition to check the output of a specific task iteration using $.TaskName[’iteration’]['loopTask'], replacing TaskName with the actual Do While task reference name and loopTask with the loop task reference name.
Execution
When a Do While loop is executed, each task in the loop will have its taskReferenceName concatenated with __i, with i as the iteration number starting at 1. If one of the loop tasks fails, the Do While task status will be set as FAILED, and upon retry, the iteration number will restart from 1.
If an exception occurs during evaluation of the loopCondition, the task is set to CANCELED.
Execution data
During execution, each iteration execution can be accessed from the dropdown box in the Conductor UI for the Do While task and all its loop tasks.
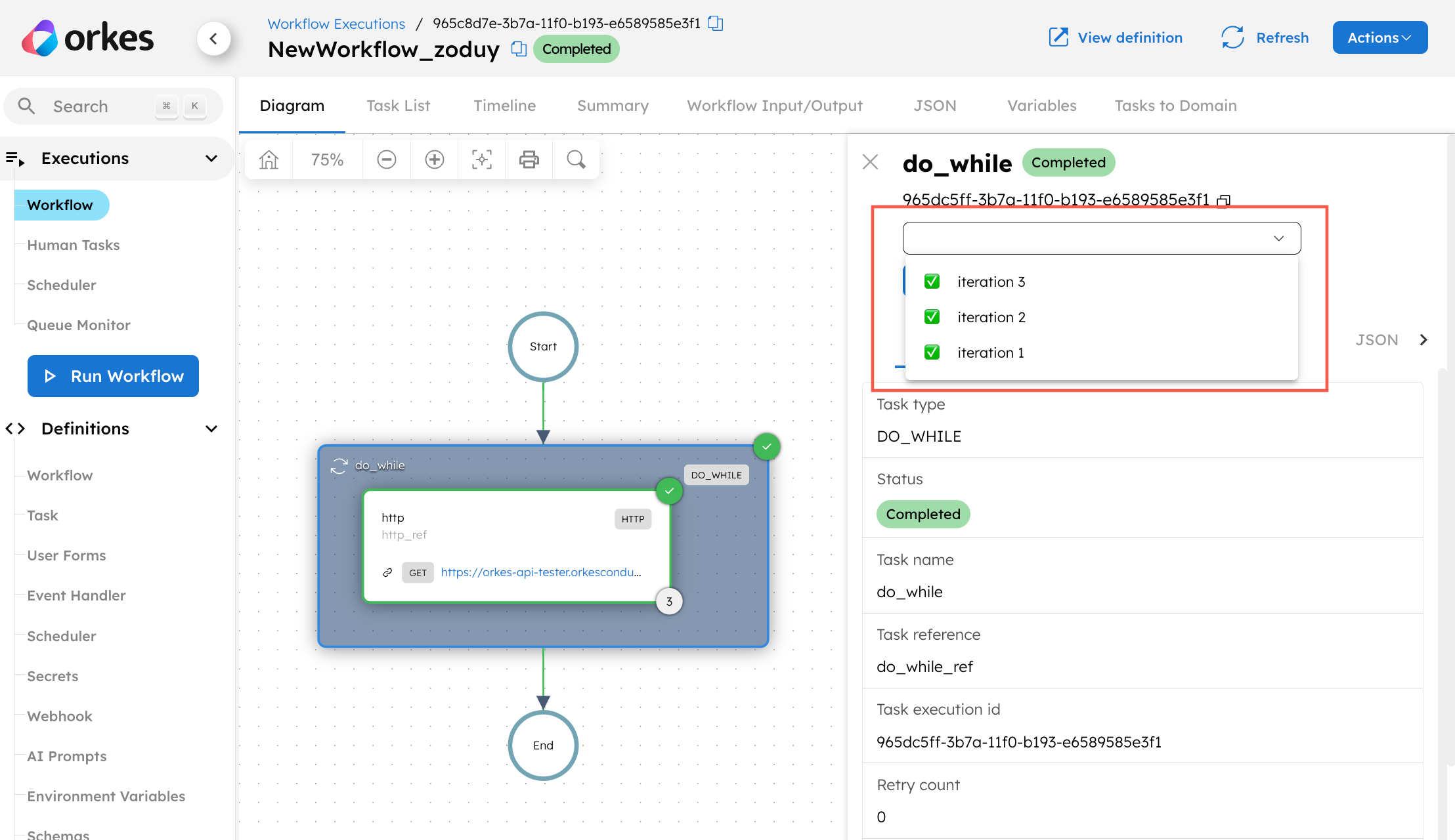
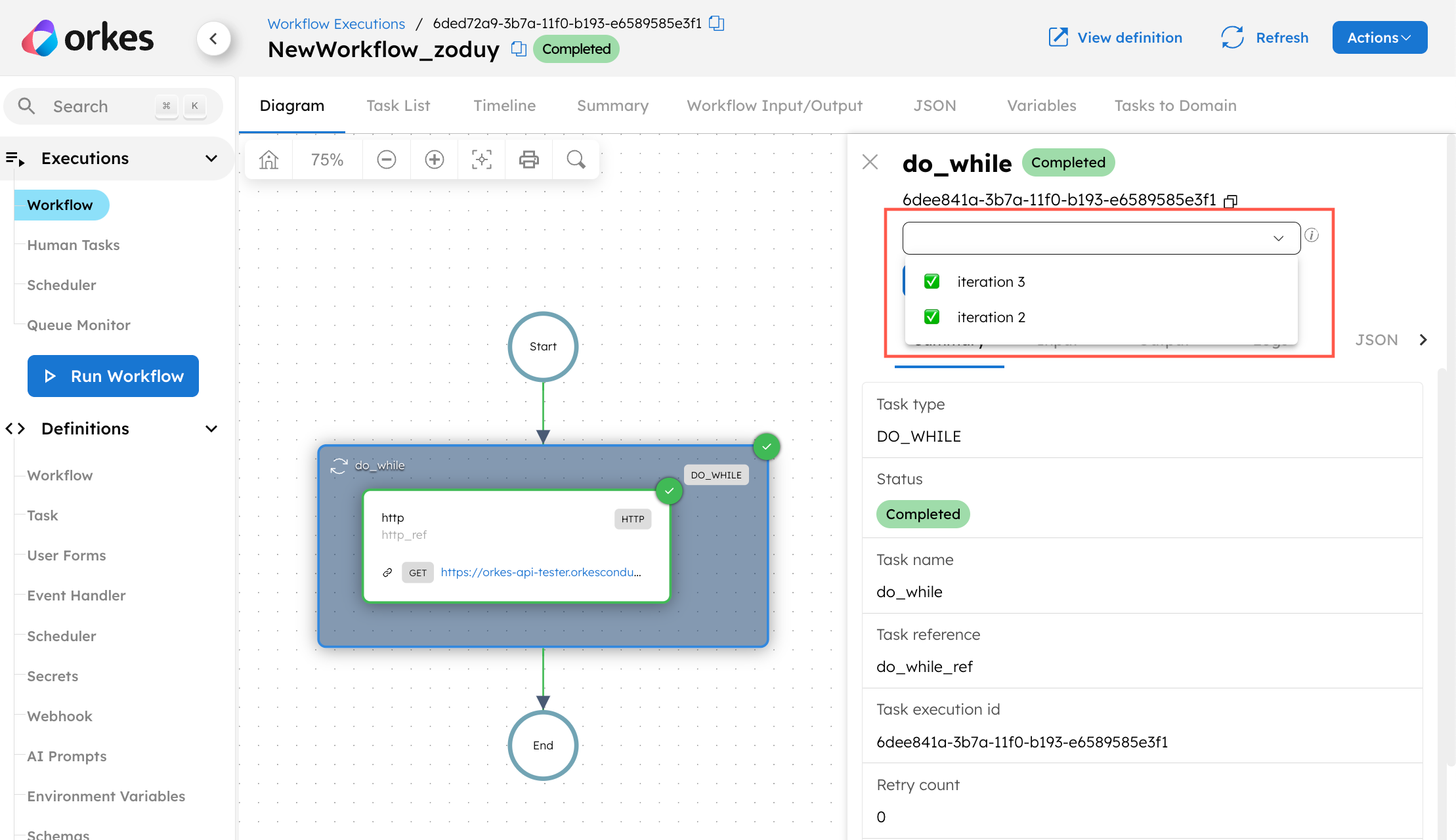
If keepLastN is used, the latest n iterations will be retained. In the example below, where keepLastN=2, the latest two iterations are accessible from the dropdown box in the UI.
