Parse Document
- v5.2.38 and later
The Parse Document task is used to parse and chunk documents from various sources such as cloud storage (S3, GCS, Azure), Git repositories, and websites. It supports multiple file types, including Office documents, PDFs, HTML, images (via OCR), ZIP archives, and text files.
During execution, the task extracts text content from the specified location and converts it into Markdown format optimized for LLM processing. The Markdown format preserves headings, tables, lists, and other document structures, making it suitable for embedding generation, summarization, and semantic search workflows.
If the location of the document is not publicly available, you must create an appropriate integration with the required access keys or tokens. Integrate the following with Orkes Conductor, depending on your source:
Task parameters
Configure these parameters for the Parse Document task.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| inputParameters.integrationName | If the location of the document to be parsed is not publicly available, select the integration name of the Git Repository or Cloud Providers integrated with your Conductor cluster. Note: If you haven’t configured any integration on your Orkes Conductor cluster, go to the Integrations tab and configure the Git Repository or required Cloud Providers. | Optional. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| inputParameters.url | The URL of the document or archive to parse. Examples for URL format:
| Required. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| inputParameters.mediaType | The media type to parse. If omitted, the system automatically detects it. All documents are converted to Markdown. Supported values:
| Optional. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| inputParameters.chunkSize | The maximum number of characters per chunk. Enter 0 for no chunking, or a value between 100 and 10,000 for semantic chunking. The default value is 0, where the entire document will be returned as a single markdown output. | Optional. |
The following are generic configuration parameters that can be applied to the task and are not specific to the Parse Document task.
Other generic parameters
Here are other parameters for configuring the task behavior.
| Parameter | Description | Required/ Optional |
|---|---|---|
| optional | Whether the task is optional. If set to true, any task failure is ignored, and the workflow continues with the task status updated to COMPLETED_WITH_ERRORS. However, the task must reach a terminal state. If the task remains incomplete, the workflow waits until it reaches a terminal state before proceeding. | Optional. |
Task configuration
This is the task configuration for a Parse Document task.
{
"name": "parse_document",
"taskReferenceName": "parse_document_ref",
"inputParameters":
{
"integrationName": "<YOUR-INTEGRATION-HERE>",
"url": "<DOCUMENT-URL>",
"mediaType": "auto",
"chunkSize": 1024
},
"type": "PARSE_DOCUMENT"
}
Task output
The Parse Document task will return the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| result | Array of strings containing the parsed document text. Each element is one text segment; if chunkSize is 0, the array contains a single element with the full content. |
Adding a Parse Document task in UI
To add a Parse Document task:
- In your workflow, select the (+) icon and add a Parse Document task.
- (Optional) For non-public URLs, in Integration Name, select the integration already added to the cluster from where the documents are to be parsed.
- In Document URL, enter the document URL to be parsed.
- (Optional) In Media Type, select the document type. Use Auto-detect for automatically detecting based on the content and file extension.
- (Optional) In Chunking Configuration, enter the Chunk Size.
Examples
Here are some examples for using the Parse Document task.
Using Parse Document task
To illustrate the Parse Document task, the following workflow parses a publicly available PDF.
To create a workflow definition using Conductor UI:
- Go to Definitions > Workflow, from the left navigation menu on your Conductor cluster.
- Select + Define workflow.
- In the Code tab, paste the following code:
Workflow definition:
{
"name": "parse_document_example_pdf",
"description": "Parse a public PDF and return text segments",
"version": 1,
"schemaVersion": 2,
"tasks": [
{
"name": "parse_document",
"taskReferenceName": "pd",
"type": "PARSE_DOCUMENT",
"inputParameters": {
"url": "https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2023-02/Annual-Report-2022-2023-English_06022023_compressed.pdf",
"mediaType": "application/pdf",
"chunkSize": 1000
}
}
]
}
- Select Save > Confirm.
Let’s execute the workflow using the Execute button.
When executed, the workflow retrieves the PDF from the provided URL, extracts readable text content, and divides it into smaller text segments based on the specified chunk size.
