Fork/Join
A Fork/Join task is used to run tasks in parallel. It contains two components: the fork and the join operation. The fork operation lets you run lists of tasks, including Sub Workflow tasks, in parallel. The fork operation is followed by a join operation that waits on the forked tasks to finish before moving to the next task. This Join task collects the outputs from each forked task.
Task parameters
Configure these parameters for the Fork/Join task.
For the Fork task:
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| forkTasks | An array of task lists. Each list represents a fork branch that will run in parallel, and each list contains a sequence of task configurations. | Required. |
| inputParameters | Input parameters for the Fork task. Use an empty object if no inputs are required. | Optional. |
The Join task will run after the forked tasks. Configure the Join task as well to complete the fork-join operations.
For the Join task:
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| joinOn | A list of task reference names that the Join task will wait for completion before proceeding with the next task. Notes: When a Join task is used after a Switch task, the Join task can complete when the Switch task completes, even if the tasks within the switch branches have not finished. To handle this, add a task such as Set Variable at the end of the outermost Switch task and configure the Join task to join on that task. This ensures the Join task waits until all switch branch execution is complete before the workflow continues. | Required. |
| expression | The join script, which controls how the Join task completes if specified. | Optional. |
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for a Fork/Join task.
// JSON schema for the Fork task
{
"name": "fork",
"taskReferenceName": "fork_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "FORK_JOIN",
"forkTasks": [
[ // fork branch
{// task configuration},
{// task configuration}
],
[ // another fork branch ]
]
}
// JSON schema for the Join task
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": [
// List of task reference names that the join should wait for
]
}
Task output
The Fork task does not produce output. The Join task returns a map containing the outputs of the tasks listed in joinOn, keyed by their task reference names. Learn more about the Join task output.