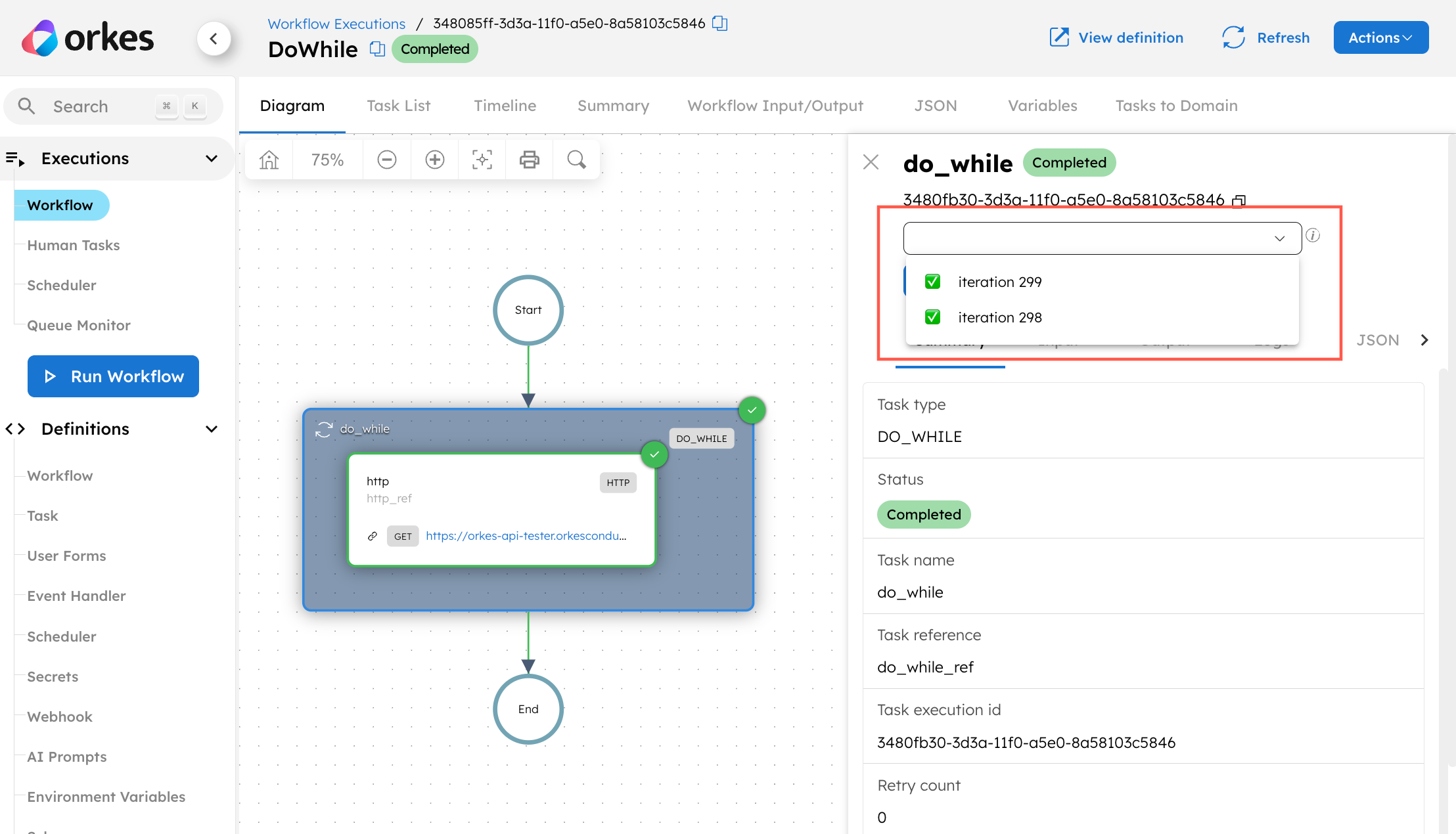
From v4.1.52 onwards, Do While executions that exceed 300 tasks across their iterations will be summarized, and the Conductor UI will only display the latest two iterations. If required, use keepLastN to display more iterations.
Here are several considerations to keep in mind when using the Do While task:
- Branching: Within a Do While task, branching using Switch, Fork/Join, and Dynamic Fork tasks is supported. However, the Do While task may not execute as expected if the branching crosses outside its scope, since the loop tasks will be executed within the scope.
- Nested loops: Nested Do While tasks are not supported. To achieve a similar functionality as a nested loop, you can use a Sub Workflow task inside the Do While task.
- Isolation group execution: Isolation group execution is not supported. However, the domain is supported for loop tasks inside the Do While task.
