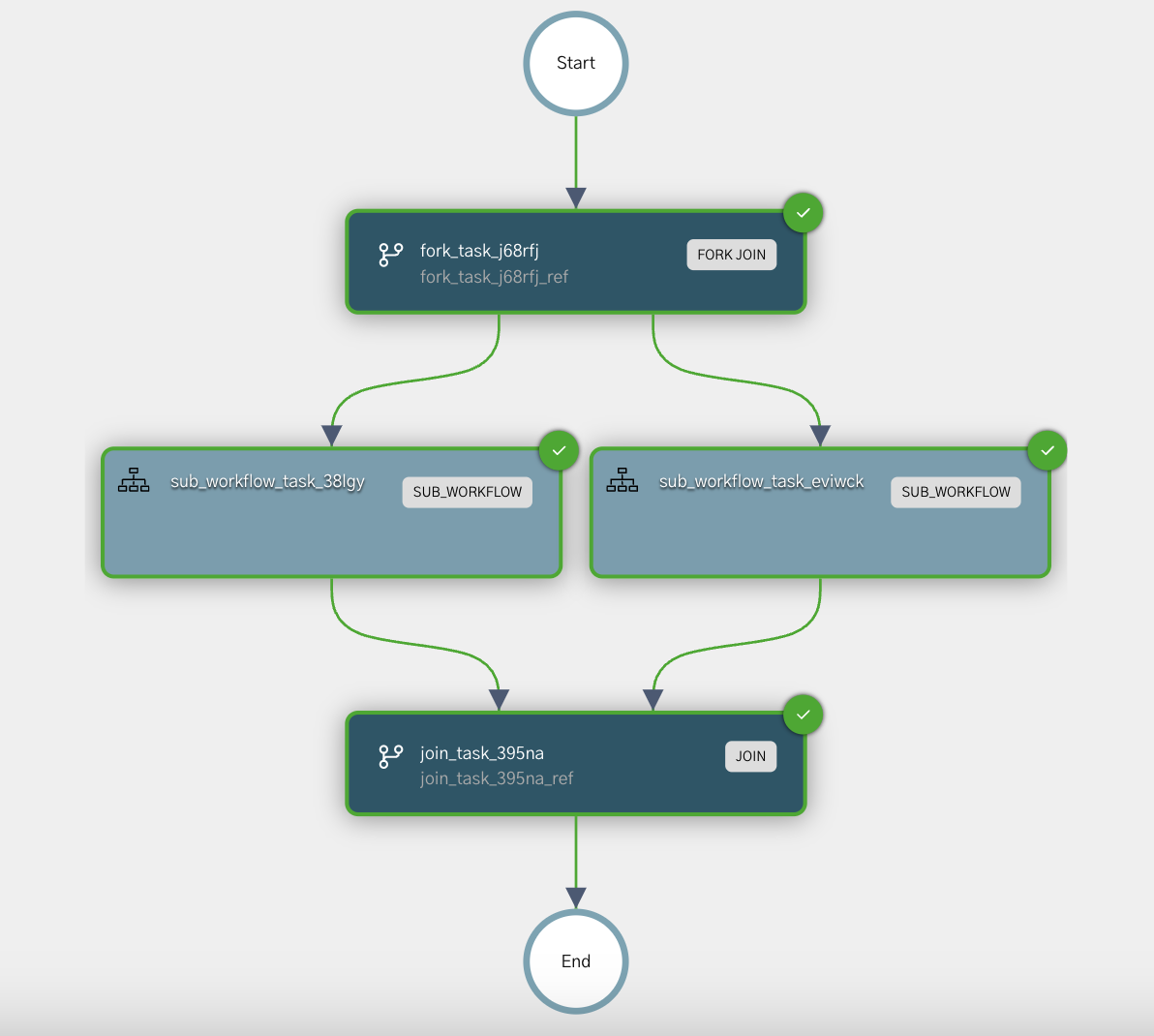
Join
A Join task is used in conjunction with a Fork Join or Dynamic Fork task to join all the tasks within the forks.
- With Fork/Join, the Join task waits for a predefined set of forked tasks.
- With Dynamic Fork, the Join task implicitly waits for all dynamically created forks, unless controlled by a join script.