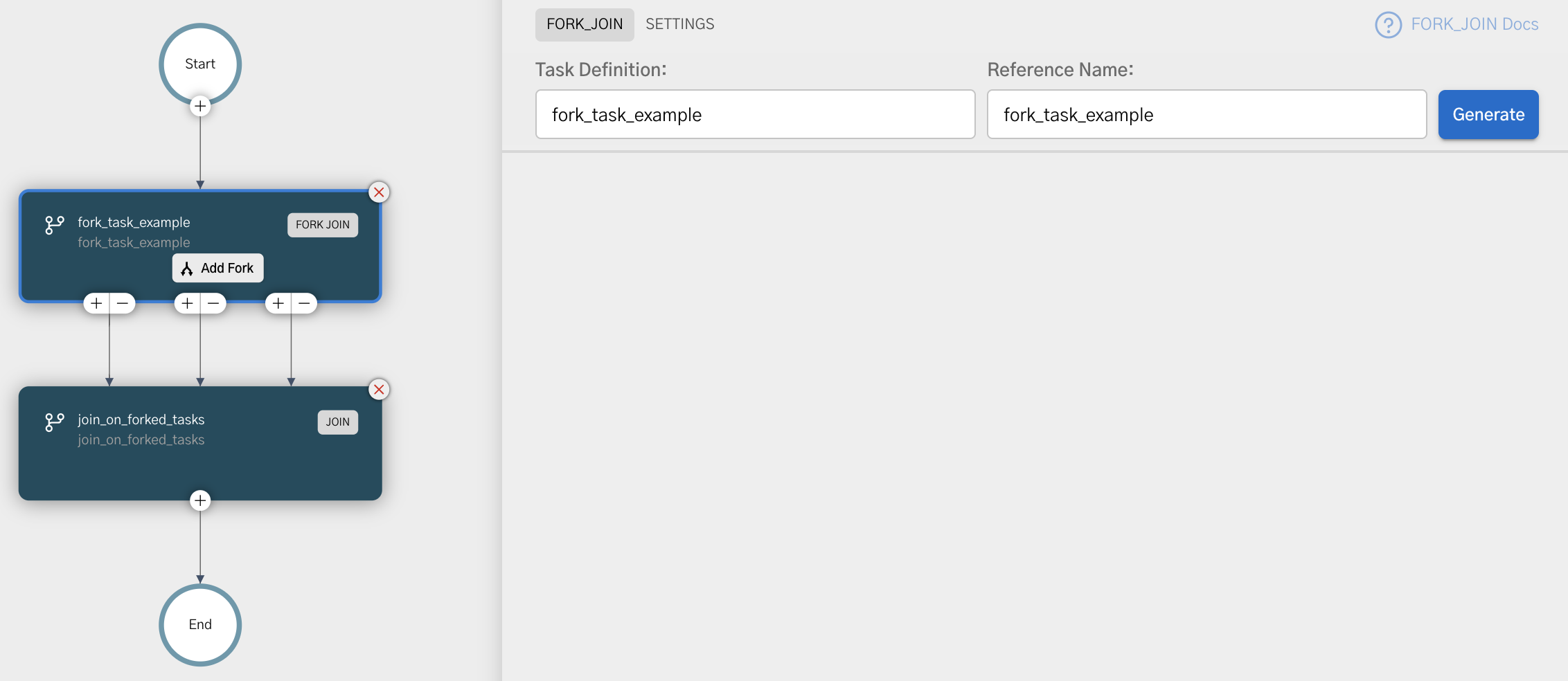
Adding a Fork/Join task in UI
To add a Fork/Join task:
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add a Fork/Join task.
- Select Add fork to add as many forks as required.
- In each fork branch, select the (+) icon to add tasks.
- Select the Join task and configure its settings to complete the fork/join operations.
Examples
Here are some examples for using the Fork/Join task.
Sending notifications in parallel
In this example workflow, email, SMS, and HTTP notifications are triggered in parallel using a Fork/Join task. The workflow continues only after the email and SMS notifications are complete, while the HTTP notification runs independently and does not block execution.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "ForkJoin_Notifications",
"description": "Runs multiple notification branches in parallel using a Fork/Join task.",
"version": 1,
"schemaVersion": 2,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "notifications_fork",
"taskReferenceName": "notifications_fork_ref",
"type": "FORK_JOIN",
"inputParameters": {},
"forkTasks": [
[
{
"name": "email_payload",
"taskReferenceName": "email_payload_ref",
"type": "INLINE",
"inputParameters": {
"evaluatorType": "graaljs",
"expression": "(function () { return { channel: 'email', to: 'test@example.com', message: 'Email sent' }; })();"
}
}
],
[
{
"name": "sms_payload",
"taskReferenceName": "sms_payload_ref",
"type": "INLINE",
"inputParameters": {
"evaluatorType": "graaljs",
"expression": "(function () { return { channel: 'sms', to: '+1-xxx-xxx-xxxx', message: 'SMS sent' }; })();"
}
}
],
[
{
"name": "http_notification",
"taskReferenceName": "http_notification_ref",
"type": "HTTP",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
}
}
]
]
},
{
"name": "notifications_join",
"taskReferenceName": "notifications_join_ref",
"type": "JOIN",
"inputParameters": {},
"joinOn": [
"email_payload_ref",
"sms_payload_ref"
]
}
],
"outputParameters": {
"joinedOutputs": "${notifications_join_ref.output}"
}
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
To run the workflow:
- Go to the Run tab.
- Select Execute.
Each fork runs tasks for each notification type (email, SMS, HTTP) in parallel, meaning that they are run independently.