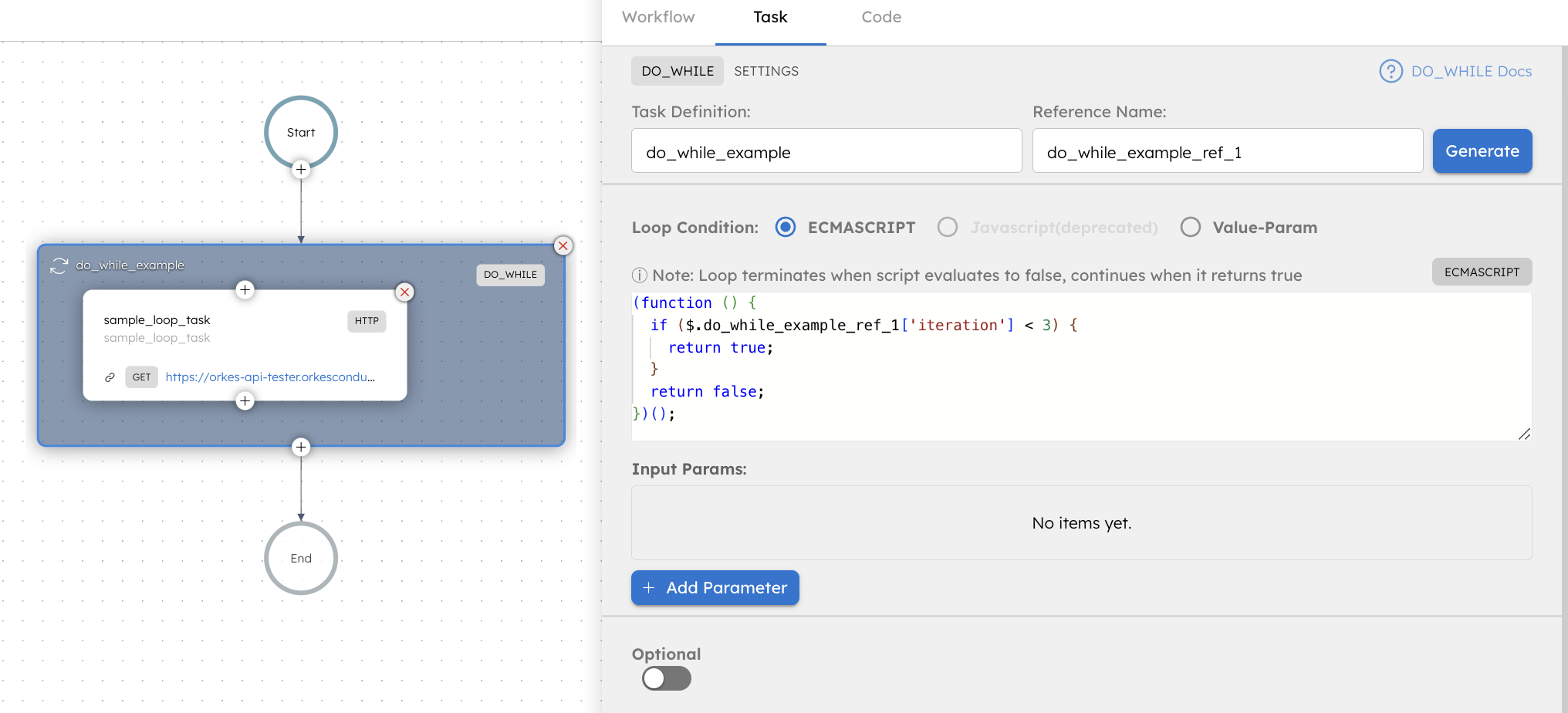
Adding a Do While task in UI
To add a Do While task:
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add a Do While task.
- In Script params, add the parameter that will be evaluated in the expression.
- In Loop condition, select the evaluator type and enter the loop condition in the Code field.
- Value-Param— Enter the parameter key you have defined in Script params.
- ECMASCRIPT—Enter a JavaScript script. Refer to Script expression for information.
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon to add tasks to the Do While loop.
- (Optional) If the number of iterations is expected to be large, turn off No Limits to set the number of iterations for which execution data to retain. By default, there is no limit on the execution data kept if the task size is below 300.
- (Optional) Use the Sample scripts to insert example JavaScript expressions for ECMASCRIPT evaluation.
Examples
Here are some examples for using the Do While task.
Using value-param evaluator
A Do While task can be used to repeatedly execute a set of tasks as long as a condition evaluates to true. This example builds a workflow that executes an HTTP task followed by a Wait task while a boolean input remains true, using the value-param evaluator type.
When using the value-param evaluator, the input key (such as state in the example below) must be a boolean value.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "Do_While_Value_Param_Demo",
"description": "Executes HTTP and Wait tasks repeatedly while a boolean input is true.",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "do_while",
"taskReferenceName": "do_while_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"state": "${workflow.input.active}"
},
"type": "DO_WHILE",
"loopCondition": "state",
"loopOver": [
{
"name": "http",
"taskReferenceName": "http_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
},
"type": "HTTP"
},
{
"name": "wait",
"taskReferenceName": "wait_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"duration": "5 seconds"
},
"type": "WAIT"
}
],
"evaluatorType": "value-param"
}
],
"inputParameters": [
"active"
],
"schemaVersion": 2
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
To run the workflow:
- Go to the Run tab, and enter the Input params. For example:
{
"active": true
}
- Select Execute.
This takes you to the workflow execution page. As long as the input parameter active remains true, the workflow continues to execute the HTTP task followed by the Wait task (5 seconds) and repeats the loop.