Task parameters
Configure these parameters for the Join task.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| joinOn | A list of task reference names that the Join task will wait for completion before proceeding with the next task. For Dynamic Fork workflows, joinOn is typically set to an empty array.Notes: When a Join task is used after a Switch task, the Join task can complete when the Switch task completes, even if the tasks within the switch branches have not finished. To handle this, add a task such as Set Variable at the end of the outermost Switch task and configure the Join task to join on that task. This ensures the Join task waits until all switch branch execution is complete before the workflow continues. | Required. |
| expression | The join script, which controls how the Join task completes if specified. | Optional. |
Join script configuration
A join script is optional and allows custom control over when the Join task completes. Script parameters can be passed through the Join task’s input parameters.
For predictable behavior, tasks referenced by the join script should be marked as optional.
Example join script
(function(){
let results = {};
let pendingJoinsFound = false;
if($.joinOn){
$.joinOn.forEach((element)=>{
if($[element] && $[element].status !== 'COMPLETED'){
results[element] = $[element].status;
pendingJoinsFound = true;
}
});
if(pendingJoinsFound){
return {
"status":"IN_PROGRESS",
"reasonForIncompletion":"Pending",
"outputData":{
"scriptResults": results
}
};
}
// To complete the Join - return true OR an object with status = 'COMPLETED' like above.
return true;
}
})();
In the example script, there is a variable called $.joinOn, which is an array containing the task references and output data of each joined task. The script is designed to check if the status of the tasks to be joined is COMPLETED. If any pending joins are found, the script changes the status of the pending join tasks to the required status (IN_PROGRESS in the example script). The example script can be modified to suit your use case.
The following are generic configuration parameters that can be applied to the task and are not specific to the Join task.
Other generic parameters