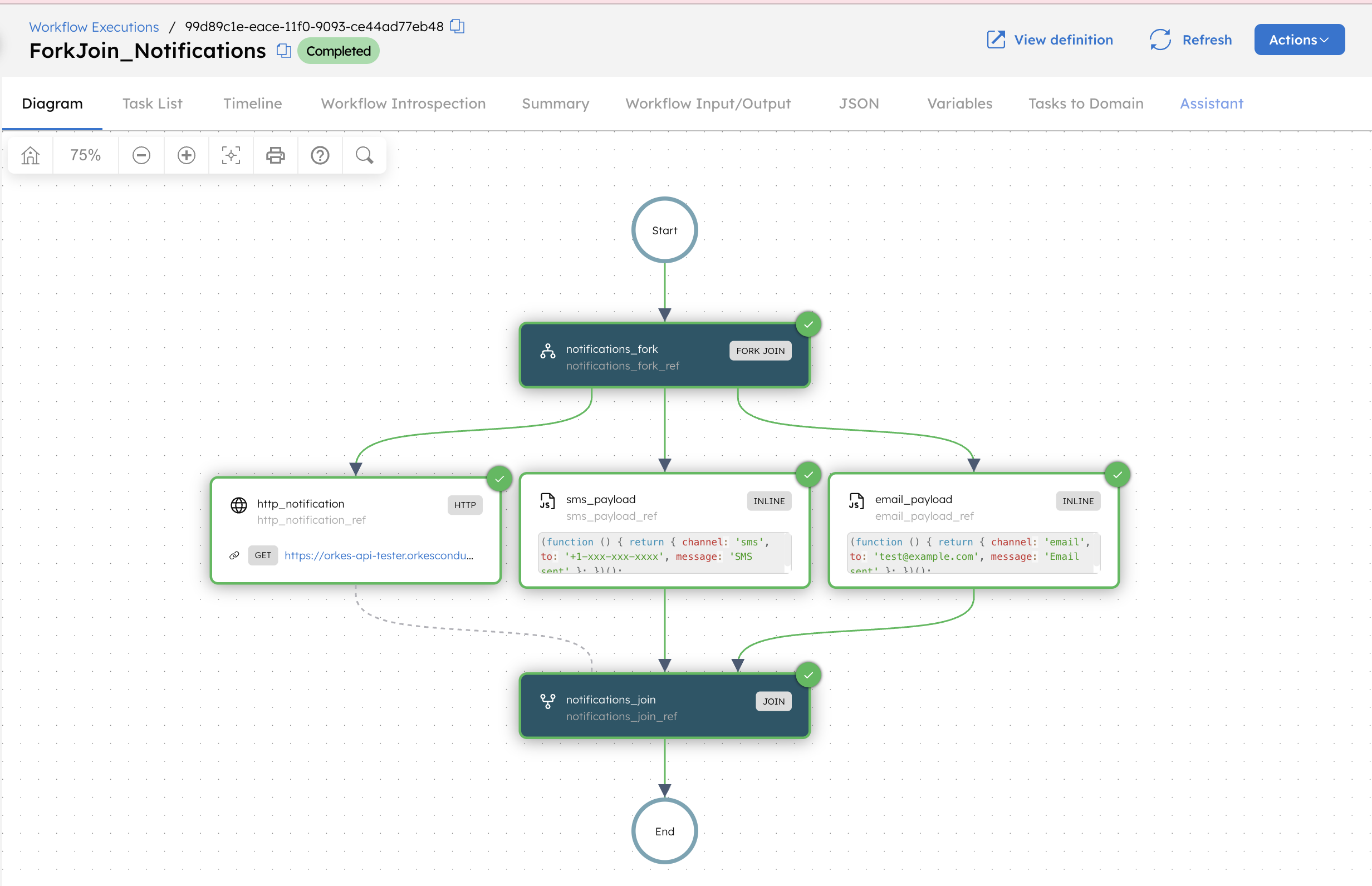
Although three forks are running in parallel, only two forks are required to continue with the workflow. The parameter joinOn is defined so that only email and SMS tasks are joined, leaving the HTTP task as optional for completing the Join task.
// Join task configuration
{
"name": "notifications_join",
"taskReferenceName": "notifications_join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"joinOn": [
"email_payload_ref",
"sms_payload_ref"
],
"type": "JOIN"
}
This workflow is completed when the email and SMS notifications are sent and does not depend on the HTTP notification status.
This is the output of notification_join. The output is a map, where the keys are the reference names of tasks being joined, and the corresponding values are the outputs of those tasks.