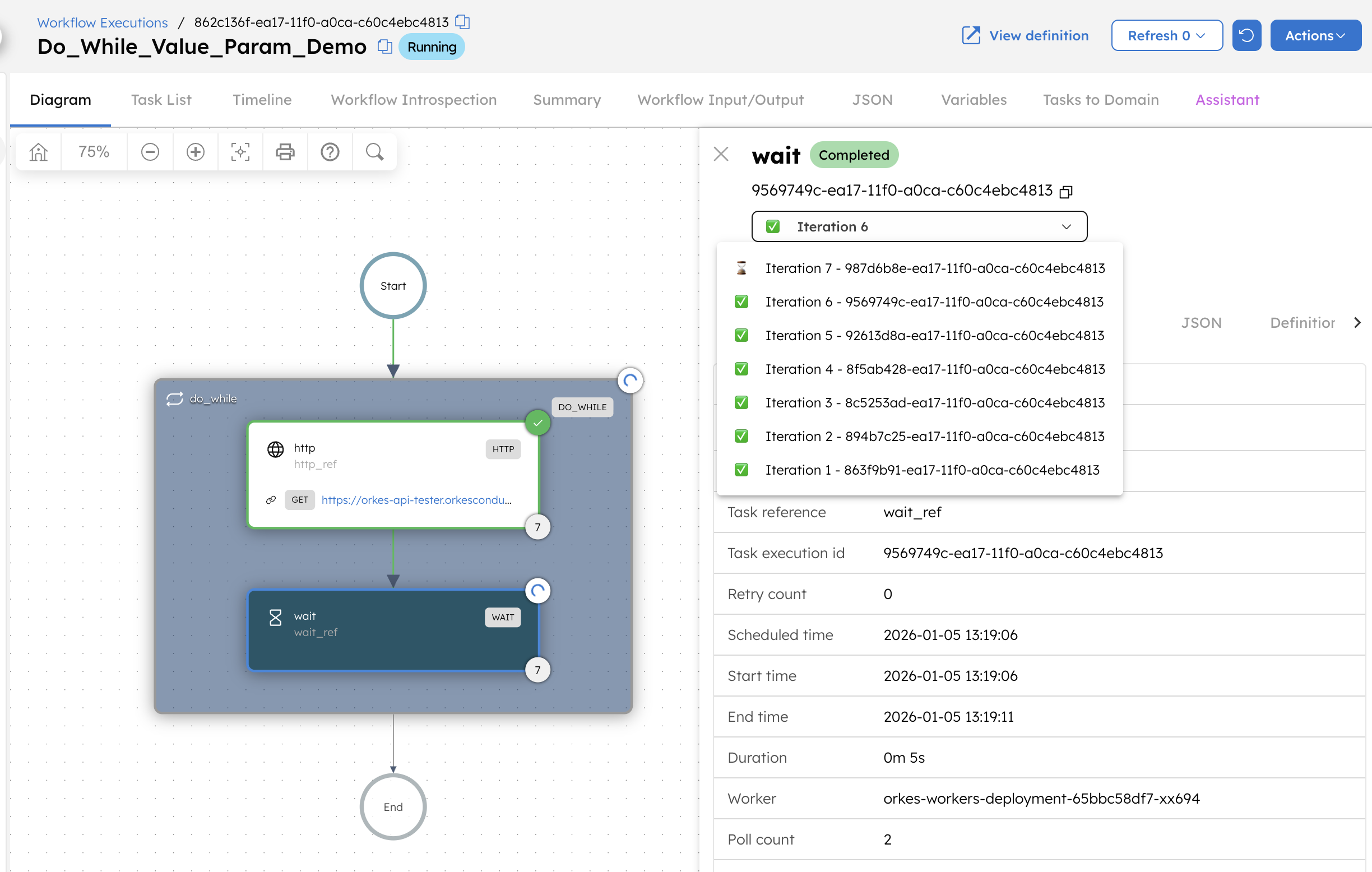
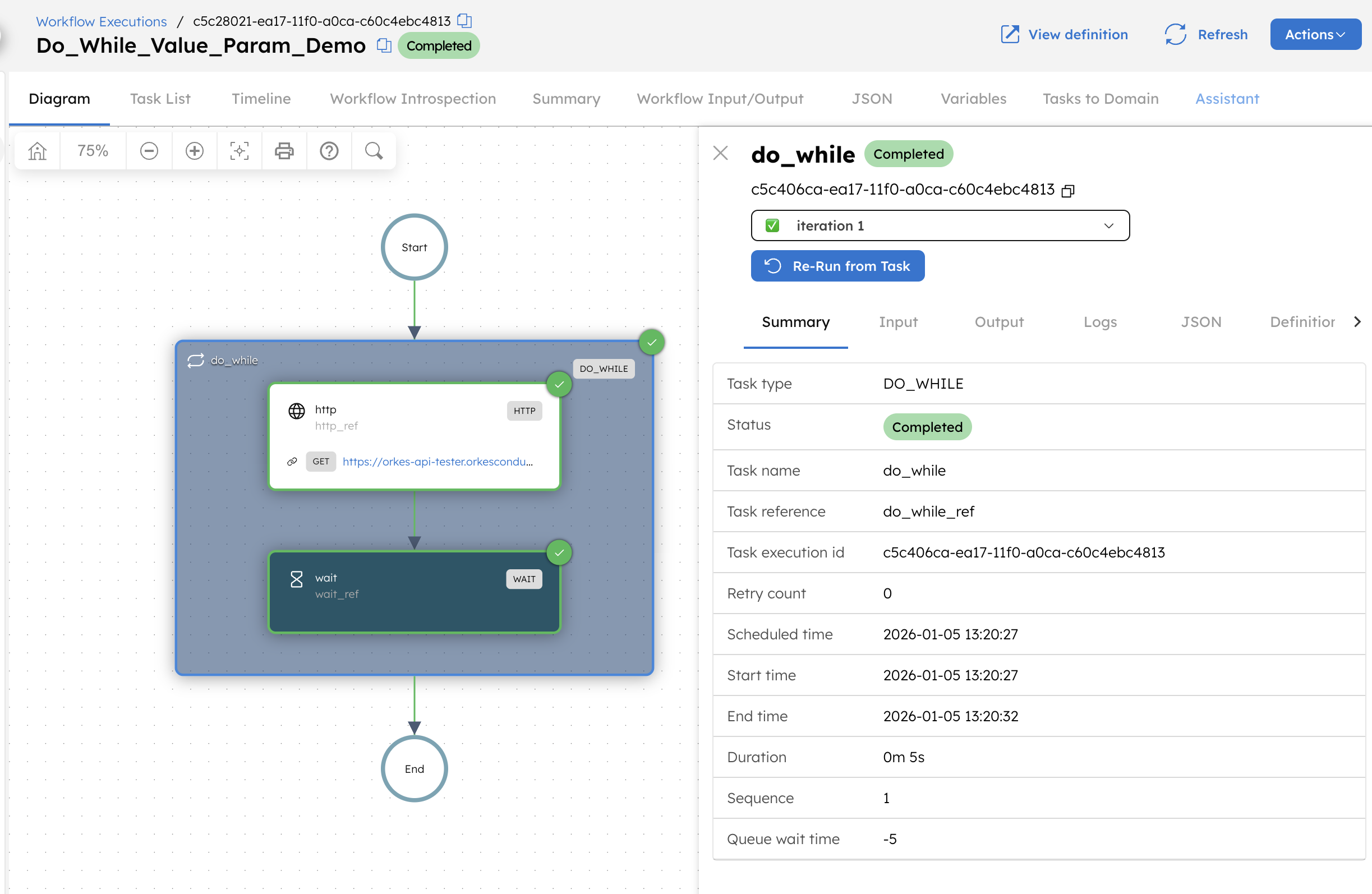
Now, rerun the workflow with the following input parameter:
{
"active": false
}
Since the workflow input active is set to false, the loop stops after the first iteration and the workflow completes.
Using graaljs evaluator
A Do While task can evaluate a JavaScript expression as the loop condition using the graaljs evaluator type. This example builds a workflow that runs a set of tasks a fixed number of times by comparing the Do While task’s iteration value with a workflow input.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "Do_While_Graaljs_Demo",
"description": "Executes tasks repeatedly until the iteration count reaches the configured limit.",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "do_while",
"taskReferenceName": "do_while_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"number": "${workflow.input.qty}"
},
"type": "DO_WHILE",
"loopCondition": "(function () { if ($.do_while_ref['iteration'] < $.number) { return true; } return false; })();",
"loopOver": [
{
"name": "first_task",
"taskReferenceName": "first_task_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
},
"type": "HTTP"
},
{
"name": "wait",
"taskReferenceName": "wait_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"duration": "5 seconds"
},
"type": "WAIT"
}
],
"evaluatorType": "graaljs"
}
],
"inputParameters": [
"qty"
],
"schemaVersion": 2
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
In this workflow, the workflow input qty sets the maximum number of loop iterations. After each iteration, the loop condition compares the current iteration count with the quantity to determine whether the loop should continue.
To run the workflow:
- Go to the Run tab, and enter the Input params. For example:
{
"qty": 3
}
- Select Execute.
This takes you to the workflow execution page. Since qty is set to 3, the Do While loop executes three iterations and then completes. On the Do While task output, verify that iteration is 3, and that the task outputs for each iteration are stored under 1, 2, and 3.