Here are other parameters for configuring the task behavior.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| optional | Whether the task is optional. If set to true, any task failure is ignored, and the workflow continues with the task status updated to COMPLETED_WITH_ERRORS. However, the task must reach a terminal state. If the task remains incomplete, the workflow waits until it reaches a terminal state before proceeding. | Optional. |
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for a Join task.
{
"name": "join",
"taskReferenceName": "join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": [
// List of task reference names that the join should wait for
],
"expression": ""
}
Task output
The Join task output depends on whether a join script is used.
Without a join script
If no join script is used, the Join task returns a map where the keys are the task reference names of the tasks being joined and the values are the corresponding outputs of those tasks. The tasks are completed in the order they are joined.
{
"taskReferenceName": {
"outputKey": "outputValue"
},
"anotherTaskReferenceName": {
"outputKey": "outputValue"
},
"someTaskReferenceName": {
"outputKey": "outputValue"
}
}
With a join script
If a join script is used, the output will also return the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| joinOn | A list of task reference names that the Join task will wait for completion before proceeding with the next task. |
{
"joinOn": [
"taskReferenceName",
"anotherTaskReferenceName",
"someTaskReferenceName"
],
"taskReferenceName": {
"outputKey": "outputValue"
},
"anotherTaskReferenceName": {
"outputKey": "outputValue"
},
"someTaskReferenceName": {
"outputKey": "outputValue"
}
}
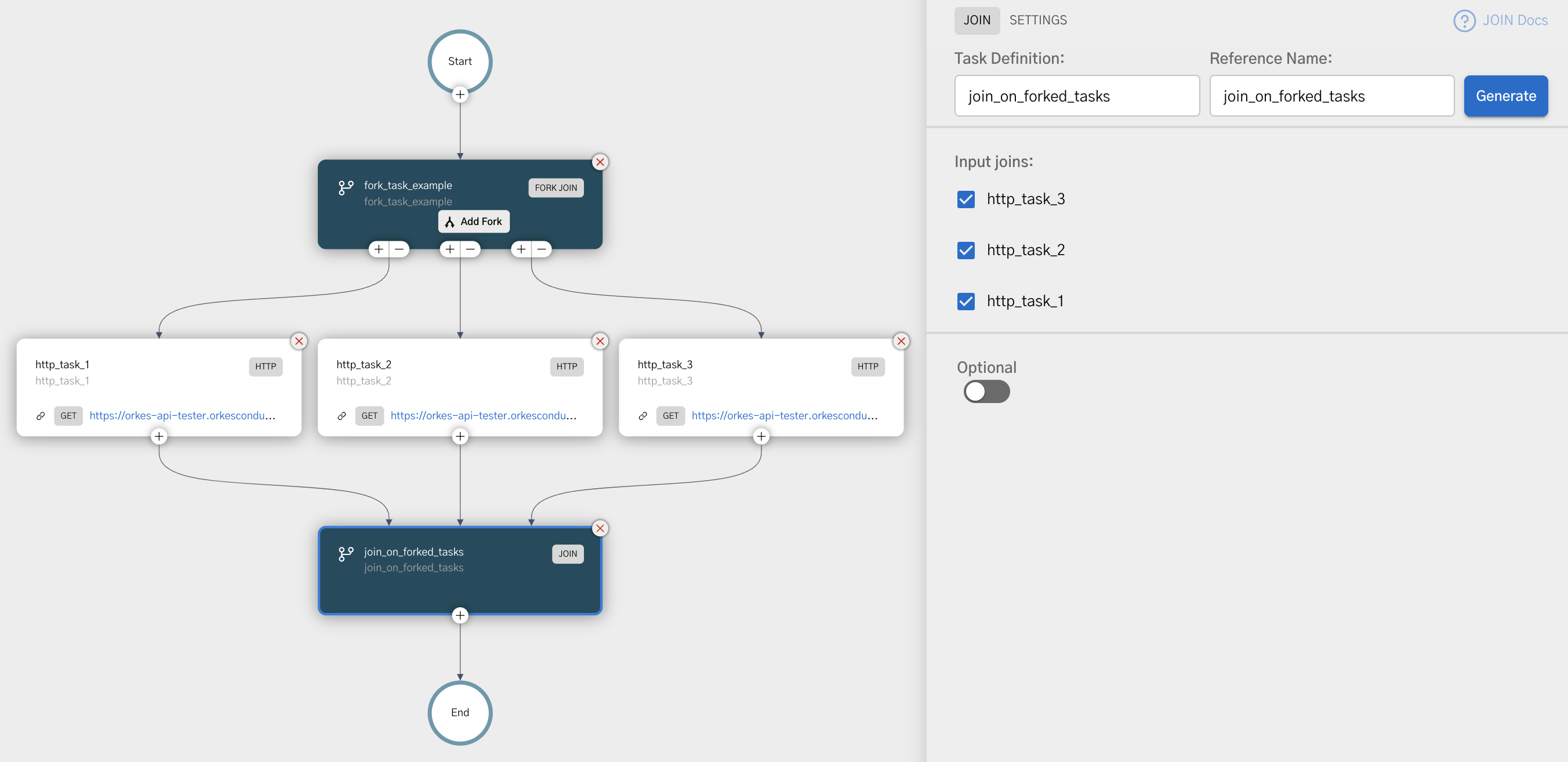
Configuring a Join task in UI
A Join task is automatically added whenever a Fork/Join task or a Dynamic Fork task is added.
To configure a Join task:
- In your workflow, which contains either a Fork or Dynamic Fork task, select the Join task.
- In Input joins, select the forks that are required for joining.
- (Optional) Use a script to control how the Join task completes.
- In Join script, enable Use scripting to determine join.
- Enter the script in the code box.
- If necessary, add the Script Parameters that will be passed into the Join task.
Examples
Here are some examples for using the Join task.
Join on all forks
In this example, the Join task waits for all forks to complete. The task will wait for the completion of my_task_ref_1 and my_task_ref_2 as specified by the joinOn attribute.