After successful execution, the Parse Document task produces the following output:
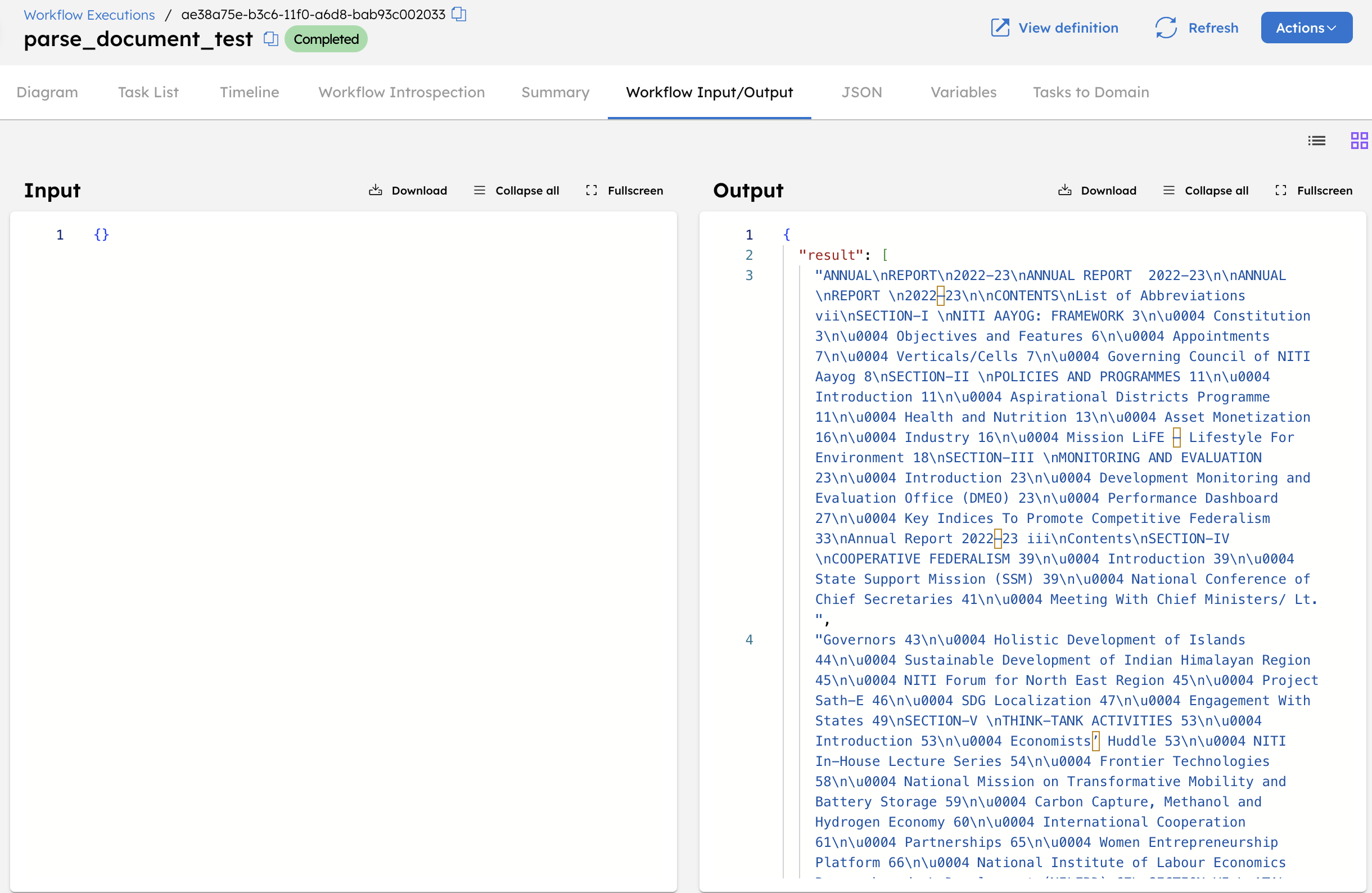
Each segment preserves the structure and order of the document, including section headers and line breaks. The extracted segments are returned in the result array and are ready for downstream processing, such as summarization, embedding generation, or indexing.