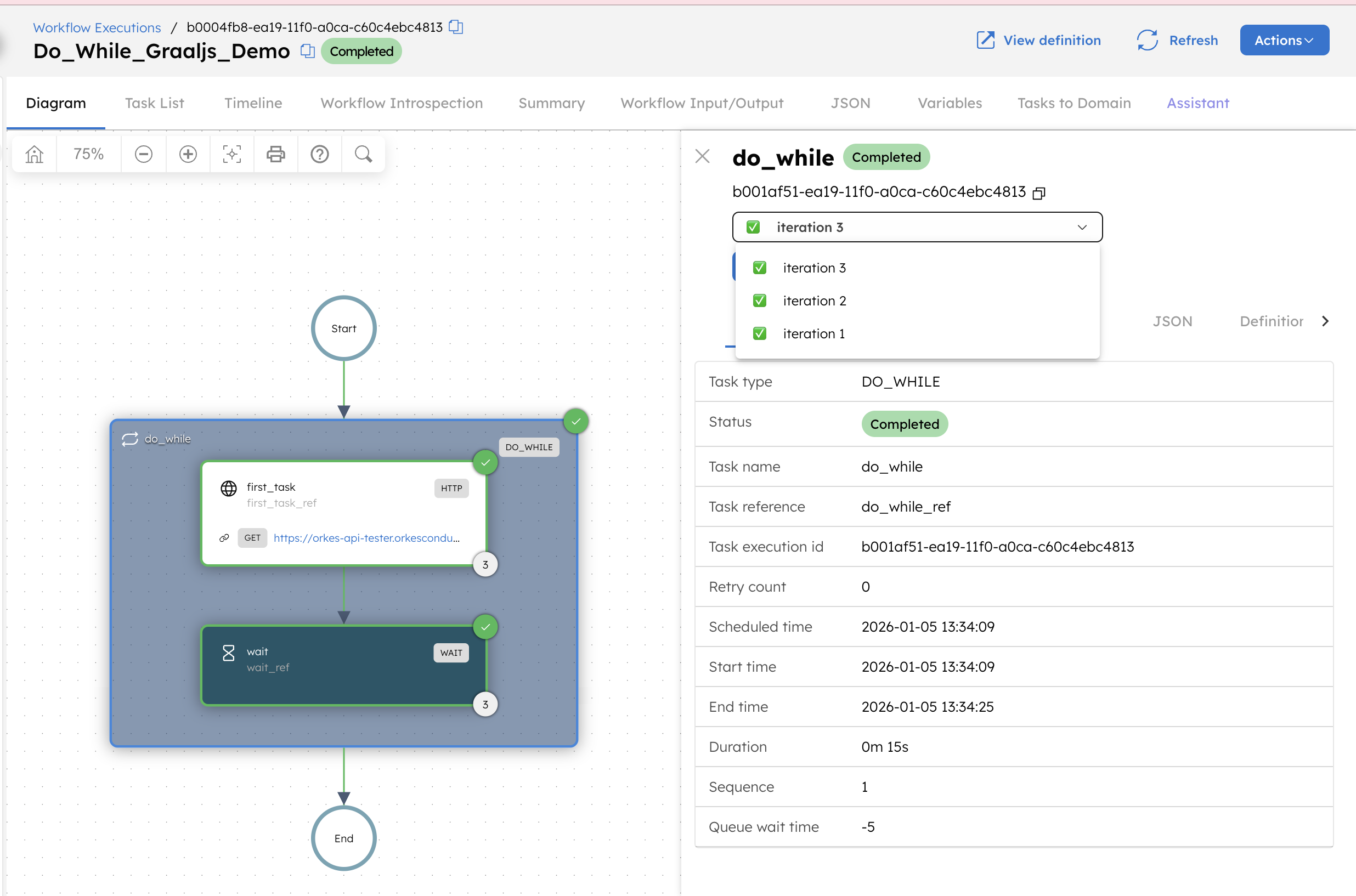
The Do While task output is returned as follows:
// truncated output
{
"1": {
"first_task_ref": {
"response": {
"headers": {
.
.
.
"wait_ref": {}
},
"2": {
"first_task_ref": {
"response": {
"headers": {
.
.
.
"wait_ref": {}
},
"3": {
"first_task_ref": {
"response": {
"headers": {
.
.
.
"wait_ref": {}
},
"iteration": 3
}
Iterate over a list of items
A Do While task can iterate over a list of items when you provide items in inputParameters. When items is used, the loop runs once for each item, and you do not need a loop condition. The current item is available in each iteration as ${do_while_ref.output.item}.
The number of iterations will be equal to the list size. If “items”=[“a”,“b”,“c”], the loop tasks will be executed three times; if “items”=[], the Do While task will be marked as completed without executing the loop tasks.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "Do_While_Items_Demo",
"description": "Iterates over a list of items and passes each item into the loop task.",
"version": 1,
"schemaVersion": 2,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "do_while",
"taskReferenceName": "do_while_ref",
"type": "DO_WHILE",
"inputParameters": {
"items": ["a", "b", "c"]
},
"evaluatorType": "value-param",
"loopCondition": "",
"loopOver": [
{
"name": "http",
"taskReferenceName": "http_ref",
"type": "HTTP",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true,
"body": {
"someInput": "${do_while_ref.output.item}"
}
}
}
]
}
]
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
- Select Execute.
In this workflow, the Do While task executes once for each value in the items and passes the current item to the loop task using ${do_while_ref.output.item}.