// Join task configuration
{
"name": "join_task",
"taskReferenceName": "my_join_task_ref",
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": ["my_task_ref_1", "my_task_ref_2"]
}
Ignore one fork
In this example workflow, email, SMS, and HTTP notifications are triggered in parallel using a Fork/Join task. The workflow continues only after the email and SMS notifications are complete, while ignoring the HTTP fork.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "ForkJoin_Notifications",
"description": "Runs multiple notification branches in parallel using a Fork/Join task.",
"version": 1,
"schemaVersion": 2,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "notifications_fork",
"taskReferenceName": "notifications_fork_ref",
"type": "FORK_JOIN",
"inputParameters": {},
"forkTasks": [
[
{
"name": "email_payload",
"taskReferenceName": "email_payload_ref",
"type": "INLINE",
"inputParameters": {
"evaluatorType": "graaljs",
"expression": "(function () { return { channel: 'email', to: 'test@example.com', message: 'Email sent' }; })();"
}
}
],
[
{
"name": "sms_payload",
"taskReferenceName": "sms_payload_ref",
"type": "INLINE",
"inputParameters": {
"evaluatorType": "graaljs",
"expression": "(function () { return { channel: 'sms', to: '+1-xxx-xxx-xxxx', message: 'SMS sent' }; })();"
}
}
],
[
{
"name": "http_notification",
"taskReferenceName": "http_notification_ref",
"type": "HTTP",
"inputParameters": {
"uri": "https://orkes-api-tester.orkesconductor.com/api",
"method": "GET",
"accept": "application/json",
"contentType": "application/json",
"encode": true
}
}
]
]
},
{
"name": "notifications_join",
"taskReferenceName": "notifications_join_ref",
"type": "JOIN",
"inputParameters": {},
"joinOn": [
"email_payload_ref",
"sms_payload_ref"
]
}
],
"outputParameters": {
"joinedOutputs": "${notifications_join_ref.output}"