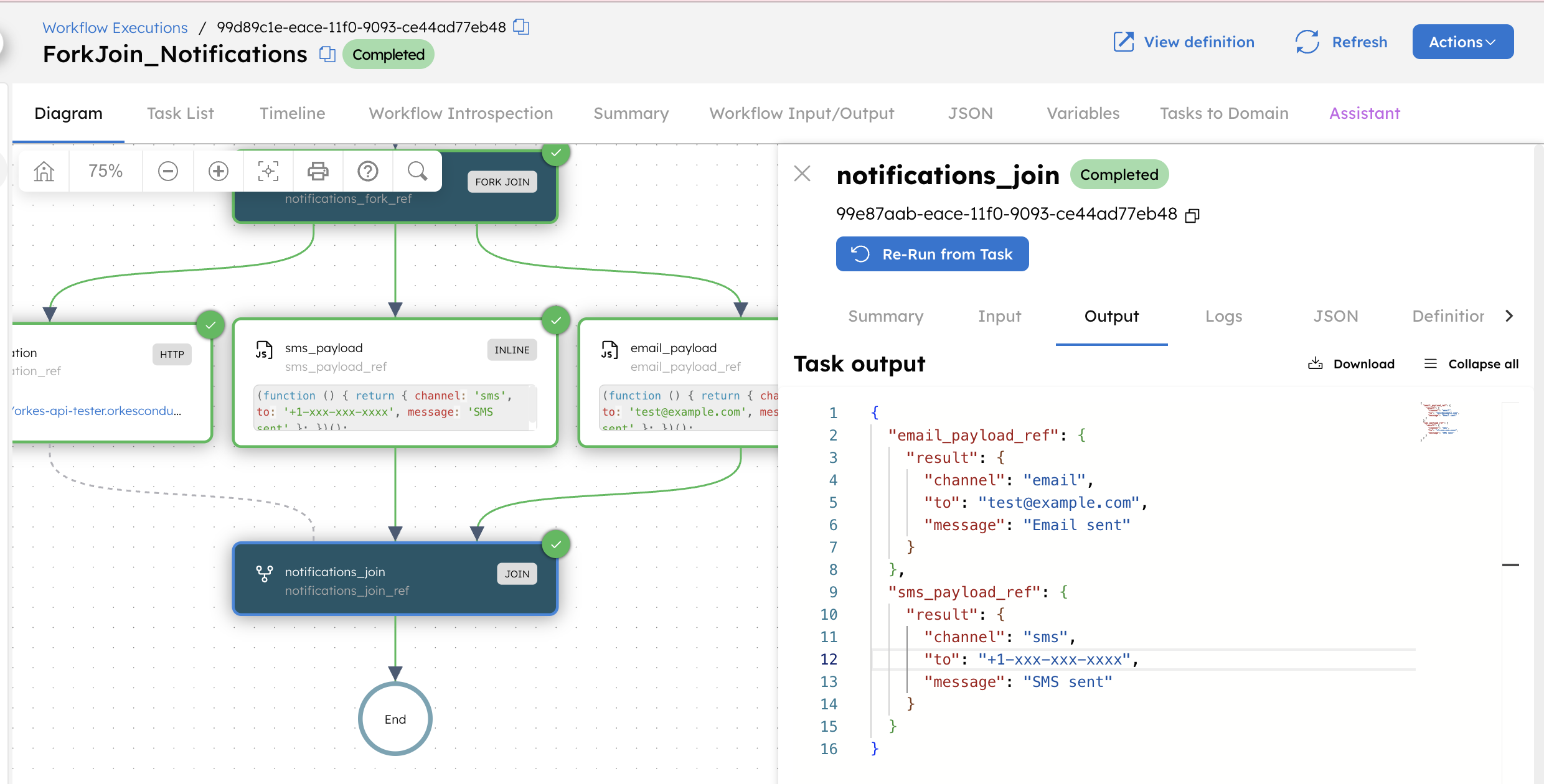
Outputs from the HTTP branch are not included because the HTTP notification is not listed in the joinOn parameter.