Here, it runs three iterations (one per item in items). When the above Do While task has been executed successfully, the input to the first iteration of the HTTP loop task will look like this:
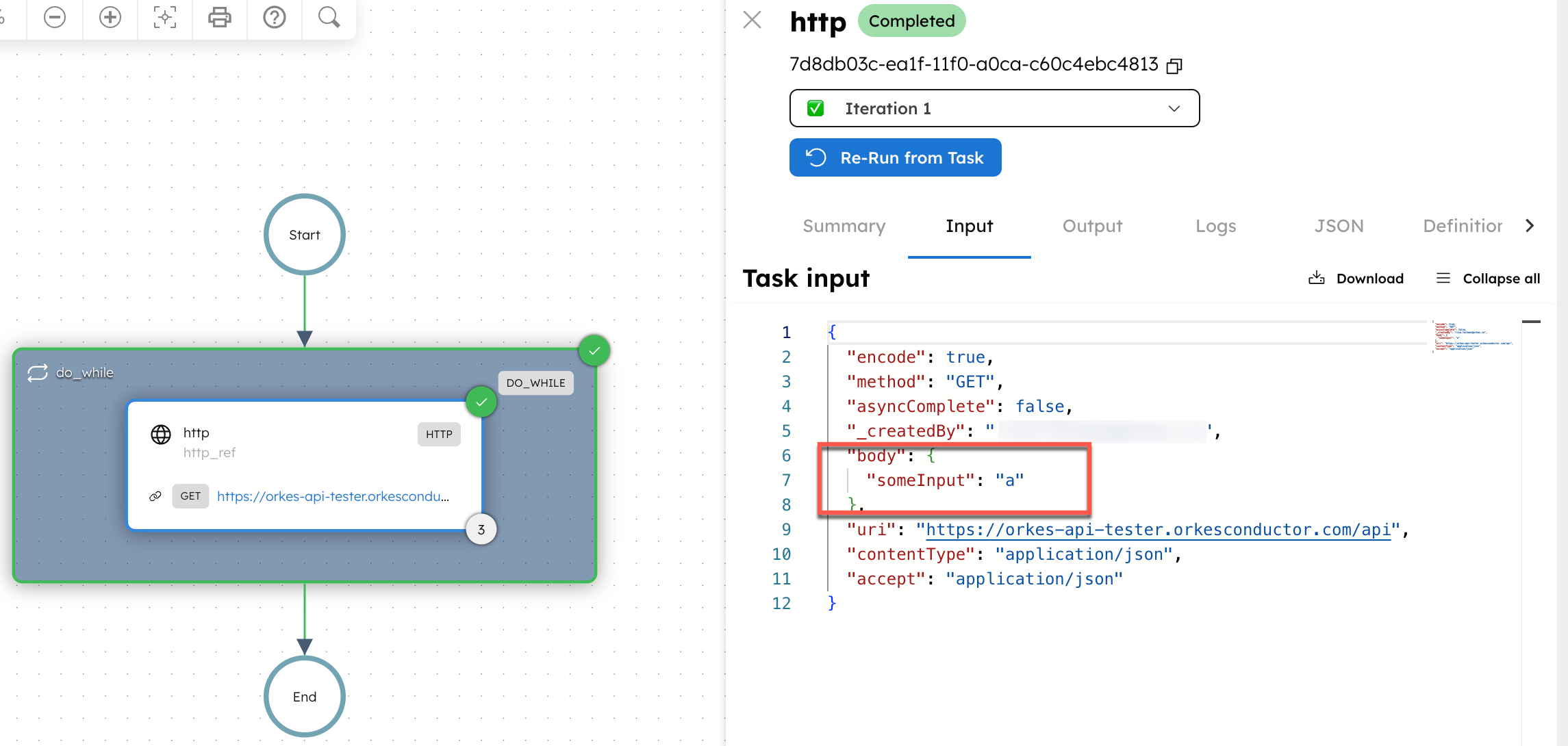
In each iteration, the HTTP task receives a different value for someInput (a, then b, then c). After the final iteration, verify that the Do While task output shows iteration: 3 and item: "c".
{
"1": {
// output data for iteration 1
},
"2": {
// output data for iteration 1
},
"3": {
"http_ref_2": {
"response": {
"headers": {
"content-length": [
"182"
],
"content-type": [
"application/json"
],
"date": [
"Tue, 09 Sep 2025 07:11:34 GMT"
],
"strict-transport-security": [
"max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains"
]
},
"reasonPhrase": "",
"body": {
"randomString": "ldkdymlgqlgujapzsrvw",
"randomInt": 1475,
"hostName": "orkes-api-sampler-67dfc8cf58-4lt28",
"apiRandomDelay": "0 ms",
"sleepFor": "0 ms",
"statusCode": "200",
"queryParams": {}
},
"statusCode": 200
}
}
},
"item": "c",
"iteration": 3
}