}
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
To run the workflow:
- Go to the Run tab.
- Select Execute.
Each fork runs tasks for each notification type (email, SMS, HTTP) in parallel, meaning that they are run independently.
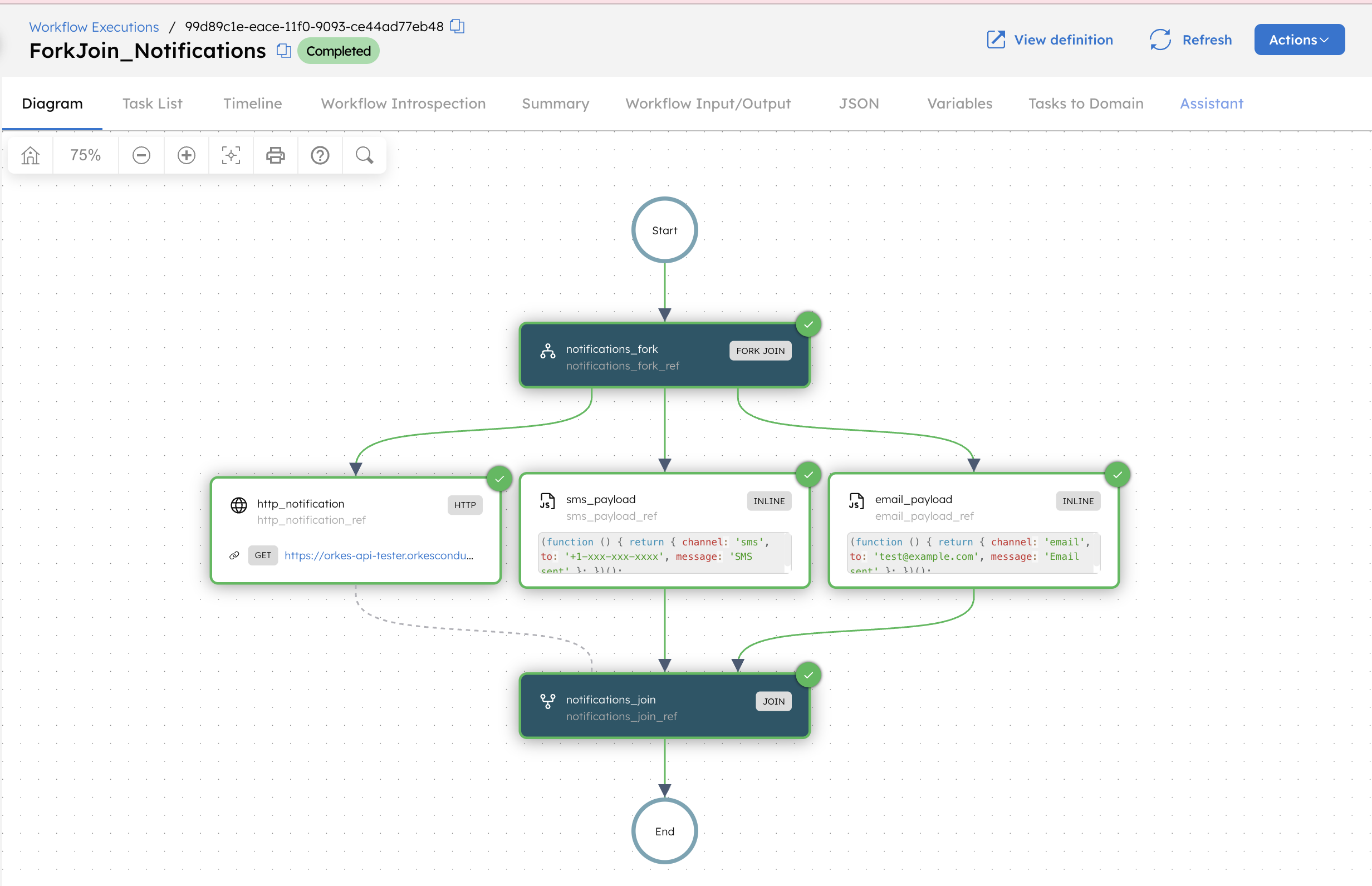
Although three forks are running in parallel, only two forks are required to continue with the workflow. The parameter joinOn is defined so that only email and SMS tasks are joined, leaving the HTTP task as optional for completing the Join task.
// Join task configuration
{
"name": "notifications_join",
"taskReferenceName": "notifications_join_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"joinOn": [
"email_payload_ref",
"sms_payload_ref"
],
"type": "JOIN"
}
This workflow is completed when the email and SMS notifications are sent and does not depend on the HTTP notification status.
This is the output of notification_join. The output is a map, where the keys are the reference names of tasks being joined, and the corresponding values are the outputs of those tasks.
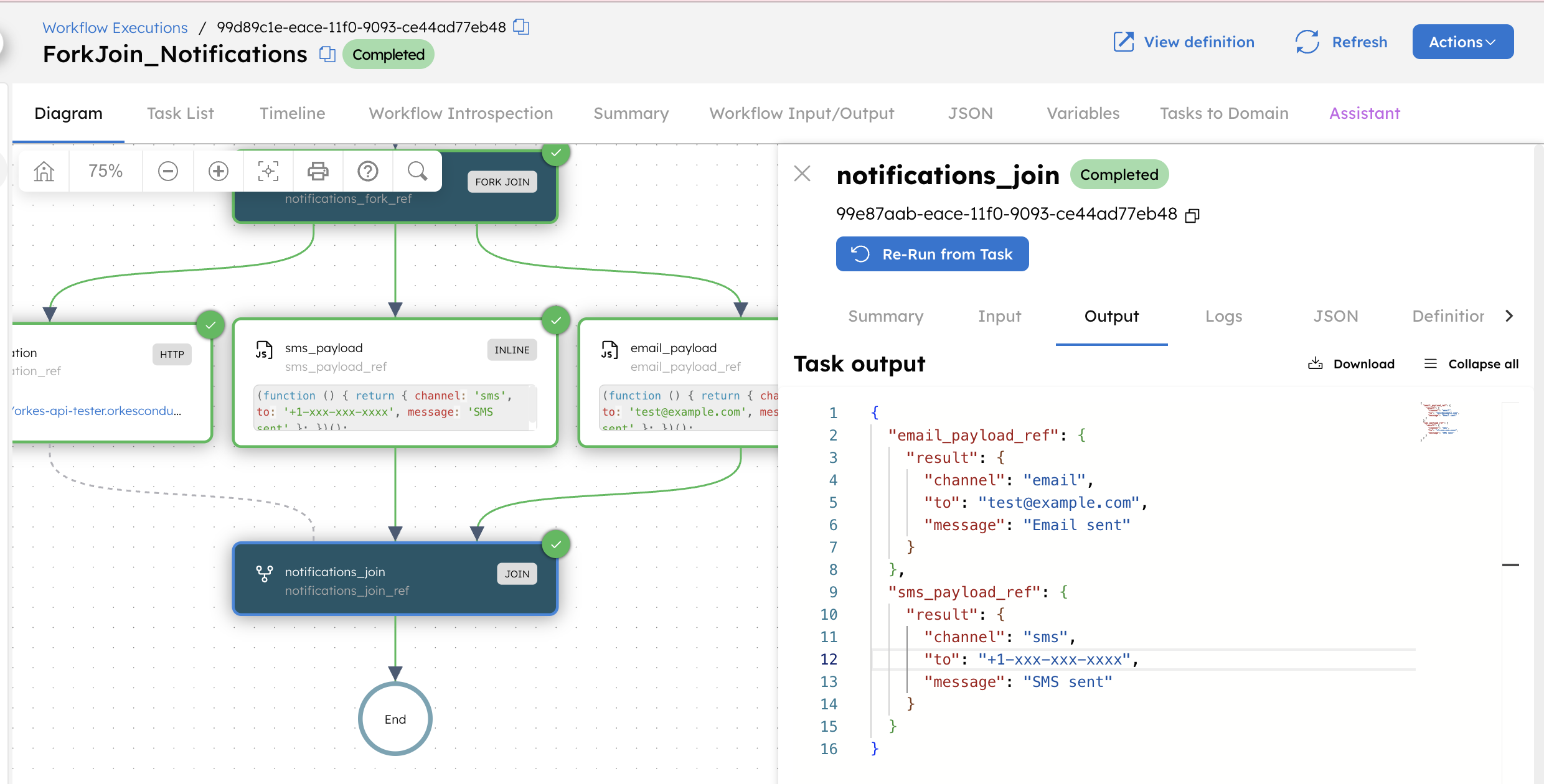
Outputs from the HTTP branch are excluded because it is not specified in the joinOn parameter.
Using a join script
In this example, a Fork/Join task runs two branches in parallel. One branch waits for 5 seconds, and the other waits for 30 seconds. Both forked tasks are marked as optional. A Join task uses a join script to control when the workflow can proceed by explicitly checking the completion status of the forked tasks.
To create a workflow:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following workflow definition:
{
"name": "Join_With_Script_Demo",
"description": "Uses a join script to control completion of parallel tasks.",
"version": 1,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "fork_tasks",
"taskReferenceName": "fork_tasks_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "FORK_JOIN",
"forkTasks": [
[
{
"name": "wait_short",
"taskReferenceName": "wait_short_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"duration": "5 seconds"
},
"type": "WAIT"
}
],
[
{
"name": "wait_long",
"taskReferenceName": "wait_long_ref",
"inputParameters": {
"duration": "30 seconds"
},
"type": "WAIT"
}
]
]
},
{
"name": "join_with_script",
"taskReferenceName": "join_with_script_ref",
"inputParameters": {},
"type": "JOIN",
"joinOn": [
"wait_short_ref",
"wait_long_ref"
],
"expression": "(function(){\n let pending = false;\n let results = {};\n\n $.joinOn.forEach((ref) => {\n if ($[ref] && $[ref].status !== 'COMPLETED') {\n pending = true;\n results[ref] = $[ref].status;\n }\n });\n\n if (pending) {\n return {\n status: 'IN_PROGRESS',\n reasonForIncompletion: 'Waiting for forked tasks',\n outputData: {\n pendingTasks: results\n }\n };\n }\n\n return true;\n})();"
}
],
"schemaVersion": 2
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
Both forked tasks are marked as optional and the Join task is joined using the following script:
(function(){
let pending = false;
let results = {};
$.joinOn.forEach((ref) => {
if ($[ref] && $[ref].status !== 'COMPLETED') {
pending = true;
results[ref] = $[ref].status;
}
});
if (pending) {
return {
status: 'IN_PROGRESS',
reasonForIncompletion: 'Waiting for forked tasks',
outputData: {
pendingTasks: results
}
};
}
return true;
})();
This script ensures that the Join task is completed only if all the forks are completed. If any pending joins are found, the script will return the Join task status to IN_PROGRESS. Only once the forked tasks are completed, the script completes the Join task.
To run the workflow:
- Go to the Run tab.
- Select Execute.
On the workflow execution page, you can observe the following behavior:
- The forked branch with the 5-second Wait task completes first (wait_short).
- The Join task remains IN_PROGRESS while the 30-second Wait task is still running.
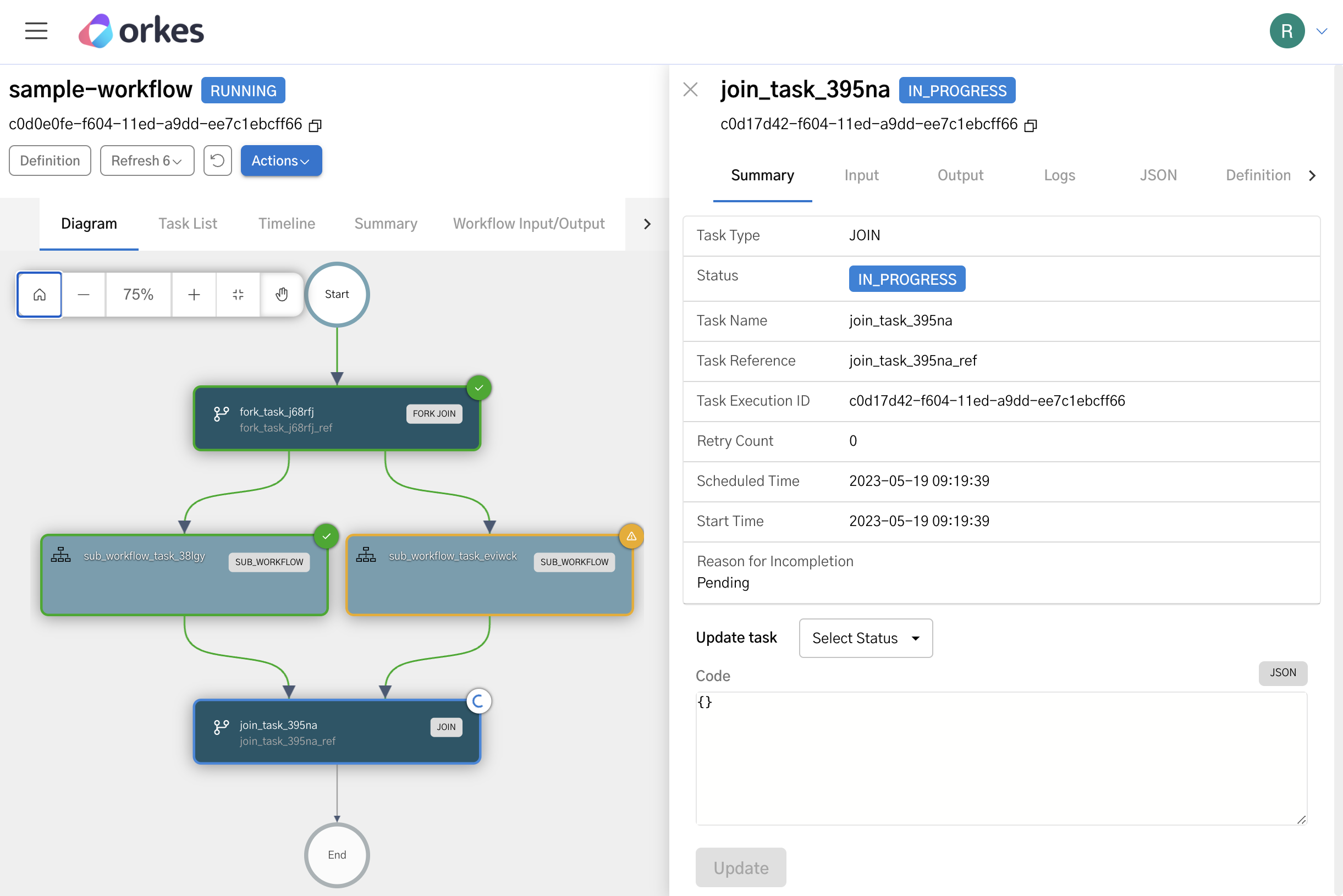
- After the 30-second Wait task completes, the join script evaluates successfully, and the Join task completes.
- The workflow finishes only after both forked tasks have completed.